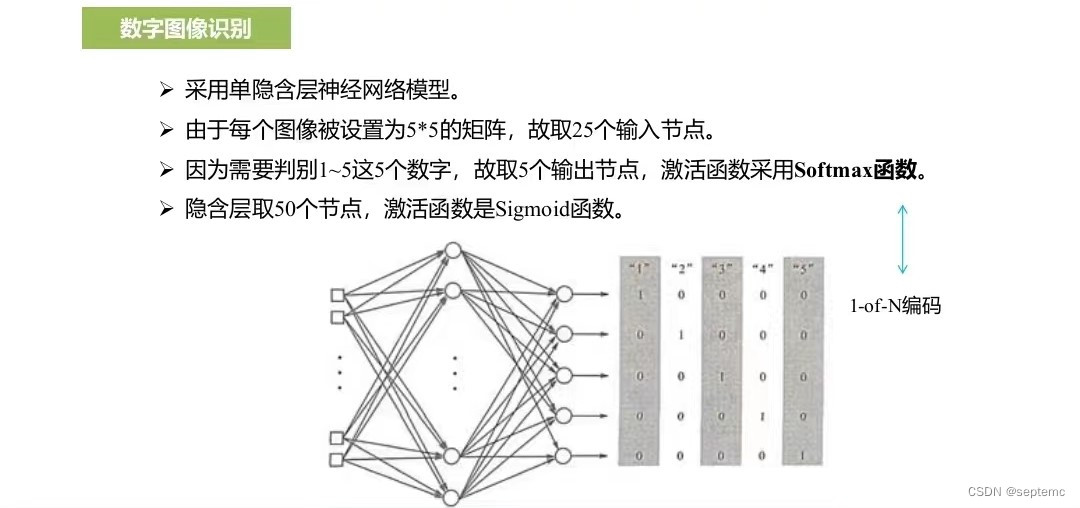
要求:
1、对C语言基本语法已经完全掌握
2、对机器学习的底层原理认识清晰
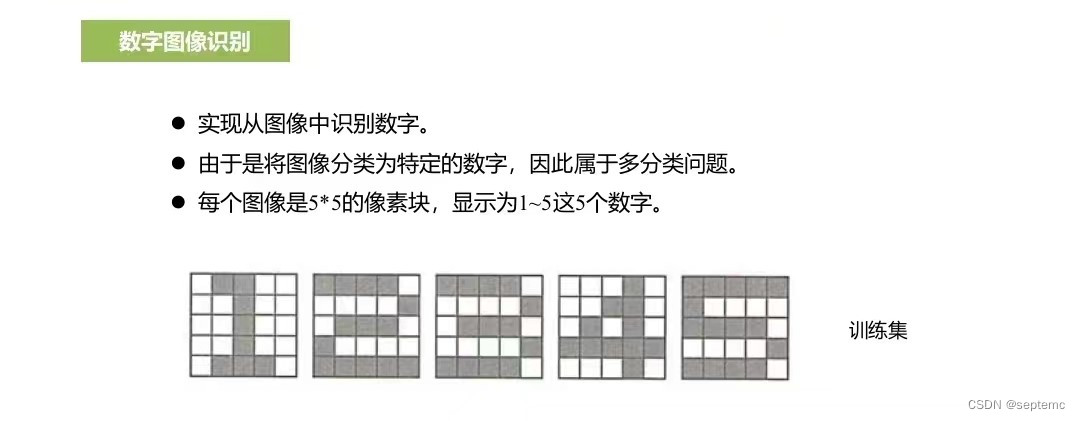
训练数据
// 训练数据
double inputs[5][ROWS * COLS] = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
};
int labels[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
// 测试数据
double test_inputs[5][ROWS * COLS] = {
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
};
int test_labels[5] = { 4, 2, 3, 5, 5 };完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define ROWS 5
#define COLS 5
#define NUM_CLASSES 5
#define LEARNING_RATE 0.01
#define EPOCHS 6000
// sigmoid激活函数
double sigmoid(double x) {
return 1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-x));
}
// softmax分类函数
void softmax(double* output, int n) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum += exp(output[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
output[i] = exp(output[i]) / sum;
}
}
// 前向传播函数
void forward(double* input, double* weights, double* output) {
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_CLASSES; i++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < ROWS * COLS; j++) {
sum += input[j] * weights[i * ROWS * COLS + j];
}
output[i] = sigmoid(sum);
}
softmax(output, NUM_CLASSES);
}
// 反向传播函数
void backward(double* input, double* weights, double* output, int label) {
double delta[NUM_CLASSES];
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_CLASSES; i++) {
delta[i] = (i == label ? 1.0 : 0.0) - output[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_CLASSES; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ROWS * COLS; j++) {
weights[i * ROWS * COLS + j] += LEARNING_RATE * delta[i] * input[j];
}
}
}
// 训练函数
void train(double* inputs, int* labels, double* weights, int num_examples) {
for (int epoch = 0; epoch < EPOCHS; epoch++) {
double loss = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_examples; i++) {
double output[NUM_CLASSES];
forward(&inputs[i * ROWS * COLS], weights, output);
backward(&inputs[i * ROWS * COLS], weights, output, labels[i]);
loss -= log(output[labels[i]]);
}
loss /= num_examples;
printf("Epoch %d\n", epoch + 1, loss);
}
}
// 测试函数
void test(double* inputs, int* labels, double* weights, int num_examples) {
int num_correct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_examples; i++) {
double output[NUM_CLASSES];
forward(&inputs[i * ROWS * COLS], weights, output);
int prediction = 0;
for (int j = 1; j < NUM_CLASSES; j++) {
if (output[j] > output[prediction]) {
prediction = j;
}
}
if (prediction == labels[i]) {
num_correct++;
}
printf("Prediction = %d\n", prediction);
}
double accuracy = (double)num_correct / num_examples;
printf("Test Accuracy = %f\n", accuracy);
}
int main() {
// 训练数据
double inputs[5][ROWS * COLS] = {
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
};
int labels[5] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
// 初始化权重
double weights[NUM_CLASSES * ROWS * COLS];
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_CLASSES * ROWS * COLS; i++) {
weights[i] = (double)rand() / RAND_MAX - 0.5;
}
// 训练模型
train((double*)inputs, labels, weights, 5);
// 测试模型
double test_inputs[5][ROWS * COLS] = {
{0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0},
};
int test_labels[5] = { 4, 2, 3, 5, 5 };
test((double*)test_inputs, test_labels, weights, 5);
return 0;
}






















 1814
1814

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








