转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/u010248330/article/details/69265370
上面的两章介绍了HttpUrlConnection的使用,HttpURLConnection是Java的标准类,没有做一些封装,用起来不方便,本篇开始介绍HttpClient,HttpClient是个开源框架,封装了访问http的请求头,参数,内容体,响应等.
下面开始简单使用一下HttpClient:
准备工作:利用eclipse新建一个java项目,导入与httpclient相关的jar包,这些jar包,自己到网上可以下载到。我还是以访问百度首页为例子吧。
导入相关jar包:
1.简单使用HttpClient(GET方式)
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.GetMethod;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpMethodParams;
public class HttpClientTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "http://www.baidu.com";
String resp=null;
InputStream inputStream=null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader=null;
HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient();
GetMethod getMethod = new GetMethod(url);
try {
int statusCode = httpclient.executeMethod(getMethod);
System.out.println(statusCode);
if (statusCode==200) {
resp = getMethod.getResponseBodyAsString();
System.out.println("请求的内容,方式1:"+resp);
inputStream=getMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream();
bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
String str = null;
StringBuffer strBuffer=new StringBuffer();
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
strBuffer.append(str);
strBuffer.append("\r\n");
}
System.out.println("请求的内容,方式2:"+strBuffer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
getMethod.releaseConnection();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
实验结果:
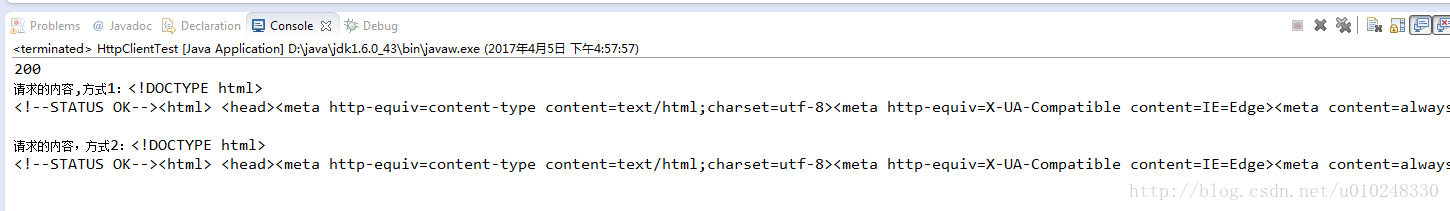
常用的获取服务器响应的内容的方式,一个是以字符串的形式获取(getResponseBodyAsString),一个是以流的形式(getResponseBodyAsStream),这里推荐用流的方式获取,避免引起中文乱码的问题。
2.简单使用HttpClient(POST方式)
我们还是按HttpUrlConnection与HttpClient的认识(一)中的使用的本地url:http://localhost:8080/test/index.jsp作为网络资源吧,这样可以传参数。
index.jsp修改如下:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String age = request.getParameter("age");
String sex = request.getParameter("sex");
%>
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
我的用户名是:<%=name%><br>
我的年龄是:<%=age%><br>
我的性别是:<%=sex%><br>
</body>
</html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
POST方式代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.HttpClient;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.methods.PostMethod;
import org.apache.commons.httpclient.params.HttpMethodParams;
public class HttpClientTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "http://localhost:8080/test/index.jsp";
InputStream inputStream=null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader=null;
HttpClient httpclient = new HttpClient();
PostMethod postMethod =new PostMethod(url);
httpclient.getParams().setParameter(HttpMethodParams.HTTP_CONTENT_CHARSET, "UTF-8");
httpclient.getParams().setConnectionManagerTimeout(60000);
httpclient.getParams().setSoTimeout(60000);
List<NameValuePair[]> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair[]>();
NameValuePair[] nameValues={new NameValuePair("name","aaa"),new NameValuePair("age","20"),new NameValuePair("sex","male")};
params.add(nameValues);
for (NameValuePair[] p : params) {
postMethod.addParameters(p);
}
try {
int statusCode = httpclient.executeMethod(postMethod);
System.out.println(statusCode);
if (statusCode==200) {
inputStream=postMethod.getResponseBodyAsStream();
bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream,"utf-8"));
String str = null;
StringBuffer strBuffer=new StringBuffer();
while ((str = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
strBuffer.append(str);
strBuffer.append("\r\n");
}
System.out.println("请求的内容:"+strBuffer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
postMethod.releaseConnection();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
实验结果:
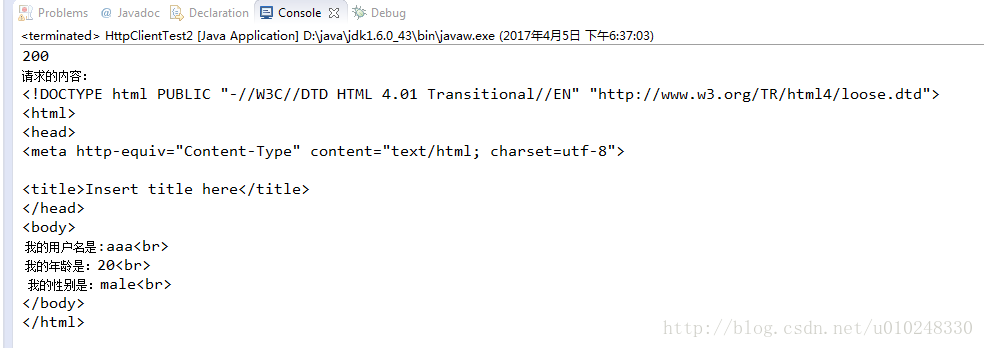
从上面的结果可以 看到,参数正确的发送给服务端了,总的来说,HttpClient的使用起来还是很简单的,需要注意POST方式中传参时,NameValuePair的使用。
参数传递有两种方式:
// 创建参数队列
NameValuePair[] nameValues={new NameValuePair("name","aaa"),new NameValuePair("age","10"),new NameValuePair("sex","male")};
//======================设置参数方式一==================
postMethod.addParameters(nameValues);
//======================设置参数方式二==================
postMethod.setRequestBody(nameValues);
//======================设置参数方式三==================
postMethod.setQueryString(nameValues);


























 2057
2057

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








