目录
3.4 indexOf(String str,int fromIdex)
3.6 lastIdexOf(int ch,int fromIdex)
3.7 int lastIndexOf(String str)
3.8 int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIdexOf)
一,什么是String类型?
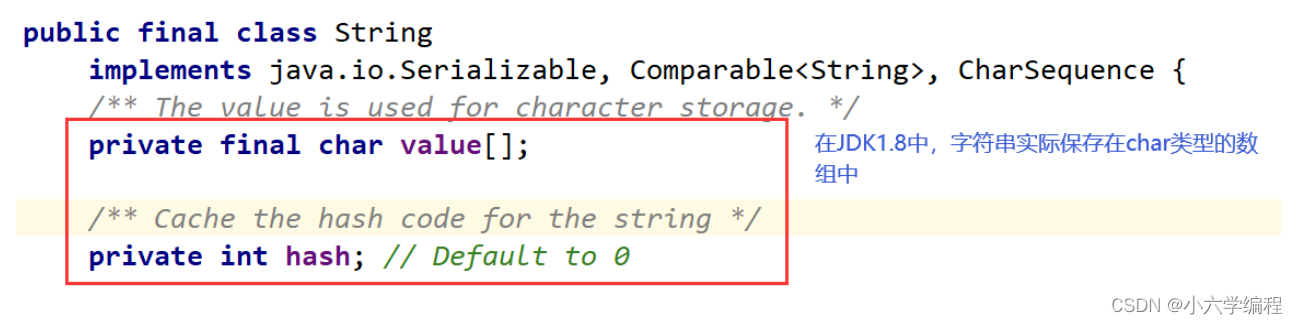
在使用编程语言处理问题时往往会遇到与字符串相关的问题,当如果我们想定义一个字符串类型,这在C语言中其实是不存在的,得使用char*p来表示我们想要表达的字符串,但这其实是一个char*类型的指针。
而在Java当中存在一个全新的数据类型——String类型:它可以直接定义我们想要表示的字符串。
在IDEA上我们可以查看String的源码:

(这里只截取了一部分)
观察发现,这其实是一个类,而对类的学习,我们一定要从从它的构造方法开始学习。

通过构造方法发现它有无参的构造,有有参的构造,有参可以传的类型也有很多,下面将介绍常用的几个。
二,常用构造方式
字符串构造:
String类提供的构造方式有很多,常用的就以下三种
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用常量串构造
String s1 = "hello bit";
System.out.println(s1);
// 直接newString对象
String s2 = new String("hello bit");
System.out.println(s1);
// 使用字符数组进行构造
char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o','b','i','t'};
String s3 = new String(array);
System.out.println(s1);
}
其他方法需要用到时,大家参考Java在线文档:Overview (Java Platform SE 8 ) (oracle.com)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// s1和s2引用的是不同对象 s1和s3引用的是同一对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("world");
String s3 = s1;
System.out.println(
System.out.println(
}

// 打印"hello"字符串(String对象)的长度
System.out.println("hello".length());
三,常用方法
String既然作为一个类,那么它一定包含了许多方法
1.String对象的长度
同数组一样,String引用的对象可以通过.length()来直接求得长度:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "你好!";
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println("str2 " + str1.length());
System.out.println("str2 " + str2.length());
System.out.println("arr " + arr.length);
}
}运行结果:

注意:
数组使用的是.length,而字符串是.length()方法。
另一个与长度有关的是.isEmpty()
当其String所引用的字符串长度为0时isEmpty()就会返回为true的布尔类型
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "";
System.out.println(str.length());
System.out.println(str.isEmpty());
}
}运行结果:

注意:
当String引用的对象为null时代表该引用不指向任何对象,并不代表该引用长度就为0,所以以下案例运行就会发生错误。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = null;
System.out.println(str.length());
System.out.println(str.isEmpty());
}
}
2.String对象的比较
2.1 equals
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
}
}
可以看到,字符串并不能使用“==”直接来判断是否相等。这是因为String和数组类似,并不是直接存储的对象的值,而是在栈区中开辟内存,存储堆区中该对象的地址。所以“==”比较的并不是str1与str2的值,而是二者所存储的地址。

那么我就是想要比较str1与str2二者的值,究竟该怎么完成呢?
答案是使用equals()
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));
}
}
2.2compareTo
equals虽然能进行比较,但只能判断二者是否相等,并不能判断大小,那当我想比较二者的大小的时候又该怎么做呢?
字符串还能比较大小?
——能
H不比h大?d不也比a大?
一切的一切,都可以通过compareTo完成
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
}
}
为什么返回的会是-32呢?

通过查看compareTo的源码会我们能够发现:
1.它会先求出字符串的长度进行比较,引用的长度大于参数的长度就会返回长度的差值的正数
2.当长度相同时就会根据Ascall码值一个字符一个字符的取,如果不一样,就返回Ascall码值的差值。

那能不能忽略大小写进行比较呢?
——能
使用compareToIgnoreCase便可
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2));
}
}
同时,equals也能忽略大小写比较
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("Hello");
String str2 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2));
}
}3.查找字符串
字符串查找也是String也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的非常常用的查找方法
| 方法 | 类型 |
|
char charAt(int index)
|
返回
index
位置上字符,如果
index
为负数或者越界,抛出
IndexOutOfBoundsException
异常
|
|
int indexOf(int ch)
|
返回
ch
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int indexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
|
从
fromIndex
位置开始找
ch
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int indexOf(String str)
|
返回
str
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int indexOf(String str,
int fromIndex)
|
从
fromIndex
位置开始找
str
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int lastIndexOf(int ch)
|
从后往前找,返回
ch
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int lastIndexOf(int ch,
int fromIndex)
|
从
fromIndex
位置开始找,从后往前找
ch
第一次出现的位置,没有返
回
-1
|
|
int lastIndexOf(String str)
|
从后往前找,返回
str
第一次出现的位置,没有返回
-1
|
|
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex)
|
从
fromIndex
位置开始找,从后往前找
str
第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1
|
3.1. charAt
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));//与数组类似,默认从0开始编号
System.out.println(str.charAt(1));
System.out.println("=============");
//一个一个字符的打印出字符串
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(str.charAt(i));
}
}
}
3.2 indexOf
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcabcabc";
//当我想要拿到第一个c出现的位置
System.out.println(str.indexOf('c'));//返回第一个c出现的位置
System.out.println("================");
//如果想要从指定位置开始找c
//假如我们想从6下标的位置开始找c
System.out.println(str.indexOf(/*ch:*/'c',/*fromIdex:*/6));
}
}
3.3 indexOf(String str)
//indexOf
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
//在主串当中查找子串,返回子串第一个字母出现的位置 KMP算法
System.out.println(str.indexOf("abcd"));
}
}
3.4 indexOf(String str,int fromIdex)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
System.out.println(str.indexOf(/*str:*/"abc",/*fromIdex:*/6));
}
}
3.5 lastIdexOf(int ch)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("a"));
}
}3.6 lastIdexOf(int ch,int fromIdex)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("a",4));
}
}3.7 int lastIndexOf(String str)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
//IndexOf就是从前往后找,lastIndexOf就是从后往前找
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("abcd"));
//返回从后往前找到的第一个”abcd“首字母'a'的位置
}
}
3.8 int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIdexOf)
//从哪个位置开始从后往前找
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcabcdabc";
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("ab",8));
}
}
4,转化
在使用Java时我们常常会遇到这样的情况:字符串需要转成数字,而数字呢又需要转成字符串。
4.1.数字转字符串
这时我们就会用到valueof来实现我们的操作
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数字转字符串
String str1 = String.valueOf(123);
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
idea也是相当的方便,当我们在使用valueof时可以看见valueof重载的相当多的类型:

4.2.字符串转数字:
字符串转数字需要使用被转化数据类型的包装类来完成,具体参考如下:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串转数字
String str = "123";
int data1 = Integer.parseInt(str);//转成int类型
double data2 = Double.parseDouble(str);//转换double类型
}
}4.3.大小写转化
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ABcd";
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase());//小写变大写
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase());//小写变大写
}
}
4.4.字符串转数组
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcd";
char[] arr = str.toCharArray();//转化成字符数组,其它同理
for (char x:arr) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
5,格式化
格式化输出字符串日是经常碰到的问题,常见的格式化输出如下
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = String.format("%d-%d-%d",2023,12,2);//括号内和c语言printf同理
System.out.println(str);
}
}
6.字符串替换
Java中字符串替换常常使用的是replace

通过idea可以看到有4个replace的重载方法,接下来让我们逐一介绍
6.1 直接将旧的替换为新的
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String ret1 = str.replace('a','x');
System.out.println(ret1);
}
}
注意:这里并不是在原本的str上直接进行替换,而是产生了一个全新的字符串,包括上述的转化大小写等,全都是产生了一个新的对象。
6.2 CharSequence
我们并不知道CharSequence是一个什么类型,但当我们查看CharSequence的源码时会发现原来是实现了一个harSequence接口
所以当我们传一个String类型的时候它一定会发生向上转型
所以我们在传参的时候可以直接传字符串了
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefg";
String ret1 = str.replace("abc","def");
System.out.println(ret1);
}
}
6.3 replaceAll
replaceAll就是替换所有的,而上述两种方法默认也是替换所有的
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ababab";
String ret1 = str.replace("ab","ooo");
System.out.println(ret1);
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ababab";
String ret1 = str.replaceAll("ab","ooo");
System.out.println(ret1);
}
}
6.4 replaceFirst
顾名思义,替换第一个
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "ababab";
String ret1 = str.replaceFirst("ab","ooo");
System.out.println(ret1);
}
}
7.字符串的拆分
字符串的分割比较智能,会将它划分为数组,打印时只需要遍历数组便可
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello classmates";
String[] strs = str.split(" ");//以空格作为拆分
for (String x:strs) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}

除此之外,还可以限制划分
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello new student";
String[] strs = str.split(" ",2);//以空格作为拆分
for (String x:strs) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}

注意:
1.当我们想以“.”“*”等作为分割时,需要先对其进行转义
比如:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "2023.12.02";
String[] strs = str.split(".");
for (String x:strs) {
System.out.println(x);
}

此时什么都没有打印出来,为什么?
因为此时编译器并不能识别“.”,在C语言当中我们学过,“\.”才表示“.”而“\\”表示一个"\",所以在这里需要使用“\\.”才能表示"."。
所以这里应该这样写:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "2023.12.02";
String[] strs = str.split("\\.");
for (String x:strs) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
2.当有多个分隔符时,使用|作为标志
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "2023=12&02";
String[] strs = str.split("=|&");
for (String x:strs) {
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
8.字符串的截取
在使用字符串时我们往往想要只获取中间某一段字符?
这时最好的方法便是使用字符串的截取
从一个完整的字符串中截取出部分内容,可用方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|
String substring(int beginIndex)
|
从指定索引截取到结尾
|
|
String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
|
截取部分内容
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "asubfiavbafj";
//返回从二位置开始,剩余截取到的所有字符
String s = str.substring(2);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abcdefghij";
//返回从2位置开始,剩余截取到的所有字符
String s1 = str.substring(2);
//返回从2位置开始,到6位置结束,不反悔6位置字符,呈左闭右开[ )的方式
String s2 = str.substring(2,6);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
}
}
注意:
截取也是返回新的字符串对象
几乎所有的字符串方法都是产生的新对象
9.其它操作方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|
String trim()
|
去掉字符串中的左右空格
,
保留中间空格
|
|
String toUpperCase()
|
字符串转大写
|
|
String toLowerCase()
|
字符串转小写
|
trim
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello world ";
String ret = str.trim();
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
待续
























 1686
1686

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










