在测试字符串相等的时候遇到个小问题,加深了理解
public class testEquals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "hell" + "o";
System.out.println("s1 == s2 ?" + s1 == s2);
System.out.println("s1 == s3 ?" + s1 == s3);
System.out.println("os1 == os2 ? " + (new String("hello") == new String("hello")));
}
}
猜猜这段代码输出啥?
答案是false,false,false。
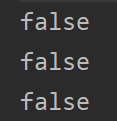
连比如"s1 == s2 ?"这类连接字符串都没了,直接输出了false。
原因:
其实是一个很基础的点,涉及到 == 运算符的比较优先级问题。
"s1 == s2 ?" + s1 == s2其实是("s1 == s2 ?" + s1) == s2
将后面的写为(s1 == s2)即可
原代码经过XJad反编译程序反编译后,从中可以看出问题所在了
public class testEquals
{
public testEquals()
{
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "hello";
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("s1 == s2 ? : ").append(s1).toString() == s2);
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("s1 == s3 ? : ").append(s1).toString() == s3);
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("os1 == os2 ? ").append(new String("hello")).toString() == new String("hello"));
}
}
修改过的代码反编译后:
public class testEquals
{
public testEquals()
{
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "hello";
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("s1 == s2 ?").append(s1 == s2).toString());
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("s1 == s3 ?").append(s1 == s3).toString());
System.out.println((new StringBuilder()).append("os1 == os2 ? ").append(new String("hello") == new String("hello")).toString());
}
}
1、回到代码
public class testEquals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
String s3 = "hell" + "o";
System.out.println("s1 == s2 ?" + (s1 == s2));
System.out.println("s1 == s3 ?" + (s1 == s3));
System.out.println("os1 == os2 ? " + (new String("hello") == new String("hello")));
}
}
在Java中,内容相同的字符串共享一份内存,所以s1,s2,s3实际上引用的是同一变量。
2、再看以下代码
String s4 = "a";
String s5 = s4;
s4 += "b";
System.out.println(s4 == "ab");
System.out.println("ab".equals(s4));
结果为false,true
Q: 为什么用==比较是false,用eqals方法比较就是true呢?
A: 由于String字符串为只读的,也就是对象是不可变的,在s4 += "b"的过程中,创建了一个新的对象赋值给s4,此s4中虽内容为“ab”,但是和字符串常量“ab”是两个截然不同的对象。使用equals则可以比较字符串内容
在使用equals方法时,如果是和常量相比较,使用 “字符串常量”.equals(字符串变量) ,防止空指针异常。

图片来自金旭亮老师java课程ppt





















 2815
2815











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








