替罪羊树基于一种暴力重构的操作来保证平衡,具体来说,就是定义一个平衡因子alphaalpha ,当某个节点x的某棵子树的x.ch.size>x.size*alphax.ch.size>x.size∗alpha *时便将这棵以x为根的子树拍扁重构。
替罪羊树的基本操作和普通二叉树差不多的,神奇的就在于它的拍扁重构。
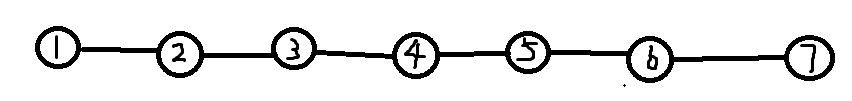
假如这有一棵树(你tm告诉我这是树?)
虽然不知道它是咋长成这样的,但是显然这种结构是要维护的。
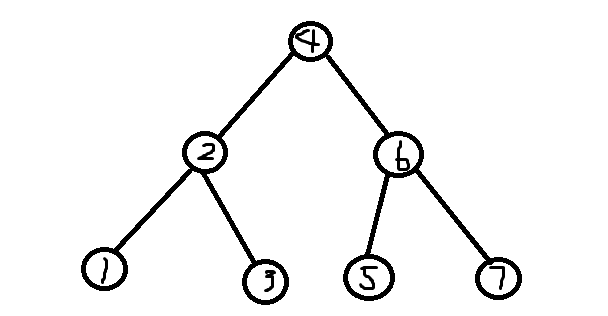
于是,我们把它拍扁重构!
完事以后树的形态变成了这样
这就是一颗很完美的二叉查找树了。可以理解为,当当前满足一定条件时就以它为跟将它的左右子树重新建一颗平衡的二叉查找树。那么,这个条件是什么呢?
正如开头所说,我们可以定义一个常数a(一般为0.7),当当前节点大小小于某个子节点与a的乘积时,就把树拍扁重构,这个a的取值可以人为控制,但太大了容易造成二叉树左右节点不平衡而影响查询效率,太小了将进行过多的拍扁重构也会影响效率,因此一般a取0.7。
基本操作:
check判断当前点是否合法:
int check(int p)
{
if(a[p].w==0)
return 0;
if ((a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].lc].w>=double(alpha*(a[p].w+a[p].s)))||
(a[a[p].rc].s+a[a[p].rc].w>=double(alpha*(a[p].w+a[p].s))))return 1;
return 0;
}查找节点
int getN(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(a[now].n!=x&&a[now].s!=0)
{
if(a[now].n>=x)
now=a[now].lc;
else now=a[now].rc;
}
return now;
}拍扁重构:先dfs一遍,找出每个节点在新树中的编号,并将相关信息储存。
void dfs(int p)
{
h[++top]=p;
if(a[p].lc!=0)
dfs(a[p].lc);
if(a[p].w!=0)
d[++tott].n=a[p].n,
d[tott].w=a[p].w;
a[p].s=0;
if(a[p].rc!=0)
dfs(a[p].rc);
}可以看出,这是按从左往右的顺序遍历的,这样就可以保证新树的大小顺序和原树是一样的。之后修改根节点的信息,并从根节点向下修改其子节点的信息。
代码:
void make(int l,int r,int p,int fa)
{
int mid=(l+r)/2;
a[p].fa=fa;
a[p].w=d[mid].w;
a[p].n=d[mid].n;
if(mid-1>=l)
a[p].lc=getnewp(),make(l,mid-1,a[p].lc,p);
else a[p].lc=0;
if(mid+1<=r)
a[p].rc=getnewp(),make(mid+1,r,a[p].rc,p);
else a[p].rc=0;
a[p].s=a[a[p].lc].w+a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].rc].w+a[a[p].rc].s;
}
void rebuild(int p)
{
if(p==0)
return;
tott=0;
dfs(p);
int now=getnewp();
a[now].fa=a[p].fa;
if(p==root)
root=now;
int mid=(1+tott)/2;
if(d[mid].n>a[a[p].fa].n)
a[a[p].fa].rc=now;
else a[a[p].fa].lc=now;
make(1,tott,now,a[p].fa);
}插入:替罪羊树的插入和一般二叉查找树相同,但当操作完成后,往上回溯时要依次判断每个节点是否合法,记录离根节点最近的一个点并拍扁重构,注意把插入结点到根的路径上所有点的子树大小加1。
代码:
void insr(int x,bool rb)
{
if(root==0)
{
root=1;
a[1].n=x;
a[1].w++;
return;
}
int now=root;
while(a[now].s!=0)
{
if(x==a[now].n)
{
a[now].w++;
return;
}
if(x>a[now].n&&a[now].rc==0)
break;
if(x<a[now].n&&a[now].lc==0)
break;
a[now].s++;
if(x>a[now].n)
now=a[now].rc;
else if(x<a[now].n)
now=a[now].lc;
}
if(x==a[now].n)
{
a[now].w++;
return;
}
a[now].s++;
int tmp=now;
if(x>a[now].n)
now=a[now].rc=++tot;
else if(x<a[now].n)
now=a[now].lc=++tot;
a[now].w++;
a[now].n=x;
if(tmp!=now)
a[now].fa=tmp;
int chk=0;
while(now!=root)
{
now=a[now].fa;
if(check(now))
chk=now;
}
if(rb)
rebuild(chk);
}
删除:删除操作基本没啥技术含量,找到要删的点把他的个数减1就好了,注意还要把它到跟上的路径所有点的子树大小减1。
代码:
void delt(int p)
{
a[p].w--;
int chk=0;
while(p!=root)
{
p=a[p].fa;
a[p].s--;
}
}查找某一节点的排名:找到该点在序列中的编号并往上跳,如果改点为父亲节点的右儿子,直接加上父亲结点的左儿子的大小和个数,注意查到根节点时要把答案加1(想想为什么)。
代码:
int XgetRk(int x)
{
int p=getN(x),ans;
ans=a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].lc].w;
while(p!=root)
{
if(a[a[p].fa].rc==p)
ans+=a[a[a[p].fa].lc].s+a[a[a[p].fa].lc].w+a[a[p].fa].w;
p=a[p].fa;
}
return ans+1;
}查找某节点的值:跟正常操作一样,直接上代码。
代码:
int RkgetX(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(true)
{
int lcS=a[a[now].lc].s+a[a[now].lc].w;
if(x<=lcS)now=a[now].lc;
else if(x>lcS&&x<=a[now].w+lcS)
return a[now].n;
else x-=lcS+a[now].w,now=a[now].rc;
if(x==0)
return a[now].fa;
}
}查前驱后继:这个操作比较神奇。以前驱为例,先插入一个值为x的节点,查找他的排名tmp,再把这个节点删了,查找tmp-1点的值。
代码:
int suc(int x)
{
insr(x+1,0);
int tmp=XgetRk(x+1),nx=getN(x+1);
delt(nx);
return RkgetX(tmp);
}
int pre(int x)
{
insr(x,0);
int tmp=XgetRk(x);
delt(getN(x));
return RkgetX(tmp-1);
}整体代码(洛谷3369)
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#define alpha 0.7
using namespace std;
struct ScapeGoatTree{
int lc,rc,n,w,s,fa;
}a[100010];
struct REbuild{
int n,w;
}d[100010];
void rebuild(int p);
int tot=1,tott=0,top=0,h[100010],n,T,X,root;
int check(int p)
{
if(a[p].w==0)
return 0;
if ((a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].lc].w>=double(alpha*(a[p].w+a[p].s)))||
(a[a[p].rc].s+a[a[p].rc].w>=double(alpha*(a[p].w+a[p].s))))return 1;
return 0;
}
int getN(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(a[now].n!=x&&a[now].s!=0)
{
if(a[now].n>=x)
now=a[now].lc;
else now=a[now].rc;
}
return now;
}
void insr(int x,bool rb)
{
if(root==0)
{
root=1;
a[1].n=x;
a[1].w++;
return;
}
int now=root;
while(a[now].s!=0)
{
if(x==a[now].n)
{
a[now].w++;
return;
}
if(x>a[now].n&&a[now].rc==0)break;
if(x<a[now].n&&a[now].lc==0)break;
a[now].s++;
if(x>a[now].n)now=a[now].rc;
else if(x<a[now].n)now=a[now].lc;
}
if(x==a[now].n)
{
a[now].w++;
return;
}
a[now].s++;
int tmp=now;
if(x>a[now].n)
now=a[now].rc=++tot;
else if(x<a[now].n)
now=a[now].lc=++tot;
a[now].w++;
a[now].n=x;
if(tmp!=now)
a[now].fa=tmp;
int chk=0;
while(now!=root)
{
now=a[now].fa;
if(check(now))
chk=now;
}
if(rb)
rebuild(chk);
}
int getnewp()
{
if(top>0)
{
top--;
return h[top+1];
}
else return ++tot;
}
void dfs(int p)
{
h[++top]=p;
if(a[p].lc!=0)
dfs(a[p].lc);
if(a[p].w!=0)
d[++tott].n=a[p].n,
d[tott].w=a[p].w;
a[p].s=0;
if(a[p].rc!=0)
dfs(a[p].rc);
}
void make(int l,int r,int p,int fa)
{
int mid=(l+r)/2;
a[p].fa=fa;
a[p].w=d[mid].w;
a[p].n=d[mid].n;
if(mid-1>=l)
a[p].lc=getnewp(),make(l,mid-1,a[p].lc,p);
else a[p].lc=0;
if(mid+1<=r)
a[p].rc=getnewp(),make(mid+1,r,a[p].rc,p);
else a[p].rc=0;
a[p].s=a[a[p].lc].w+a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].rc].w+a[a[p].rc].s;
}
void rebuild(int p)
{
if(p==0)
return;
tott=0;
dfs(p);
int now=getnewp();
a[now].fa=a[p].fa;
if(p==root)
root=now;
int mid=(1+tott)/2;
if(d[mid].n>a[a[p].fa].n)
a[a[p].fa].rc=now;
else a[a[p].fa].lc=now;
make(1,tott,now,a[p].fa);
}
void delt(int p)
{
a[p].w--;
int chk=0;
while(p!=root)
{
p=a[p].fa;
a[p].s--;
}
}
int XgetRk(int x);
int RkgetX(int x);
int suc(int x)
{
insr(x+1,0);
int tmp=XgetRk(x+1),nx=getN(x+1);
delt(nx);
return RkgetX(tmp);
}
int pre(int x)
{
insr(x,0);
int tmp=XgetRk(x);
delt(getN(x));
return RkgetX(tmp-1);
}
int XgetRk(int x)
{
int p=getN(x),ans;
ans=a[a[p].lc].s+a[a[p].lc].w;
while(p!=root)
{
if(a[a[p].fa].rc==p)
ans+=a[a[a[p].fa].lc].s+a[a[a[p].fa].lc].w+a[a[p].fa].w;
p=a[p].fa;
}
return ans+1;
}
int RkgetX(int x)
{
int now=root;
while(true)
{
int lcS=a[a[now].lc].s+a[a[now].lc].w;
if(x<=lcS)now=a[now].lc;
else if(x>lcS&&x<=a[now].w+lcS)
return a[now].n;
else x-=lcS+a[now].w,now=a[now].rc;
if(x==0)
return a[now].fa;
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i%1000==0)
{
int ttott;
ttott++;
}
scanf("%d%d",&T,&X);
if(T==1)insr(X,1);
else if(T==2)delt(getN(X));
else if(T==3)printf("%d\n",XgetRk(X));
else if(T==4)printf("%d\n",RkgetX(X));
else if(T==5)printf("%d\n",pre(X));
else if(T==6)printf("%d\n",suc(X));
}
}























 2345
2345











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








