Introduction
I would like to share the basics of MVC design patterns. I have collected the following contents from various web resources and tried to summarize them in my words.
Understanding MVC with Relationship diagram
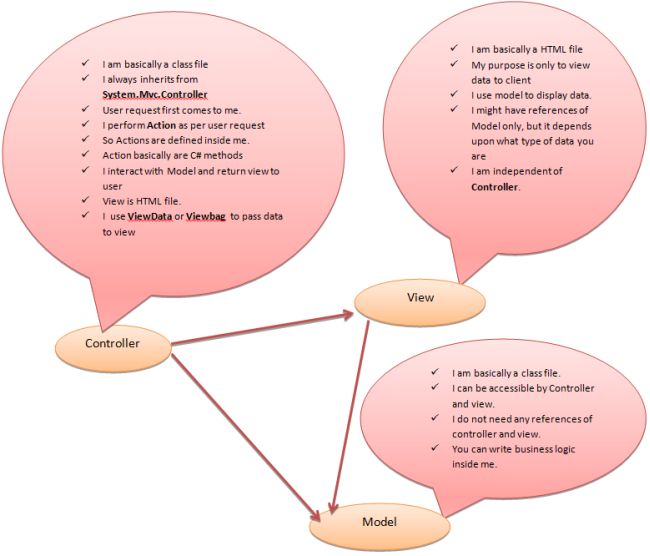
What is a Model?
- The MVC model is basically a C# or VB.NET class
- A model is accessible by both controller and view
- A model can be used to pass data from a controller to a view
- A Model is considered to be smart and handles the business rules, logic and data and will be independent of other parts of MVC (controller and view).
What is a View?
- A View is an ASPX page without a code behind file
- A view is considered to be dumb and is an output representation of the model data
- A view knows only about the model.
What is a Controller?
- A Controller is basically a C# or VB.NET class that inherits system.mvc.controller
- A Controller is the heart of the entire MVC architecture
- Inside the Controller's class, action methods can be implemented that are responsible for responding to browser or calling views.
- A Controller can access and use a model class to pass data to views
- A Controller uses ViewData to pass any data to the view
- A Controller receives and dispatches the request; in short, it handles the user interaction and input logic. It knows about both the Model and View.
Difference between ASP.NET Web form and MVC
| Page controller pattern | MVC |
| Typical page life cycle | No page life cycle |
| Viewstate | No Viewstate |
| Slow due to maintaining the state of controls in hidden fields | Fast |
| Testing is difficult | Testing is easy |
| Need to create Arch for business logic | No need to create arch, the business logic is already separated into different folders |
| No concepts of actions | We can reuse the actions at the controller |
| Large page size due to viewstate | Small page size due to no viewstate concept |
| Each page attached with its code behind | View and controller are not dependent each other |
| Good for small applications | Good for big applications |
| Postbacks occurs | No postbacks |
Request lifecycle in MVC applications
- Browers request to the server (URL like pqr.com]/home/index/ or pqr.com]/emp/edit/)
- Global.asax will read the URL and try to find the corresponding requested controller and Action
- Here Controller is Home and Action is index.
- MVC will try to find the corresponding Controller for Home, it will be the HomeController class in the controller directly
- The Controller class might contain various Actions as methods defined
- Here the Action will be HomeController.Index()
- Invoking the method Index() will return the corresponding view (HTML page)

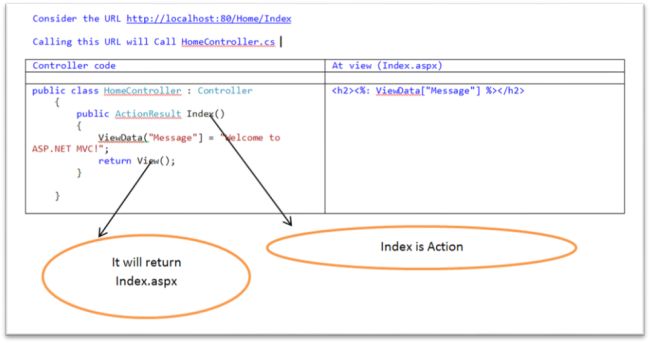
ViewData can be used for this purpose, it is a dictionary.
The ActionResult class is the base class for action results. Common return types are:
- Returning a View.
Here in the following example Index.aspx will be returned as the view because Index() is the action here.
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
- Rendering a plain text in the browser.
public ActionResult Index()
{
return Content("hello world");
}
Here we will get hello world in the DOM.
- Modifying the return type to void.
public void Index()
{
Response.write(“hello world”);
}
Here we will get hello world at DOM.
- Modifying the return type to ContentResult class.
public JSONResult Index()
{
return Content("hello world");
}
- Returning a specific view.
Here in the example below we have the Index() Action but we are returning Result.aspx because View() also accepts a parameter that is the name of the View.
public ViewResult Index()
{
return View("Result");
}
- Simple returing string.
public string Index()
{
return "This is my default action...";
}
Conclusion
Here we learned the basics of MVC Design Patterns.
原文转载地址:http://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/deveshomar/basic-of-mvc-design-pattern/

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








