You are given two arrays A and B, each of size n. The error, E, between these two arrays is defined 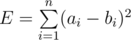 . You have to perform exactly k1 operations on array A and exactly k2 operations on array B. In one operation, you have to choose one element of the array and increase or decrease it by 1.
. You have to perform exactly k1 operations on array A and exactly k2 operations on array B. In one operation, you have to choose one element of the array and increase or decrease it by 1.
Output the minimum possible value of error after k1 operations on array A and k2 operations on array B have been performed.
The first line contains three space-separated integers n (1 ≤ n ≤ 103), k1 and k2 (0 ≤ k1 + k2 ≤ 103, k1 and k2 are non-negative) — size of arrays and number of operations to perform on A and B respectively.
Second line contains n space separated integers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 106 ≤ ai ≤ 106) — array A.
Third line contains n space separated integers b1, b2, ..., bn ( - 106 ≤ bi ≤ 106)— array B.
Output a single integer — the minimum possible value of 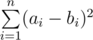 after doing exactly k1 operations on array A and exactly k2operations on array B.
after doing exactly k1 operations on array A and exactly k2operations on array B.
2 0 0 1 2 2 3
2
2 1 0 1 2 2 2
0
2 5 7 3 4 14 4
1
In the first sample case, we cannot perform any operations on A or B. Therefore the minimum possible error E = (1 - 2)2 + (2 - 3)2 = 2.
In the second sample case, we are required to perform exactly one operation on A. In order to minimize error, we increment the first element of A by 1. Now, A = [2, 2]. The error is now E = (2 - 2)2 + (2 - 2)2 = 0. This is the minimum possible error obtainable.
In the third sample case, we can increase the first element of A to 8, using the all of the 5 moves available to us. Also, the first element of B can be reduced to 8 using the 6 of the 7 available moves. Now A = [8, 4] and B = [8, 4]. The error is now E = (8 - 8)2 + (4 - 4)2 = 0, but we are still left with 1 move for array B. Increasing the second element of B to 5 using the left move, we get B = [8, 5] and E = (8 - 8)2 + (4 - 5)2 = 1.
题意:给你两个数组A和B,长度都为n,你可以对A进行k1次操作,对B进行k2次操作,操作为:对数组中的一个元素加一或减一。
求最小的 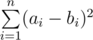 值。
值。
题解:直接存每个数组的差值放入一个优先队列,然后一个一个减,注意不能每次都选择最大差值使其差值变为0再对其它数进行操作。
例如差值为:2 4 6 ,进行四次操作,如果每次选最大差值使其变为0则结果为2 4 2,平方和为:24,然而用优先队列每次选最大的数减一再计算结果为:2 3 3 ,平方和为:22,显然后者要小的多。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
#define INIT ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
#define LL long long int
LL max(LL a, LL b) {
if (a > b)return a;
return b;
}
//2 4 6 4 2 4 2 2 3 3
bool cmp(int x, int y) {
return x > y;
}
int main() {
int n, k1, k2;
int a[1005], b[1005];
priority_queue<LL>q;
int c[1005];
while (cin >> n >> k1 >> k2) {
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
scanf("%d",a + i);
}
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) {
scanf("%d", b + i);
c[i] = abs(a[i] - b[i]);
q.push(c[i]);
}
LL ans = 0;
int sum = k1 + k2;
while (sum > 0)
{
int tmp = q.top();
q.pop();
//注意绝对值
q.push(abs(tmp - 1));
sum--;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
ans += pow(q.top(), 2);
q.pop();
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}























 3391
3391











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








