MyBatis-Plus基础–入门
MyBatis-Plus(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis 的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
快速入门





























步骤
maven依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
<!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Mybatis-Plus启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
说明:我们使用 mybatis-plus 可以节省我们大量的代码,尽量不要同时导入 mybatis 和 mybatisplus! 版本的差异!
application.yml配置文件
配置数据库连接数据源,日志输出
# 配置名称(别名)
spring:
application:
name: student-puls
# 配置数据库
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: root
# 配置端口号
server:
port: 8080
# 配置日志 输出SQL语句
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 注意: mysql数据是8.0以上的必须指定时区
#//北京时间东八区 serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
#或者使用上海时间 serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
# 加载驱动类 必须加cj
实体类
使用lombok注解
@Data // 代替写set/get方法
@AllArgsConstructor //有参构造方法
@NoArgsConstructor //无参构造方法
public class Student {
/**
* 主键ID
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 性别
*/
private String gender;
/**
* 电话
*/
private String telephone;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
private String email;
/**
* 班级编号
*/
@TableField(value = "classId")
private Long classId;
}
Mapper接口
主要继承MP提供的BaseMapper<>接口,该接口里面包含增删改查方法。
@Repository // 代表持久层
// 在对应的Mapper上面继承基本的类 BaseMapper
// Mapper 继承该接口后,无需编写 mapper.xml 文件,即可获得CRUD功能
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
启动类
主要加上@MapperScan(“com.zzz.mapper”)注解扫描mapper接口包
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.zzz.mapper")
public class StudentPlusApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StudentPlusApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试类
@SpringBootTest
class StudentPlusApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Test
void test(){
System.out.println(("----- selectAll method test ------"));
List<Student> students = studentMapper.selectList(null);
//jdk8:支持的循环
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
结果展示
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-lU2h1JrE-1616153572818)
注意 注意 注意
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-n4xrkWAS-1616153572819)
出现说找不到这个列、或者说你的列突然多出一个下划线。
数据库中却没有下划线
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5CO0Qk09-1616153572821)
这是因为mybati-puls 没有对驼峰命名进行处理,需要自己配置

[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4kHH75m7-1616153572823)




























.png)]
在实体类的字段上加上驼峰命名,即可解决问题。
BaseMapper 接口的所有方法。
public interface BaseMapper<T> {
/**
* 插入一条记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int insert(T entity);
/**
* 根据 ID 删除
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
int deleteById(Serializable id);
/**
* 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,删除记录
*
* @param wrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> wrapper);
/**
* 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
/**
* 根据 ID 修改
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
/**
* 根据 whereEntity 条件,更新记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可以为 null)
* @param updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句)
*/
int update(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);
/**
* 根据 ID 查询
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
T selectById(Serializable id);
/**
* 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
/**
* 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
List<T> selectByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,查询一条记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
T selectOne(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询总记录数
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
Integer selectCount(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List<T> selectList(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录
* <p>注意: 只返回第一个字段的值</p>
*
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页)
*
* @param page 分页查询条件(可以为 RowBounds.DEFAULT)
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录(并翻页)
*
* @param page 分页查询条件
* @param queryWrapper 实体对象封装操作类
*/
IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
}
内置Mapper CRUD
实体类Student
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
//描述:表名注解,当实体类的表名和数据库中的表名不一致的时候会出错,此注解可以使用表名保持一致。
@TableName(value="student")
public class Student {
/**
* 主键ID
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 性别
*/
private String gender;
/**
* 电话
*/
private String telephone;
/**
* 邮箱
*/
private String email;
/**
* 班级编号
*/
//解决数据库和实体类中驼峰命名问题
@TableField(value = "classId")
private Long classId;
//描述:字段注解(非主键),false表示实体类中有该属性,但是数据库中可以没有该字段,默认值true
@TableField(exist = false)
private String className;
}
CRUD操作
**1,Insert ** 增加
/**
* 插入一条数据
* int insert(T entity);
*/
@Test
void AddStudent(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("若贞");
student.setAge(320);
student.setGender("男");
student.setTelephone("13545678945");
student.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student.setClassId(4L);
int insert = studentMapper.insert(student);
System.out.println(insert);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-44fR6PXT-1616153572824)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118104344964.png)]
主键生成策略
默认 ID_WORKER 全局唯一id
分布式系统唯一id生成:https://www.cnblogs.com/haoxinyue/p/5208136.html
雪花算法:
snowflake是Twitter开源的分布式ID生成算法,结果是一个long型的ID。其核心思想是:使用41bit作为 毫秒数,10bit作为机器的ID(5个bit是数据中心,5个bit的机器ID),12bit作为毫秒内的流水号(意味 着每个节点在每毫秒可以产生 4096 个 ID),最后还有一个符号位,永远是0。可以保证几乎全球唯 一!
主键自增
我们需要配置主键自增:
1、实体类字段上 @TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
2、数据库字段一定要是自增!
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AGzyF1mP-1616153572825)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119095836287.png)]
3、再次测试插入即可!
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-uT6EaF8A-1616153572826)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119101350757.png)]
注意:如果未能成功 请重置表主键
truncate table student; //重置后数据就没了
其与的源码解释
public enum IdType {
AUTO(0), // 数据库id自增
NONE(1), // 未设置主键
INPUT(2), // 手动输入
ID_WORKER(3), // 默认的全局唯一id
UUID(4), // 全局唯一id uuid
ID_WORKER_STR(5); //ID_WORKER 字符串表示法
}
**2,Delete ** 删除
/**
*删除,(1)根据id删除
*(2)根据map删除
*(3)根据条件构造器删除
*/
@Test
public void bDelete() {
/**
* (1)sql:DELETE FROM student WHERE id=?
*/
studentMapper.deleteById(1328890985682128898L);
/**
* (2)sql:DELETE FROM student WHERE name = ? AND age = ?
*/
Map<String, Object> columnMap=new HashMap<String, Object>();
//key为数据库字段名,value为数据库字段值
columnMap.put("name", "若贞");
columnMap.put("age", "66");
studentMapper.deleteByMap(columnMap);
/**
* (3)sql:DELETE FROM student WHERE name = ? AND age = ?
* QueryWrapper条件构造器,QueryWrapper:Entity 对象封装操作类,Wrapper接口实现类
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> wrapper=new QueryWrapper<Student>();
//eq表示等于。
wrapper.eq("name", "若贞2").eq("age", "12");
studentMapper.delete(wrapper);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-f2hF6EN1-1616153572827)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118105034214.png)]
**3,Update ** 修改
/**
* (1)根据id修改
* (2)根据updateWrapper条件构造器修改
*/
@Test
public void cUpdate() {
//(1)sql:UPDATE student SET name=?, age=? WHERE id=?
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("若贞");
student1.setAge(22);
student1.setId(6L);
studentMapper.updateById(student1);
/**
* (2-1)uupdateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类允许null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句
* sql:UPDATE student SET age=? WHERE id = ?
*/
UpdateWrapper<Student> studentUpdateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
studentUpdateWrapper.set("age",20).eq("id","4L");
//加条件1,可以设置为null,逗号后面加条件2
studentMapper.update(null,studentUpdateWrapper);
/**
* (2-2)updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类not null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句
* sql:UPDATE student SET name=?, age=? WHERE id = ?
*/
//加条件1
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setName("like loyal");
//加条件2
UpdateWrapper<Student> studentUpdateWrapper2 = new UpdateWrapper<>();
studentUpdateWrapper2.set("age",25).eq("id","3L");
studentMapper.update(student2,studentUpdateWrapper2);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jMDLkv1r-1616153572827)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118110436639.png)]
4,Select 查询
(1)基本查询
/**
* 查询
*/
@Test
public void dSelect() {
/**
* (1)T selectById(Serializable id);根据 ID 查询,主键
* sql:SELECT id,name,age,email FROM student WHERE id=?
*/
studentMapper.selectById(6L);
/**
* (2)selectOne:根据 entity 条件,只能查询一条记录,如果数据库中存在多条,那么查询出错。
* sql:SELECT id,name,age,email FROM student WHERE name LIKE ? AND age = ?
* Parameters: %m%(String), 25(String)
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","o");
queryWrapper.eq("age","25");
studentMapper.selectOne(queryWrapper);
/**
* (3)selectList: 根据 entity 条件,查询全部记录
* sql:SELECT id,name FROM student
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper1 = new QueryWrapper<>();
//设置查询字段,查询全部数据
queryWrapper1.select("id","name");
studentMapper.selectList(queryWrapper1);
//查询全部字段+全部数据
//studentMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<User>());
//查询全部字段+全部数据
//studentMapper.selectList(null);
/**
* (4)selectMaps:根据 Wrapper 条件,查询全部记录,得到一个Map集合。
* List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = studentMapper.selectMaps(Wrappers.<Student>query().orderByAsc("age"));
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper2 = new QueryWrapper<>();
// orderByDesc() 排序
queryWrapper2.orderByDesc("id");
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList2 = studentMapper.selectMaps(queryWrapper2);
// 输出的形式 [{key,value},...]
System.out.println(mapList2);
/**
* (5) 排序order by; condition 执行条件是否有效,treu表示有效。isAsc 是否是 ASC排序。columns 字段数组
* sql:SELECT id,name,age,email FROM student ORDER BY id DESC
* List<Student> users = studentMapper.selectList(Wrappers.<User>query().orderByAsc("id"));
* studentMapper.selectList(new QueryWrapper<User>().orderByDesc("id"));//查询全部字段+全部数据
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper3 = new QueryWrapper<>();
//查询全部字段+全部数据
//condition 执行条件是否有效,treu表示有效。isAsc 是否是 ASC排序。columns 字段数组
queryWrapper3.orderBy(true,false,"id");
studentMapper.selectList(queryWrapper3);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-J4EHyTNw-1616153572828)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118113223331.png)]
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tnMRjbbU-1616153572829)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118113434454.png)]
注意:**selectOne()**方法只能查询出一条数据 多条数据会报错
(1-1)通过多个id批量查询,完成了动态sql的foreach的功能
@Test
public void selectBatchIdstt(){
List<Student> students = studentMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(4L, 5L, 6L));
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
(1-2)通过map封装查询条件
@Test
public void SelectByMaptt(){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//map中的key对应的是数据库中的列名。
//如数据库中的字段为user_id,map的key也需要填写user_id。
map.put("name", "若贞");
map.put("age", 22);
List<Student> users = studentMapper.selectByMap(map);
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
(2)聚合函数
@Test
public void eSelect() {
/**
* (1)最大值max 最小值min 数量count 总数sum
* sql:SELECT max(id) as id FROM student //聚合函数
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.select("count(id) as id");//查询id单列总记录数
Student student = studentMapper.selectOne(wrapper);
System.out.println("maxId=" + student.getId());
/**
* (2-1)分组,sql:SELECT age, count(*) FROM student GROUP BY age
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> wrapper2 = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper2.select("age, count(*)").groupBy("age");
List<Student> lis2t = studentMapper.selectList(wrapper2);
lis2t.forEach(System.out::println);
//结果:Student(id=null, name=null, age=18, email=null, count=null)
/**
* (2-2)分组,sql: SELECT age, count(age) as count FROM student GROUP BY age
*/
QueryWrapper<Student> wrapper3 = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper3.select("age, count(age) as count").groupBy("age");
List<Student> list = studentMapper.selectList(wrapper3);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//结果:Student(id=null, name=null, age=18, email=null, count=1)
}
(3)分页查询(PaginationInterceptor)
MyBatis-Plus 提供了物理分页的功能,使用前我们需要要进行相关的插件配置:
逻辑分页与物理分页比较:
-
逻辑分页:内存开销比较大,在数据量比较小的情况下效率比物理分页高;在数据量很大的情况下,内存开销过大,容易内存溢出,不建议使用。
-
物理分页:内存开销比较小,在数据量比较小的情况下效率比逻辑分页还是低;在数据量很大的情况下,建议使用物理分页。
a,使用前先配置分页插件
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
//分页插件
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor = new PaginationInterceptor();
// paginationInterceptor.setLimit(你的最大单页限制数量,默认 500 条,小于 0 如 -1 不受限制);
return paginationInterceptor;
}
}
b,Mapper接口提供了2个分页方法selectPage()和selectMapsPage()
1、selectPage()
IPage<T> selectPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 返回IPage<User>
参数1:实体类,参数2:条件构造器
*/
@Test
public void selectPage() {
// sql:SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user LIMIT ?,?
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<Student>();
//当为true的时候条件生效,false不生效。
Page<Student> page = new Page<Student>(1, 3,true);
IPage<Student> ipage = studentMapper.selectPage(page, queryWrapper);
//查询分页数据列表
System.out.println(ipage.getRecords());
//查询总数
System.out.println(ipage.getTotal());
//分页总页数
System.out.println(ipage.getPages());
//当前页
System.out.println(ipage.getCurrent());
//当前分页数量
System.out.println(ipage.getSize());
}
2、selectMapsPage()
IPage<Map<String, Object>> selectMapsPage(IPage<T> page, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
/**
* 返回 IPage<Map<String, Object>> page
参数1:实体类,参数2:条件构造器
*/
@Test
public void selectMapsPage() {
// sql:SELECT id,name,age,email FROM user ORDER BY age ASC LIMIT ?,?
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.orderByDesc("age");
IPage<Map<String, Object>> page = studentMapper.selectMapsPage(new Page<>(0, 2), queryWrapper);
//IPage<Map<String, Object>> page = userMapper.selectMapsPage(new Page<>(1, 2), new QueryWrapper<User>());
//查询分页数据列表
System.out.println(page.getRecords());
//查询总数
System.out.println(page.getTotal());
//分页总页数
System.out.println(page.getPages());
//当前页
System.out.println(page.getCurrent());
//当前分页数量
System.out.println(page.getSize());
}
区别:selectMapsPage 的用法和上面的 selectPage 很像,都是传入分页查询条件、以及查询构造器进行查询,然后返回一个 List。不同在于 selectMapsPage 返回的结果里面是 Map:
Service的CRUD
准备工作
StudentMapper 接口,并继承 BaseMapper 接口,就可以使用 Mapper 的各种 CRUD 方法了
@Repository
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
}
继承 IService 创建 Service 接口,并创建对应的实现类,这样便可以使用 Service 的各种 CRUD 方法了:
- StudentService 接口代码如下:
public interface StudentService extends IService<Student> {
}
-
StudentServiceImpl 实现类代码如下:
// @Service 注入到ico容器中 @Service public class StudentServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper, Student> implements StudentService { }
1、Select 查询
getById(根据 id 查询一条记录)
@Test
void getById(){
/**
* (1)getById(根据 id 查询一条记录)
* sql: SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE id=?
*/
Student byId = studentService.getById(6L);
}
getOne(使用查询构造器,查询一条记录)
@Test
void getOne(){
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄小于40
//sql:SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",24);
// **开始查询符合的单条记录(如果满足条件的记录有多条,那就不能用这个方法,会报错。)**
Student one = studentService.getOne(queryWrapper);
}
getMap(使用查询构造器,查询一条记录,返回的是 Map)
getMap 的用法和上面的 getOne 很像,都是传入一个查询构造器进行查询。不同的是 getMap 返回的是一个 Map,而不是实体类对象:
注意: Map 里的 key 为表字段名,而不是对应实体类的属性名。
@Test
void getMap(){
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于24
//sql:SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",24);
// 开始查询符合的单条记录(如果满足条件的记录有多条,那就不能用这个方法,会报错。)
Map<String, Object> user = studentService.getMap(queryWrapper);
}
getObj(使用查询构造器,查询一条记录,返回这条记录的第一个字段值)
getObj 的用法和上面的 getOne 很像,都是传入一个查询构造器进行查询。不同的是 getObj 返回的是一个字段值(该方法第二个参数是转换函数,必填)
@Test
void getObj(){
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于24
//sql:SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",24);
// 开始查询符合的单条记录的第一个字段值
Integer id = studentService.getObj(queryWrapper, (o) -> {
return Integer.parseInt(o.toString());
});
System.out.println(id);
}
listByIds(根据 ID 批量查询,返回一个 List)
// 注意主键id 的数据类型。
List<Student> student = studentService.listByIds(Arrays.asList(4L,5L,6L));
listByMap(通过 Map 封装的条件查询,返回一个 List)
注意:map 写的是数据表中的列名,而非实体类的属性名。比如属性名为 userName,数据表中字段为 user_name,这里应该写的是 user_name。
Map<String,Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("name", "若贞");
columnMap.put("age", 22);
List<Student> students = studentService.listByMap(columnMap);
list(使用查询构造器,返回一个 List)
1、list 方法如果参数为空,则查询所有的数据:
// 查询所有数据
List<Student> students = studentService.list();
2、list 方法也可以传入查询条件构造器进行查询:
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于24
//sql: SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
// Parameters: %like%(String), 20(Integer)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",20);
//可以查询多条数据
List<Student> students = studentService.list(queryWrapper);
listMaps(使用查询构造器,返回一个 List)
listMaps 的用法和上面的 list 很像,都是传入一个查询构造器进行查询,然后返回一个 List。不同在于 listMaps 返回的 List 里面是 Map。
注意: Map 里的 key 为表字段名,而不是对应实体类的属性名。
1、listMaps 方法如果参数为空,则查询所有的数据:
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = studentService.listMaps();
System.out.println(mapList);
2、listMaps 方法也可以传入查询条件构造器进行查询:
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于20
//sql: SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
// Parameters: %like%(String), 20(Integer)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",20);
// 开始查询
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = studentService.listMaps(queryWrapper);
count(使用查询构造器,查询总记录数)
1、count 方法如果参数为空,则查询所有数据的记录数:
Integer count = studentService.count();
System.out.println(count);
2、count 方法也可以传入查询条件构造器进行查询
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于20
//sql: SELECT COUNT( 1 ) FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?)
// Parameters: %like%(String), 20(Integer)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",20);
//开始根据条件查询总记录
Integer count = studentService.count(queryWrapper);
System.out.println(count);
2、Page分页查询
添加配置
MyBatis-Plus 提供了物理分页的功能,使用前我们需要要进行相关的插件配置:
逻辑分页与物理分页比较:
- 逻辑分页:内存开销比较大,在数据量比较小的情况下效率比物理分页高;在数据量很大的情况下,内存开销过大,容易内存溢出,不建议使用。
- 物理分页:内存开销比较小,在数据量比较小的情况下效率比逻辑分页还是低;在数据量很大的情况下,建议使用物理分页。
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
//mybatis-plus分页插件
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor() {
PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor = new PaginationInterceptor();
// 设置请求的页面大于最大页后操作, true调回到首页,false 继续请求 默认false
// paginationInterceptor.setOverflow(false);
// 设置最大单页限制数量,默认 500 条,-1 不受限制
// paginationInterceptor.setLimit(500);
// 开启 count 的 join 优化,只针对部分 left join
paginationInterceptor.setCountSqlParser(new JsqlParserCountOptimize(true));
return paginationInterceptor;
}
}
IService 接口提供了 page 方法实现分页查询,比如下面我们查询第一页的数据(每页两条记录):
@Test
void page(){
// 查询条件:名字中包含'like'并且年龄大于20
//sql: SELECT id,name,age,gender,telephone,email,classId FROM student WHERE (name LIKE ? AND age > ?) LIMIT ?,?
// Parameters: %like%(String), 20(Integer), 1(Long), 2(Long)
QueryWrapper<Student> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","like");
queryWrapper.gt("age",20);
// 开始查询
IPage<Student> page = studentService.page(new Page<>(1,2), queryWrapper);
}
自定义 SQL 语句的分页查询
MyBatis-Plus 也支持对自定义的查询语句进行分页
1、mapper 只需要传递参数 Page 即自动会实现分页:
注意:递参数 Page 即自动分页,必须放在第一位(我们也可以继承 Page 实现自己的分页对象)
@Repository
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<Student> {
/**
* 自定义分页
* @param page 分页对象
* @param age 查询条件
* @return
*/
IPage<Student> selectPage2(Page<?> page, @Param("age") Integer age);
}
2、mapper.xml 写好sql语句
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.zzz.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="selectPage2" resultType="Student">
SELECT * FROM student
WHERE age > #{age}
</select>
</mapper>
3、StudentService 接口中也添加相应的方法:
public interface StudentService extends IService<Student> {
/**
* 根据条件自定义分页
* @param page page对象
* @param age 查询参数
* @return
*/
IPage<Student> selectPage2(Page<?> page, Integer age);
}
4、StudentServiceImpl.java 里调用 mapper 自定义的分页方法:
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper, Student> implements StudentService {
@Override
public IPage<Student> selectPage2(Page<?> page, Integer age) {
// 不进行 count sql 优化,解决 MP 无法自动优化 SQL 问题,这时候你需要自己查询 count 部分
// page.setOptimizeCountSql(false);
// 当 total 为小于 0 或者设置 setSearchCount(false) 分页插件不会进行 count 查询
// 要点!! 分页返回的对象与传入的对象是同一个
return baseMapper.selectPage2(page, age);
}
}
5、我们调用一下这个自定义方法进行测试:
@Test
void page2(){
// 查询条件:年龄大于20
//sql: SELECT * FROM student WHERE age > ? LIMIT ?,?
// Parameters: 20(Integer), 0(Long), 2(Long)
//Page<Student> page = new Page<>(1, 2);
studentService.selectPage2(new Page<>(1,2),20);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qXgwicfW-1616153572830)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118152453103.png)]
3、Insert 新增数据
save 方法可以将一个实体对象插入到对应的数据表中
注意:插入成功后,当前插入对象在数据库中的 id 会写回到该实体中。
@Test
void serviceAddStudent(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("若贞");
student.setAge(320);
student.setGender("男");
student.setTelephone("13545678945");
student.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student.setClassId(4L);
boolean save = studentService.save(student);
System.out.println(save);
}
saveBatch 方法可以批量插入数据
@Test
void serviceBatchStudent(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("若贞");
student.setAge(25);
student.setGender("男");
student.setTelephone("13545678945");
student.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student.setClassId(1L);
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("若贞1");
student1.setAge(20);
student1.setGender("男");
student1.setTelephone("13545678945");
student1.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student1.setClassId(3L);
Student student2 = new Student();
student2.setName("若贞2");
student2.setAge(18);
student2.setGender("男");
student2.setTelephone("13545678945");
student2.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student2.setClassId(2L);
//批量插入数据
studentService.saveBatch(Arrays.asList(student, student1, student2));
}
结果:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-xZUkRzwH-1616153572831)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118154121381.png)]
saveBatch 方法还可以设置每个批次的插入数量:
//批量插入数据 每次插入两条数据
studentService.saveBatch(Arrays.asList(student, student1, student2),2);
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-FgcJNx7P-1616153572831)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118154405605.png)]
4、Update修改数据
updateById 方法根据实体对象中的 ID 进行修改:
注意:如果实体对象中某个属性为 null,不会更新该属性(即不会把对应的数据库字段值设置为 null)
@Test
void sUpdate(){
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("樱花");
student.setAge(66);
student.setId(1328966765497917443L);
studentService.updateById(student);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AjCsybxe-1616153572832)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118154942341.png)]
updateBatchById 方法根据实体对象中的 ID 进行批量修改:跟添加一样的 只需要把方法名 换成updateBatchById()
updateBatchById 方法还可以设置每个批次的修改的数量:跟添加一样的 只需要把方法名 换成updateBatchById() 传入三个参数
5、Delete删除数据
removeById 方法可以根据 id 删除一条记录
@Test
void sDelete(){
// 返回删除结果
Boolean success = studentService.removeById(1328966765497917443L);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zN9NE8Lb-1616153572832)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118155355188.png)]
removeByIds 方法根据 id 批量删除:
@Test
void removeByIds(){
// 返回删除结果
Boolean success = studentService.removeByIds(Arrays.asList(7L,8L,9L,10L));
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-J0CQikwF-1616153572833)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118155618820.png)]
removeByMap 方法通过 Map 封装的条件删除记录
注意:map 写的是数据表中的列名,而非实体类的属性名。比如属性名为 userName,数据表中字段为 user_name,这里应该写的是 user_name。
@Test
void removeByMap(){
Map<String,Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("name", "若贞1");
columnMap.put("age", 20);
// 返回删除结果
studentService.removeByMap(columnMap);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kaXRX4pF-1616153572834)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118155915705.png)]
Service CRUD 接口 跟Mapper CRUD 接口区别
Service CRUD 接口
说明:
- 通用 Service CRUD 封装IService接口,进一步封装 CRUD 采用
get 查询单行remove 删除list 查询集合page 分页前缀命名方式区分Mapper层避免混淆, - 泛型
T为任意实体对象 - 建议如果存在自定义通用 Service 方法的可能,请创建自己的
IBaseService继承Mybatis-Plus提供的基类 - 对象
Wrapper为 条件构造器
Mapper CRUD 接口
说明:
- 通用 CRUD 封装BaseMapper接口,为
Mybatis-Plus启动时自动解析实体表关系映射转换为Mybatis内部对象注入容器 - 泛型
T为任意实体对象 - 参数
Serializable为任意类型主键Mybatis-Plus不推荐使用复合主键约定每一张表都有自己的唯一id主键 - 对象
Wrapper为 条件构造器
两者区别
Service CRUD 返回的boolean的值
Mapper CRUD 返回的是int值
扩展
乐观锁
基本介绍
乐观锁的应用场景是当要更新一条记录的时候,希望这条记录没有被别人更新。
注意:
- 目前乐观锁仅支持 updateById(id) 与 update(entity, wrapper) 方法
- 在 update(entity, wrapper) 方法下,wrapper 不能复用!!!
乐观锁实现方式如下:
- 取出记录时,获取当前 version
- 执行更新时,带上这个 version,即 set version = new Version where version = old Version
- 如果 version 不对,就更新失败
原理:通俗的说, 就是查询的时候拿出一个值,跟更改时拿出同一个值 进行对比。如果一样表示在你这查询期间每一修改,如果不一样就是别人已经修改了
准备工作
1、首先在项目中添加乐观锁插件配置:
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusOptLockerConfig {
@Bean
public OptimisticLockerInterceptor optimisticLockerInterceptor() {
return new OptimisticLockerInterceptor();
}
}
2、接着数据库表中增加一个字段用于记录版本,我这里使用 int 类型,默认值为 0(默认值不能为 null,否则乐观锁无效)
提示:
- 支持的数据类型只有:int,Integer,long,Long,Date,Timestamp,LocalDateTime
- 整数类型下 newVersion = oldVersion + 1
- newVersion 会回写到 entity 中
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jdcXPhaB-1616153572834)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201118165055474.png)]
3、最后在对应的实体类字段上添加 @Version 注解
/**
* 乐观锁
*/
@Version
private Integer version;
测试
/**
* 测试乐观锁
* 一定要注意, 这前提条件是在同一条的数据下
*/
@Test
void versionTest() {
Student student1 = studentMapper.selectById(5L);
Student student2 = studentMapper.selectById(5L);
student1.setAge(111);
if (studentMapper.updateById(student1) > 0) {
System.out.println("student1 更新成功");
} else {
System.out.println("student1 更新失败,该记录已被其他人修改!");
}
student2.setAge(222);
if (studentMapper.updateById(student2) > 0) {
System.out.println("student2 更新成功");
} else {
System.out.println("student2 更新失败,该记录已被其他人修改!");
}
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-7QeWc3r5-1616153572835)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119093906203.png)]
字段数据自动填充
创建时间、修改时间! 这些个操作一遍都是自动化完成的,我们不希望手动更新!
阿里巴巴开发手册:所有的数据库表:gmt_create、gmt_modified几乎所有的表都要配置上!而且需 要自动化!
方式一:数据库级别(工作中不允许你修改数据库)
1、在表中新增字段 create_time, update_time
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-qy1kmeLH-1616153572836)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119111332273.png)]
2、再次测试插入方法,我们需要先把实体类同步!
/**
* 添加时间
*/
private Date createTime;
/**
* 修改时间
*/
private Date updateTime;
3、再次更新查看结果即可
@Test
void update(){
//(1)sql:UPDATE student SET name=?, age=? WHERE id=?
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("若贞");
student1.setAge(22);
student1.setId(3L);
studentMapper.updateById(student1);
}
结果
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Yj3WMSXp-1616153572837)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119111846473.png)]
方式二:代码级别
1、删除数据库的默认值、更新操作!
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jLIzTozG-1616153572837)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119112112067.png)]
说明:如果无法删除默认值,请把非空的选项也去除掉
2、实体类字段属性上需要增加注解 @TableField
FieldFill 是一个枚举,用于指定在何种情况下会自动填充,有如下几种可选值:
- DEFAULT:默认不处理
- INSERT:插入填充字段
- UPDATE:更新填充字段
- INSERT_UPDATE:插入和更新填充字段
/**
* 添加时间
* 插入时要填充时间
*/
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Date createTime;
/**
* 修改时间
* 插入和修改都填充时间,因为添加的时候也要加上时间
*/
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Date updateTime;
3、接着编写公共字段填充处理器类,该类继承了 MetaObjectHandler 类,重写 insertFill 和 updateFill 方法,我们在这两个方法中获取需要填充的字段以及默认填充的值。()
注意:
- 填充处理器 MyMetaObjectHandler 在 Spring Boot 中需要声明 @Component 或 @Bean 注入
- strictInsertFill 和 strictUpdateFill 方法第二个参数写的是实体类里的属性名,不是对应数据库字段名。
package com.zzz.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
@Slf4j // 日志注解
@Component //一定不要忘记把处理器加到IOC容器中!
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
/**
* 插入时的填充策略
* @param metaObject
*/
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
//log日志输出
log.info("start insert fill.....");
//添加时间的策略
this.setFieldValByName("createTime",new Date(),metaObject);
//修改时间的策略
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
/**
* 更新时的填充策略
* @param metaObject
*/
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
//log日志输出
log.info("start update fill.....");
//修改时间策略
this.setFieldValByName("updateTime",new Date(),metaObject);
}
}
4、测试
添加
/**
* 插入一条数据
* int insert(T entity);
*/
@Test
void AddStudent() {
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("若贞");
student.setAge(11);
student.setGender("男");
student.setTelephone("13545678945");
student.setEmail("1131270557@qq.com");
student.setClassId(4L);
int insert = studentMapper.insert(student);
System.out.println(insert);
System.out.println(student);
}
结果:观察时间 自动帮我们填充了
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-edupysdI-1616153572838)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119113849266.png)]
修改
@Test
void update(){
//(1)sql:UPDATE student SET name=?, age=? WHERE id=?
Student student1 = new Student();
student1.setName("若小贞");
student1.setAge(22);
student1.setId(10L);
studentMapper.updateById(student1);
}
结果:观察时间 添加的时间没用变 而修改的时间变化了
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-O0ySSQfa-1616153572838)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119114200998.png)]
逻辑删除
物理删除 :从数据库中直接移除
逻辑删除 :逻辑删除并不会真正的从数据库中将数据删除掉,而是将当前被删除的这条数据中的一个逻辑删除字段置为删除状态。
比如该数据有一个字段 deleted,当其值为 0 表示未删除,值为 1 表示删除。那么逻辑删除就是将 0 变成 1。
逻辑删除字段说明:
- 字段支持所有数据类型(推荐使用 Integer、Boolean、LocalDateTime)
- 如果使用 LocalDateTime,建议逻辑未删除值设置为字符串 null,逻辑删除值只支持数据库函数例如 now()
管理员可以查看被删除的记录!防止数据的丢失,类似于回收站!
步骤
1、在数据表中增加一个 deleted 字段
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wL2W73lF-1616153572838)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119115122831.png)]
2、实体类中增加属性
/**
* 逻辑删除
* 给对应的实体类字段上加上 @TableLogic 注解
*/
@TableLogic
private Integer deleted;
3、配置!
mybatis-plus:
#配置逻辑删除
global-config:
db-config:
logic-delete-value: 1
logic-not-delete-value: 0
4、测试
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kItD0ykO-1616153572840)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119120337603.png)]
记录依旧在数据库,但是值确已经变化了!
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aj9cxiLd-1616153572840)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119120417573.png)]
测试查询:
@Test
void test() {
System.out.println(("----- selectAll method test ------"));
List<Student> students = studentMapper.selectList(null);
//jdk8:支持的循环
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-nqSoE4pw-1616153572840)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119120643294.png)]
性能分析插件
我们在平时的开发中,会遇到一些慢sql。测试! druid,
作用:性能分析拦截器,用于输出每条 SQL 语句及其执行时间,如果超过这个时间就停止运行!
性能分析拦截器,用于输出每条 SQL 语句及其执行时间
该插件
3.2.0以上版本移除 推荐使用第三方扩展执行 SQL 分析打印功能使用性能分析插件,可以帮助我们提高效率!
1、导入插件
注意:我们mybatis_plus插件不要太高,不然它会不识别
/**
* SQL执行效率插件
* 在工作中,不允许用户等待超过多长时间,这样我们根据这个进行sql优化
*/
@Bean
@Profile({"dev","test"})// 设置 dev test 环境开启,保证我们的效率
public PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor() {
PerformanceInterceptor performanceInterceptor = new PerformanceInterceptor();
//(1表示为1豪秒ms)设置sql执行的最大时间,如果超过了则不执行
performanceInterceptor.setMaxTime(100);
// 是否格式化代码
performanceInterceptor.setFormat(true);
return performanceInterceptor;
}
记住,要在SpringBoot中配置环境为dev或者 test 环境!
# 配置环境为de
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
2、测试使用!
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-iQ1sC0t2-1616153572841)(Y:\ \MyBatis-Plus基础–入门程序.assets\image-20201119123115316.png)]
条件构造器 Wrapper
1、相等、不相等
- allEq 表示全部 eq(或个别 isNull)
方法最后一个参数 null2IsNull是可选的(默认为true),为 true时则在map的value为null时调用isNull方法,为false时则忽略:
- allEq({id:1,user_name:“xxname”,age:null}) — 生成的sql为 —> id = 1 and user_name = ‘xxname’ and age is null
- allEq({id:1,user_name:“xxname”,age:null}, false) — 生成的sql为 —> id = 1 and user_name = 'xxname’
Map<SFunction<UserInfo, ?>, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(UserInfo::getId, 3);
map.put(UserInfo::getUserName, "xxname");
map.put(UserInfo::getAge, null);
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.allEq(map)
.list();
- eq 表示等于(=),ne 表示不等于(<>)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.eq(UserInfo::getId, 1) // id = 1
.ne(UserInfo::getAge, 22) // age <> 22
.list();
2、大于、小于
- gt 表示大于(>)、ge 表示大于等于(>=)、lt 表示小于(<)、le 表示小于等于(<=)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.gt(UserInfo::getId, 1) // id > 1
.ge(UserInfo::getAge, 22) // age >=18
.lt(UserInfo::getId, 3) // id < 3
.le(UserInfo::getAge, 50) // age <=50
.list();
- between 表示(BETWEEN 值1 AND 值2),notBetween 表示(NOT BETWEEN 值1 AND 值2)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.between(UserInfo::getId, 1,3) // id between 1 and 3
.notBetween(UserInfo::getAge, 40, 50) // age not between 40 and 50
.list();
3、模糊查询
- like 表示包含指定的值(like ‘%值%’),likeLeft 表示以指定的值结尾(like ‘%值’),likeRight 表示以指定的值开头(like ‘值%’)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.like(UserInfo::getUserName, "ha") // user_name like '%ha%'
.likeLeft(UserInfo::getUserName, "ha") // user_name like '%ha'
.likeRight(UserInfo::getUserName, "ha") // user_name like 'ha%'
.list();
- notLike 表示不包含指定的值(not like ‘%值%’)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.notLike(UserInfo::getUserName, "xxname") // user_name not like '%xxname%'
.list();
4、是否为 null
isNull 表示字段是否为 null(is null),isNotNull 表示字段是否不为 null(is not null)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.isNull(UserInfo::getUserName) // user_name is null
.isNotNull(UserInfo::getAge) // age is not null
.list();
5、in、notIn
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.in(UserInfo::getId, Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3)) // id in (1,2,3)
.notIn(UserInfo::getAge, Arrays.asList(22, 33)) // age not in (22,33)
.list();
6、带子查询(sql 注入)
- 下面是 inSql 的用法:
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.inSql(UserInfo::getAge, "22,33") // age in (22,33)
// id in (select id from vip where level > 3)
.inSql(UserInfo::getId, "select id from vip where level > 3")
.list();
- 下面是 notInSql 的用法:
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.notInSql(UserInfo::getAge, "22,33") // age not in (22,33)
// id not in (select id from vip where level > 3)
.notInSql(UserInfo::getId, "select id from vip where level > 3")
.list();
7、排序
orderByAsc 表示升序(ASC),orderByDesc 表示降序(DESC)
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.orderByAsc(UserInfo::getId, UserInfo::getUserName) // ORDER BY id ASC,user_name ASC
.orderByDesc(UserInfo::getAge) // ORDER BY age DESC
.list();
8、分组、筛选
下面是 groupBy 和 having 的用法:
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.groupBy(UserInfo::getUserName, UserInfo::getAge) // group by user_name,age
.having("sum(age) > 20") // HAVING sum(age) > 20
.having("sum(age) > {0}", 30) // HAVING sum(age) > 30
.select(UserInfo::getUserName, UserInfo::getAge)
.list();
9、or、 and、nested
- 主动调用 or 表示紧接着下一个方法是用 or 连接(不调用 or 则默认为使用 and 连接)
// WHERE age = 22 or age = 33
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.eq(UserInfo::getAge, 22)
.or()
.eq(UserInfo::getAge, 33)
.list();
- or、 and、nested 可以实现带嵌套的查询:
- or 为 OR 嵌套
- and 为 AND 嵌套
- nested 为正常嵌套(不带 AND 或者 OR)
// WHERE age IS NOT NULL AND ((id = 1 AND user_name = 'xxname') OR (id = 2 AND user_name = 'xxname'))
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.isNotNull(UserInfo::getAge)
.and(i -> i.nested(
j -> j.eq(UserInfo::getId,1).eq(UserInfo::getUserName,"xxname")
)
.or(j -> j.eq(UserInfo::getId,2).eq(UserInfo::getUserName,"xxname"))
)
.list();
10、拼接 sql(sql 注入)
- apply 方法可以直接将自定义的 sql 拼接到查询条件中:
// WHERE age IS NOT NULL AND id = 3 AND user_name = 'xxname'
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.isNotNull(UserInfo::getAge)
.apply("id = 3") // 有sql注入的风险
.apply("user_name = {0}", "xxname") //无sql注入的风险
.list();
- last 无视优化规则直接拼接到 sql 的最后:
注意: last 只能调用一次,多次调用以最后一次为准。该方法有 sql 注入的风险,请谨慎使用。
// WHERE age IS NOT NULL limit 2
List<UserInfo> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userInfoMapper)
.isNotNull(UserInfo::getAge)
.last("limit 2")
.list();
11、exists、notExists
- exists 方法可以拼接 EXISTS ( sql 语句 ),比如下面查询底下有用户的所有区域:
// SELECT id,area_name FROM area WHERE
// (EXISTS (select * from user_info where user_info.area_id = area.id))
List<Area> areas = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(areaMapper)
.exists("select * from user_info where user_info.area_id = area.id")
.list();
- notExists 方法用于拼接 NOT EXISTS ( sql 语句 ),比如下面查询底下没有用户的所有区域:
// SELECT id,area_name FROM area WHERE
// (NOT EXISTS (select * from user_info where user_info.area_id = area.id))
List<Area> areas = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(areaMapper)
.notExists("select * from user_info where user_info.area_id = area.id")
.list();
12、设置查询字段(select)
select 方法可以设置最终查询返回的字段:
List<Student> userInfos = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(studentMapper)
.select(Student::getName, Student::getAge)
.list();
代码自动生成器
AutoGenerator 是 MyBatis-Plus 的代码生成器,通过 AutoGenerator 可以快速生成 Entity、Mapper、Mapper XML、Service、Controller 等
各个模块的代码,极大的提升了开发效率。
1、添加依赖
<!--
添加muybatis-plus的依赖
如果之前添加了就不用添加这个依赖了。
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 代码生成器依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.3.1.tmp</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 模板引擎依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
</dependency>
2、开始生成代码
public void startGenerator() {
/**
* 1、全局配置
*/
GlobalConfig config = new GlobalConfig();
String projectPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
//开启AR模式
config.setActiveRecord(true);
//设置作者
config.setAuthor("若贞");
//生成路径(一般在此项目的src/main/java下)
config.setOutputDir(projectPath + "/src/main/java");
//第二次生成会把第一次生成的覆盖掉
config.setFileOverride(true);
//生成完毕后是否自动打开输出目录
config.setOpen(true);
//实体属性 Swagger2 注解
//config.setSwagger2(true)
//设置主键生成策略 自动增长
config.setIdType(IdType.AUTO);
//生成的service接口名字首字母是否为I,这样设置就没有I
config.setServiceName("%sService");
//生成resultMap
config.setBaseResultMap(true);
//在xml中生成基础列
config.setBaseColumnList(true);
/**
* 2、数据源配置
*/
DataSourceConfig dsc = new DataSourceConfig();
//数据库类型
dsc.setDbType(DbType.MYSQL);
//加载驱动
dsc.setDriverName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//数据库url路径
dsc.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8");
//用户名
dsc.setUsername("root");
//密码
dsc.setPassword("root");
/**
* 3、策略配置
*/
StrategyConfig strategy = new StrategyConfig();
//开启全局大写命名
strategy.setCapitalMode(true);
//表名映射到实体的命名策略(下划线到驼峰)
strategy.setNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
//表字段映射属性名策略(未指定按naming)
strategy.setColumnNaming(NamingStrategy.underline_to_camel);
//表名前缀
//strategy.setTablePrefix("tb_")
//strategy.setSuperEntityClass("你自己的父类实体,没有就不用设置!")
//写于父类中的公共字段
//strategy.setSuperEntityColumns("id");
//strategy.setSuperControllerClass("自定义继承的Controller类全称,带包名,没有就不用设置!")
//生成 @RestController 控制器
strategy.setRestControllerStyle(true);
//使用lombok
strategy.setEntityLombokModel(true);
//设置要映射的表名
strategy.setInclude("", "");
//4、包名策略配置
PackageConfig pc = new PackageConfig();
//设置版块名字
pc.setParent("com.zzz.student");
//设置数据访问层文件的目录
pc.setMapper("mapper");
//设置逻辑业务文件的目录
pc.setService("service");
//设置控制层文件的目录
pc.setController("controller");
//设置实体类文件的目录
pc.setEntity("entity");
//设置mapper.xml文件的目录
pc.setXml("mapper");//设置xml文件的目录
/**
* 5、整合配置
*/
// 需要构建一个 代码自动生成器 对象
AutoGenerator autoGenerator = new AutoGenerator();
autoGenerator.setGlobalConfig(config);
autoGenerator.setDataSource(dsc);
autoGenerator.setStrategy(strategy);
autoGenerator.setPackageInfo(pc);
/**
* 6、执行
*/
autoGenerator.execute();
}
多表关联查询
一、多表关联查询(使用注解)
1、自定义 sql
- 假设我们有如下两张表:用户表(User)、区域表(Area),其中用户表里通过 area_id 字段关联区域表的 id 主键:
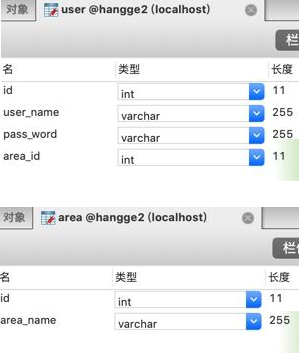
- 假设我们希望查询 User 时也能获取其所属的区域名称,这里对 User 实体类增加 areaName 属性:
提示:由于 area_name 不是 User 数据库表里的字段,因此需要添加 @TableField 注解,并将 exist 属性设置为 false。
@Data
public class User {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private Integer areaId;
@TableField(exist = false)
private String areaName;
}
- 然后在 UserMapper 中添加相关查询方法以及关联查询语句
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Select("SELECT user.*, area.area_name FROM user, area " +
"WHERE user.area_id = area.id and user.id = #{id}")
User getUserById(int id);
}
2、使用 @One 注解实现一对一关联
- 这里我们对 User 实体类稍作修改,这次不再是增加 areaName 属性,而是直接增加 area 关联对象:
@Data
public class User {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private Integer areaId;
@TableField(exist = false)
private Area area;
}
- 我们对 UserMapper 做如下修改,使用 @Results 注解来映射查询结果集到实体类属性:
提示:
- 当我们需要通过查询到的一个字段值作为参数,去执行另外一个方法来查询关联的内容,而且两者是一对一关系时,可以使用 @One 注解来便捷的实现
- selectById 方法是 BaseMapper 就提供的,所以我们不需要在 AreaMapper 中手动定义。
- @Result(column = “area_id”, property = “areaId”) 可以不写,也不会报错。但是会导致我们查询结果(User 实体)的 areaId 属性没有值(因为第二个 Result 将 area_id 值作为查询条件传入子查询)。
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Results({
@Result(column = "area_id", property = "areaId"),
@Result(column = "area_id", property = "area",
one = @One(select = "com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper.selectById"))
})
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}")
User getUserById(int id);
}
3、使用 @Many 注解实现一对多关联
- 假设我们需要查询一个区域及其下面的所有用户,首先对 Area 实体类稍作修改,增加 users 集合属性:
@Data
public class Area {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String areaName;
@TableField(exist = false)
private List<User> users;
}
- 我们对 AreaMapper 做如下修改,使用 @Results 注解来映射查询结果集到实体类属性:
提示:
- @Many 的用法与 @One 类似,只不过如果使用 @One 查询到的结果是多行,会抛出 TooManyResultException 异常,这种时候应该使用的是 @Many 注解,实现一对多的查询。
- @Result(column = “id”, property = “id”) 可以不写,也不会报错。但是会导致我们查询结果(Area 实体)的 id 属性没有值(因为第二个 Result 将 id 值作为查询条件传入子查询)。
public interface AreaMapper extends BaseMapper<Area> {
@Results({
@Result(column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "id", property = "users",
many = @Many(select =="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper.selectByAreaId"))
})
@Select("SELECT * FROM area WHERE id = #{id}")
Area getAreaById(int id);
}
- 由于上面调用了 UserMapper 的 selectByAreaId 方法进行嵌套查询,因此 UserMapper 中要添加该方法:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE area_id = #{areaId}")
User selectByAreaId(int areaId);
}
二、多表关联查询(使用 xml 文件)
1、自定义 sql
- 假设我们有如下两张表:用户表(User)、区域表(Area),其中用户表里通过 area_id 字段关联区域表的 id 主键:
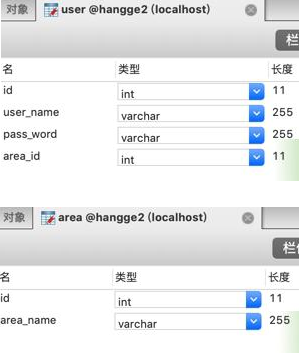
- 假设我们希望查询 User 时也能获取其所属的区域名称,这里对 User 实体类增加 areaName 属性:
提示:由于 area_name 不是 User 数据库表里的字段,因此需要添加 @TableField 注解,并将 exist 属性设置为 false。
@Data
public class User {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private Integer areaId;
@TableField(exist = false)
private String areaName;
}
- 然后在 UserMapper 中添加相关查询方法:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
User getUserById(int id);
}
- 接着在 UserMapper 同一个文件夹下创建一个 UserMapper.xml,在里面编写对应的 sql 语句:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.User" id="BaseResultMap">
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT user.*, area.area_name FROM user, area
WHERE user.area_id = area.id and user.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
2、实现一对一关联
- 这里我们对 User 实体类稍作修改,这次不再是增加 areaName 属性,而是直接增加 area 关联对象:
@Data
public class User {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private Integer areaId;
@TableField(exist = false)
private Area area;
}
- UserMapper 里代码同上面一样,主要对 UserMapper.xml 稍作修改,使用子查询来查询关联的区域:
提示:
- selectById 方法是 BaseMapper 本身就提供的,所以我们不需要在 AreaMapper 中手动定义。
- resultMap 中的第一个 result 可以不写,也不会报错。但是会导致我们查询结果(User 实体)的 areaId 属性没有值(因为后面将 area_id 值作为查询条件传入子查询)。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.User" id="BaseResultMap">
<result property="areaId" column="area_id"/>
<association property="area" column="area_id"
select="com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper.selectById"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 当然我们也可以使用嵌套结果集来实现相同的效果(嵌套结果集这种方式是单纯使用注解没法做到的):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.User" id="BaseResultMap">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="userName" column="user_name"/>
<result property="passWord" column="pass_word"/>
<result property="areaId" column="area_id"/>
<association property="area">
<id property="id" column="area_id"/>
<result property="areaName" column="area_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getUserById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT user.*, area.area_name, area.id as area_id
FROM user, area
WHERE user.area_id = area.id and user.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
3、实现一对多关联
- 假设我们需要查询一个区域及其下面的所有用户,首先对 Area 实体类稍作修改,增加 users 集合属性:
@Data
public class Area {
//指定主键使用数据库ID自增策略
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String areaName;
@TableField(exist = false)
private List<User> users;
}
- 我们对 AreaMapper 做如下修改,增加一个查询方法:
public interface AreaMapper extends BaseMapper<Area> {
Area getAreaById(int id);
}
1234
- 接着在 AreaMapper 同一个文件夹下创建一个 AreaMapper.xml,在里面编写对应的 sql 语句,这里我们使用嵌套查询来实现:
提示: 可以不写,也不会报错。但是会导致我们查询结果(Area 实体)的 id 属性没有值(因为后面将 id 值作为查询条件传入子查询)。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.Area" id="BaseResultMap">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<collection property="users" column="id"
select="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper.selectByAreaId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAreaById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM area WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 由于上面调用了 UserMapper 的 selectByAreaId 方法进行嵌套查询,因此 UserMapper 中要添加该方法:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
User selectByAreaId(int id);
}
- 对应的 UserMapper.xml 中也要增加相应的 SQL 语句:
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.User" id="BaseResultMap">
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByAreaId" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE area_id = #{areaId}
</select>
</mapper>
- 当然,我还可以使用嵌套结果集来实现相同的效果(嵌套结果集这种方式是单纯使用注解没法做到的),AreaMapper.xml 代码如下(而 UserMapper 就不用像上面一样增加接口了):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.Area" id="BaseResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<id property="areaName" column="area_name"/>
<collection property="users" ofType="com.example.demo.model.User">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="userName" column="user_name"/>
<result property="passWord" column="pass_word"/>
<result property="areaId" column="area_id"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAreaById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT area.*, user.id as user_id, user.user_name, user.pass_word, user.area_id
FROM area, user
WHERE area.id = user.area_id AND area.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
语句,这里我们使用嵌套查询来实现:
> **提示**: 可以不写,也不会报错。但是会导致我们查询结果(**Area** 实体)的 **id** 属性没有值(因为后面将 **id** 值作为查询条件传入子查询)。
```xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.Area" id="BaseResultMap">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<collection property="users" column="id"
select="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper.selectByAreaId"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAreaById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM area WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 由于上面调用了 UserMapper 的 selectByAreaId 方法进行嵌套查询,因此 UserMapper 中要添加该方法:
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
User selectByAreaId(int id);
}
- 对应的 UserMapper.xml 中也要增加相应的 SQL 语句:
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.User" id="BaseResultMap">
</resultMap>
<select id="selectByAreaId" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM user WHERE area_id = #{areaId}
</select>
</mapper>
- 当然,我还可以使用嵌套结果集来实现相同的效果(嵌套结果集这种方式是单纯使用注解没法做到的),AreaMapper.xml 代码如下(而 UserMapper 就不用像上面一样增加接口了):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.AreaMapper">
<resultMap type="com.example.demo.model.Area" id="BaseResultMap">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<id property="areaName" column="area_name"/>
<collection property="users" ofType="com.example.demo.model.User">
<id property="id" column="user_id"/>
<result property="userName" column="user_name"/>
<result property="passWord" column="pass_word"/>
<result property="areaId" column="area_id"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAreaById" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT area.*, user.id as user_id, user.user_name, user.pass_word, user.area_id
FROM area, user
WHERE area.id = user.area_id AND area.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>






















 1267
1267











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








