知识点
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度
二叉树根节点的高度:使用后序遍历
二叉树的最大深度:使用前序遍历
刷题
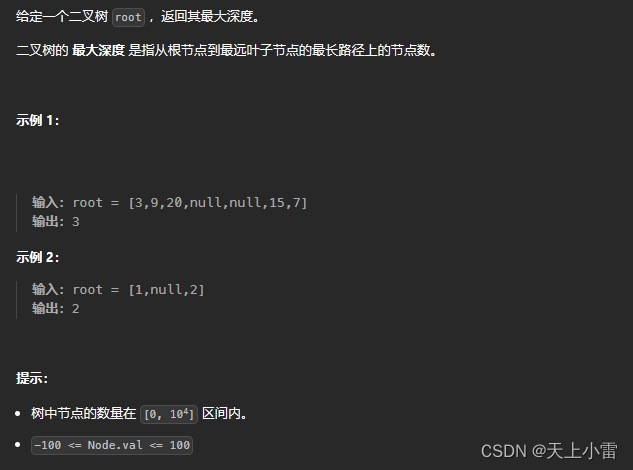
104.二叉树的最大深度
LeetCode链接 104. 二叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiDaShengDu104_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.通过层序遍历,计算有多少层即可
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.addLast(root);
int num = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//队里中维护的是每层的所有节点,size就是这层有多少个节点
int size = queue.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
size--;
}
//遍历完一层+1
num++;
}
return num;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiDaShengDu104_3 {
/**
* 方法2:dfs+递归
* 1.递归记录左子树对应的最大深度
* 2.递归记录右子树对应的最大深度
* 3.取左右子树的最大值
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
int maxDep = 0;
return dfs(root, maxDep);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int maxDep) {
// baseCase
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 左边的最大深度
int left = dfs(root.left, maxDep);
// 右边的最大深度
int right = dfs(root.right, maxDep);
// 取左右两边的最大值,再加上本层
maxDep = Math.max(left, right) + 1;
return maxDep;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
599.n叉树的最大深度
LeetCode链接 559. N 叉树的最大深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day15_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/6
* @Description todo
*/
public class NChaShuDeZuiDaShenDu559_2 {
/**
* 方法1:bfs-队列
* 1.层序遍历,计算有多少层,就是最大深度
* 2.队列中维持的是每层所有的节点
* 3.队列中元素出队列,将出队列的元素的所有child加入的队列中
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
return bfs(root);
}
private int bfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
ArrayDeque<Node> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int depth = 0;
queue.addLast(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
depth++;//计算深度
//队列大小就是这层节点数的大小
int size = queue.size();
//遍历这层的所有节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Node node = queue.pollFirst();
//将出队列元素的所有child加入到队列中
if (node.children != null) {
int childSize = node.children.size();
for (int j = 0; j < childSize; j++) {
queue.addLast(node.children.get(j));
}
}
}
}
return depth;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
}
;
}
方法2:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day15_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/6
* @Description todo
*/
public class NChaShuDeZuiDaShenDu559_3 {
/**
* 方法2:dfs-递归
* 0.中序遍历
* 1.递归获取所有child的最大深度
* 2.选出最大的一个
* 3.最大深度+1就是本节点的最大深度
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private int dfs(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//获取root节点所有child的最大深度
int childSize = root.children.size();
int[] childDepths = new int[childSize];
for (int i = 0; i < childSize; i++) {
Node child = root.children.get(i);
int childDepth = dfs(child);
childDepths[i] = childDepth;
}
//从所有child的最大深度中选出最大的一个
int childMaxDepth = 0;
for (int childDepth : childDepths) {
if (childDepth > childMaxDepth) {
childMaxDepth = childDepth;
}
}
return childMaxDepth + 1;
}
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
}
}
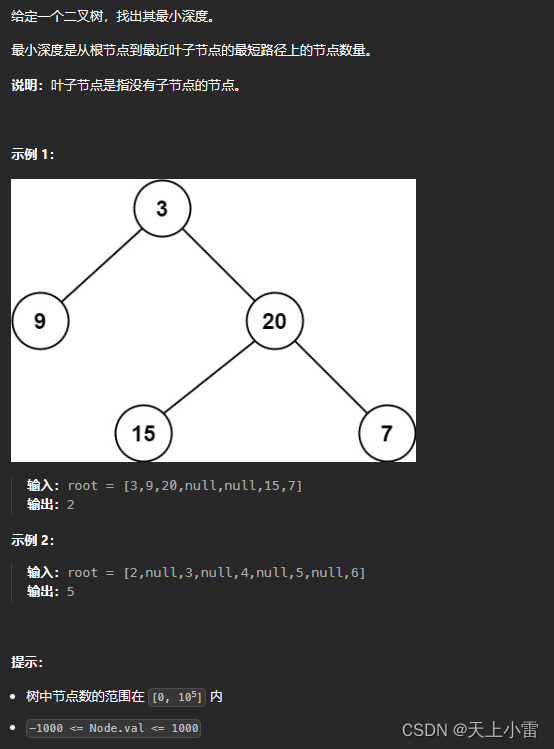
111.二叉树的最小深度
LeetCode链接 111. 二叉树的最小深度 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiXiaoShenDu111_2 {
/**
* 方法2:bfs-队列
* 1.层序遍历
* 2.当左右孩子都为null的时候,说明到了最低点,有一个孩子不为null,则不是最低点
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int depth = 0;
ArrayDeque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
// 记录最小深度
depth++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.pollFirst();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
// 当左右孩子都为空的时候,说明是最低点的一层了,退出
return depth;
}
}
}
return depth;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day14_erchashu;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/5
* @Description todo
*/
public class ErChaShuDeZuiXiaoShenDu111_3 {
/**
* 方法1:dfs-递归,后序遍历
* 1.注意要到达叶子节点
* 2.注意左子树为null,右子树不为null的情况
* 3.注意右子树为null,左子树不为null的情况
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMinDep = dfs(root.left);
int rightMinDep = dfs(root.right);
//左子树为null,右子树不为null
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return rightMinDep + 1;
}
//右子树为null,左子树不为null
if (root.right == null && root.left != null) {
return leftMinDep + 1;
}
return Math.min(leftMinDep, rightMinDep) + 1;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
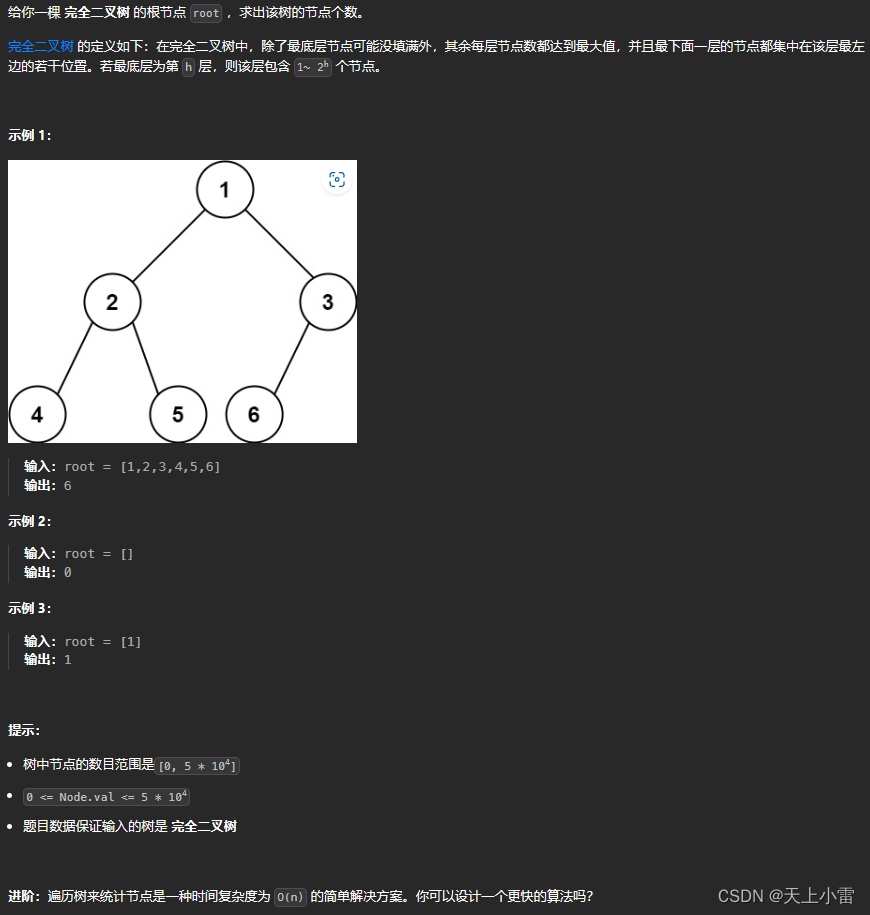
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
LeetCode链接 222. 完全二叉树的节点个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目描述
方法1:普通二叉树节点个数-dfs+递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day15_erchashu;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/6
* @Description todo
*/
public class WanQuanErChaShuDeJieDianGeShu222_1 {
/**
* 普通二叉树的节点个数:
* 方法1:dfs+递归
* 本节点个数=左子树节点个数+右子树节点个数+1
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
return dfs1(root);
}
private int dfs1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = dfs1(root.left);
int right = dfs1(root.right);
return (left + right) + 1;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法2:普通二叉树节点个数-bfs+队列
package daimasuixiangshuati.day15_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/6
* @Description todo
*/
public class WanQuanErChaShuDeJieDianGeShu222_2 {
/**
* 普通二叉树的节点个数:
* 方法2:bfs+队列
* 层序遍历,每处理一个节点,统计节点个数的变量值+1
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int result = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
result++;
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}
方法3:完全二叉树节点个数-递归
package daimasuixiangshuati.day15_erchashu;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* @Author LeiGe
* @Date 2023/11/6
* @Description todo
*/
public class WanQuanErChaShuDeJieDianGeShu222_3 {
/**
* 完全二叉树的节点个数:根据完全二叉树的性质独有的解法
* 完全二叉树只有两种情况,情况一:是二叉树,情况二:最有一层叶子节点没有满
* 对于情况一:可以直接通过2^树深度-1来计算总个数
* 对于情况二:分别递归左孩子和右孩子,递归到某一深度一定会有左孩子或者右孩子为满二叉树,这时就可以按照情况一来计算了
* 如何判断一颗树不是满二叉树呢?
* 在完全二叉树中,如果递归向左遍历的深度等于递归向右的深度,那么就说明这颗树是满二叉树
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// 左右子树
TreeNode left = root.left;
TreeNode right = root.right;
// 初始化树的深度为1,此时处理的节点
int leftDepth = 1;
int rightDepth = 1;
// 计算左侧的深度
while (left != null) {
left = left.left;
leftDepth++;
}
// 计算右侧的深度
while (right != null) {
right = right.right;
rightDepth++;
}
// 如果左右深度深度说明是满二叉树,直接计算
if (leftDepth == rightDepth) {
return (int) Math.pow(2, leftDepth) - 1;
}
// 否则递归处理左右子树,直到他们都为满二叉树
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {
}
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
}





















 885
885











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








