文章目录
MySQL_jdbc连接
1. JDBC介绍
我们之前学习MYSQL时,为了使用MYSQL服务,我们通常要使用客户端与MYSQL服务进行连接,然后才能输入SQL语句进行数据库的各种操作。客户端有命令行与图形界面2种。
但是在更多的环境下,由我们人直接操作数据是很低效的,比如双11这种业务场景下,一秒中往往要在库中生成上千万甚至几亿条数据,靠人来手工操作是不现实的,只能依赖于程序进行这种高并发的操作。
程序语言有多种,比如Java、Python、C/C++等,程序语言如果想执行SQL语句,也必须要先与数据库进行连接,数据库也有多种,比如MySQL、Oracle、SQL Server等。
不同的程序语言去连接不同的数据库,如果没有一个统一的标准或者规范,肯定是相当混乱的。Java语言对此的解决方案就是JDBC。
JDBC定义了一套规范标准,它对应的是各种接口与抽象类(通常对应java.sql包下面的各种类与接口),具体实现交给各数据库厂商去完成, MySQL的有自己的实现类并打成jar包发布,供程序开发人员使用;Oracle也有自己的实现jar包。
我们开发人员在使用的时候,要根据连接数据库的不同,去对应的官网上下载对应数据库版本与程序语言的数据库驱动(Java语言对应的是一个jar包)。(比如我们使用MySQL 5.1,就要去MySQL官网下载Java语言对应的jar包)
JDBC : Java DataBase Connectivity (java数据库链接)
是让java链接数据库的API
API : Application Programming Intergace (应用程序接口)
就是函数库
所以 JDBC 就是提供java连接数据库的应用程序接口的,只是接口或者抽象类
而JDBC就是java中提供的一个规范,基本都是接口和抽象类作为父类,具体的实现,是数据库厂商去弄的,只不过这些厂商需要按照我的接口标准来实现
如果我们要想操作数据库,就需要把厂商开发的实现类,导入进来

然后在项目上右键 -> Build Path -> Configure Build Path…,将之加入我们项目的CLASSPATH。
2. JDBC使用步骤
第0步: 导包
第1步:注册驱动 (仅仅做一次)
第2步:建立连接(Connection)
第3步:创建运行SQL的语句(Statement)
第4步:运行语句
第5步:处理运行结果(ResultSet)
第6步:释放资源
其中 如果是添加,删除,更新操作,可以没有第5步,查询肯定会有第五步
- 2.0 导包
创建java项目
创建lib文件夹
把mysql-connector-java-5.1.38-bin.jar复制到lib中
右键 -> Build Path -> Add to Build Path

2.1 注冊驱动
创建java类 JDBC_01_Base_DQL
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");

2.2 建立连接(Connection)
第一个参数是url
jdbc:mysql://IP:端口/数据库
第二个参数是数据库用户名
第三个参数是数据库密码
2.3 创建运行SQL的语句(Statement)
2.4 运行语句

2.5 处理运行结果(ResultSet)
while (rs.next()) {
// 在循环遍历中,把数据取出来
System.out.print(rs.getInt("id") + " ");
// 如果传入是整型值 就会获取对应的列,比如下面 就是获取第一列的值,不建议使用
System.out.print(rs.getInt(1) + " ");
System.out.print(rs.getString("id") + " ");
// 字符串不能用int来接收,除非这个 字符串是纯数字
// System.out.print(rs.getInt("name") +" ");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name") + " ");
System.out.print(rs.getString("course") + " ");
System.out.print(rs.getDouble("score")+" ");
// 3 对应的是name列,如果更改表结构,把name列放到第四位了,那么这里就获取不到name了
// 所以 不灵活,不推荐使用
System.out.println(rs.getString(3));
}
2.6 释放资源
// 6 关闭资源
resultSet.close();
stmtStatement.close();
conn.close();
先打开的资源后关闭
示例:JDBC_01_BASE_DQL_00
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 0 导包 src 平级创建一个 lib 文件夹,把 jar 包方进去,Build Path 配置到 classpath 中
*
* 1 驱动注册 Class.forName() Class.forName().newInstance() new DriverName() 向
* DriverManager 中进行注册
*
* 2 数据库连接 DriverManager.getConnection()
*
* 3 执行 sql 语句 Connection.CreateStatement() statement.executeQuery()
* statement.executeUpdate()
*
* 4 接收结果数据 rs.next()
*
* 5 遍历展示结果集
*
* 6 关闭资源
*
* @author lenovo
* @date 2020年8月6日 @time 上午11:26:35
*/
public class JDBC_01_base_DQL {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 数据库连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day_03", "root", "root");
// 3 语句传输对象
String sql = "select * from test_jdbc";
Statement stmtStatement = conn.createStatement();
// 4 接收结果集
ResultSet resultSet = stmtStatement.executeQuery(sql);
// 5 遍历获取数据
// next 就等于 迭代器中 hasNext() 和 next() 连用
// 判断下面有没有元素,如果有就指向下一行元素
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getInt("id") + " ");
// getString 也可以获取 int 类型的值,但是不推荐
// System.out.println(resultSet.getString("id"));
System.out.print(resultSet.getString("name") + " ");
System.out.println(resultSet.getDouble("money") + " ");
}
// 6 关闭资源
resultSet.close();
stmtStatement.close();
conn.close();
}
}
3. 代码优化
上面程序中,有可能会导致释放资源出现问题
比如查询语句写错了等,这时候会抛出异常,那么关闭语句就不会执行
所以我们应该使用try…catch…finally来优化一下
以刚才的练习为例,对test_jdbc表的查询进行优化
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null ;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
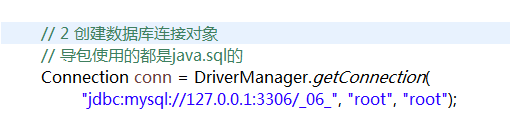
// 2 创建数据库连接对象
// 导包使用的都是java.sql的
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/_06_", "root", "root");
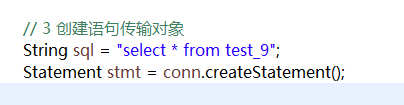
// 3 创建语句传输对象
String sql = "select * from test_jdbc";
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 4 接收数据库结果集
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next()) {
// 在循环遍历中,把数据取出来
System.out.print(rs.getInt("id") + " ");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name") + " ");
System.out.println(rs.getDouble("money")+" ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4. DML
Data Manipulation Language : 数据操作语言
涉及的关键字有 : delete,update,insert
和查询的操作几乎一样,就是把第4步和第5步更改一下
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 创建数据库连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/_06_", "root", "root");
// 3 语句传输对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values (4,'小小',999.9)";
// sql = "update test_jdbc set money=money+1000 where id=1 ";
// sql = "delete from test_jdbc where id = 1";
// 如果是查询,就返回true,不是就返回false,价值不大,所以用的不多,添加,删除,更新都可以用这个方法
// stmt.execute(sql);
// 返回值是int,返回影响了几条数据(更改了几条/删除了几条/添加了几条),添加,删除,更新都可以用这个方法
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了 " + count + " 条数据");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 关闭资源,从上到下依次关闭,后打开的先关闭
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
示例:JDBC_02_DML
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* 0 导包 src 平级创建一个 lib 文件夹,把 jar 包方进去,Build Path 配置到 classpath 中
*
* 1 驱动注册 Class.forName() Class.forName().newInstance() new DriverName() 向
* DriverManager 中进行注册
*
* 2 数据库连接 DriverManager.getConnection()
*
* 3 执行 sql 语句 Connection.CreateStatement() statement.executeQuery()
* statement.executeUpdate()
*
* 4 接收结果数据 rs.next()
*
* 5 遍历展示结果集
*
* 6 关闭资源
*
* @author lenovo
* @date 2020年8月6日 @time 上午11:26:35
*/
public class JDBC_02_DML {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
// 1 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 创建数据库连接对象
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day_03", "root", "root");
// 3 语句传输对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// String sql = "inset into student (name,age) values ('test1',11)";
// String sql = "update student set name = 'test2' where name = 'test1'";
String sql = "delete from student where name = 'test2'";
// 查询语句 返回 true , 否则返回 false
// statement.execute(sql);
// 返回值是 int 返回影响(操作)了几条数据
int count = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("影响了" + count + "条数据");
// resultSet.close();
// stmtStatement.close();
// connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5. PreparedStatement
添加或者更新的时候,尽量使用 PreparedStatement ,而不是使用Statement
Statement 和 PreparedStatement 的区别
Statement用于执行静态SQL语句,在执行的时候,必须指定一个事先准备好的SQL语句,并且相对不安全,会有SQL注入的风险
PreparedStatement是预编译的SQL语句对象,sql语句被预编译并保存在对象中, 被封装的sql语句中可以使用动态包含的参数 ? ,
在执行的时候,可以为?传递参数
使用PreparedStatement对象执行sql的时候,sql被数据库进行预编译和预解析,然后被放到缓冲区,
每当执行同一个PreparedStatement对象时,他就会被解析一次,单不会被再次编译 可以重复使用,可以减少编译次数,提高数据库性能
并且能够避免SQL注入,相对安全
5.1 DQL
使用PreparedStatement 执行查询
public static void load(int id) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement prst = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 创建数据库连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/_06_", "root", "root");
// 这里我们用? 问号代替值,可以叫占位符,也可以叫通配符
String sql = "select * from test_jdbc where id = ?";
// 3 语句传输对象
prst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第一个?的值
prst.setInt(1, id);
rs = prst.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.print(rs.getInt("id") + " ");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name") + " ");
System.out.println(rs.getString("money") + " ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 关闭资源,从上到下依次关闭,后打开的先关闭
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (prst != null) {
prst.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
示例:JDBC_03_PREPAREDSTATEMENT_LOAD
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* sql 注入
*
* @author lenovo
* @date 2020年8月7日 @time 上午8:28:26
*/
public class JDBC_04_PreparedStatement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// login("root", "root");
login("'or 1=1 or 1>'", "11");
// where username = '1=1' and password = '11'
// where username = "or 1=1 or 1='1' and password = '11'"
}
public static void login(String username, String password) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 数据库连接
// jdbc:mysql://IP地址 : 端口号 / 数据库
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day_03", "root", "root");
// 3 语句传输对象
// 使用通配符 ? 替代值
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = ? and password = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第一个 ? 的值
preparedStatement.setString(1, username);
preparedStatement.setString(2, password);
// 4 接收结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功 ,欢迎:" + resultSet.getString("nickname"));
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败 , 用户名或密码错误");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5.1 DML
使用PreparedStatement 执行增删改,以添加为例
public static void add(int id, String name, double money) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement prst = null;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 创建数据库连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/_06_", "root", "root");
// 这里我们用? 问号代替值,可以叫占位符,也可以叫通配符
String sql = "insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values (?,?,?)";
// 3 语句传输对象
prst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第一个?的值
prst.setInt(1, id);
prst.setString(2, name);
prst.setDouble(3, money);
// 返回也是影响的条数
int count = prst.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("影响了 "+count+" 条数据");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 关闭资源,从上到下依次关闭,后打开的先关闭
if (prst != null) {
prst.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
示例:JDBC_03_PREPAREDSTATEMENT_ADD
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* sql 注入
*
* @author lenovo
* @date 2020年8月7日 @time 上午8:28:26
*/
public class JDBC_04_PreparedStatement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// login("root", "root");
login("'or 1=1 or 1>'", "11");
// where username = '1=1' and password = '11'
// where username = "or 1=1 or 1='1' and password = '11'"
}
public static void login(String username, String password) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2 数据库连接
// jdbc:mysql://IP地址 : 端口号 / 数据库
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day_03", "root", "root");
// 3 语句传输对象
// 使用通配符 ? 替代值
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = ? and password = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 设置第一个 ? 的值
preparedStatement.setString(1, username);
preparedStatement.setString(2, password);
// 4 接收结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(sql);
if (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println("登录成功 ,欢迎:" + resultSet.getString("nickname"));
} else {
System.out.println("登录失败 , 用户名或密码错误");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
6. 封装工具类
主要针对2个方面进行改进封装。
以下的代码我们每个方法中都会重复一次,这是没必要的,因为不同的方法其实只是具体执行的SQL语句的内容不同,对于获取连接与释放资源,对应的逻辑是相同的。我们完全可以把这一段逻辑抽取出来,形成独立的类与方法,再在实际应用时调用对应的类和方法就可以了。
-
创建连接这些
-
关闭资源这些
创建链接这些可以这样进行优化
public static Connection getConnection() throws ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
String username = "root";
String password = "root";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/_06_";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username,
password);
return connection;
}
- 关闭资源这些可以这样进行优化
因为Connection和Statement/PreparedStatement以及ResultSet都实现了AutoCloseable接口
所以我们可以直接写AutoCloseable
public static void close(AutoCloseable obj) {
if (obj != null) {
try {
obj.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
演示示例:DBUTIL和JDBC_04_TESTDBUTIL
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBC_06_TestDBUtil {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from t_user");
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getInt("id") + " ");
System.out.print(resultSet.getString("username") + " ");
System.out.print(resultSet.getString("password") + " ");
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("nickname") + " ");
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
DBUtil.close(resultSet);
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement);
DBUtil.close(connection);
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
练习:使用DBUtil对test_jdbc表进行增删改查各一次
DBUtil 工具类 :
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* jdbc工具类
*
* @author lenovo
* @date 2020年8月6日 @time 下午5:08:52
*/
public class DBUtil {
public static Connection getConnection() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day_03", "root", "root");
return connection;
}
public static void close(AutoCloseable autoCloseable) {
try {
if (autoCloseable != null) {
autoCloseable.close();
}
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试类 :
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
public class JDBC_test_base_DML {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**
* 增加
*/
Connection connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "INSERT INTO test_jdbc (id,name,money)VALUES(5,'啊啊',33.22)";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
int count = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count);
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement);
DBUtil.close(connection);
/**
* 删除
*/
Connection connection1 = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql1 = "delete from test_jdbc where id = 1";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement1 = connection1.prepareStatement(sql1);
int count1 = preparedStatement1.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count1);
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement1);
DBUtil.close(connection1);
/**
* 更改
*/
Connection connection2 = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql2 = "UPDATE test_jdbc set name = '123' WHERE name = '王五'";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement2 = connection2.prepareStatement(sql2);
int count2 = preparedStatement2.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count2);
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement2);
DBUtil.close(connection2);
/**
* 查找
*/
Connection connection3 = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql3 = "select * from test_jdbc ";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement3 = connection3.prepareStatement(sql3);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement3.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.print(resultSet.getInt("id") + " ");
System.out.print(resultSet.getString("name") + " ");
System.out.println(resultSet.getDouble("money") + " ");
}
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement3);
DBUtil.close(connection3);
DBUtil.close(resultSet);
}
}
7. Batch多语句操作
在一次任务中,执行多条数据
7.1 Statement实现
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.addBatch("insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values(21,'stmt多条测试1',99.12)");
stmt.addBatch("insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values(22,'stmt多条测试2',99.22)");
stmt.addBatch("insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values(23,'stmt多条测试3',99.32)");
stmt.addBatch("insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values(24,'stmt多条测试4',99.42)");
stmt.executeBatch();
System.out.println("执行成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(stmt);
DBUtil.close(conn);
}
示例:JDBC_05_BATCH_STATEMENT
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBC_01_Batch_Statement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
statement = connection.createStatement();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
statement.addBatch("insert into test (name,age) values ('张三_" + i + "',18)");
}
statement.executeBatch();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行成功 : " + (endTime - startTime));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
DBUtil.close(statement);
DBUtil.close(connection);
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
7.1 PreparedStatement实现
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement prst = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into test_jdbc (id,name,money) values(?,?,?)";
prst = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
prst.setInt(1, 31);
prst.setString(2, "prst多条测试1");
prst.setDouble(3, 11.1);
prst.addBatch();
prst.setInt(1, 32);
prst.setString(2, "prst多条测试2");
prst.setDouble(3, 21.1);
prst.addBatch();
prst.setInt(1, 33);
prst.setString(2, "prst多条测试3");
prst.setDouble(3, 31.1);
prst.addBatch();
prst.executeBatch();
System.out.println("执行成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(prst);
DBUtil.close(conn);
}
示例:
JDBC_05_BATCH_PREPAREDSTATEMENT
package com;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class JDBC_02_Batch_PreparedStatement {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into test (name,age) values (?,?)";
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "张三_" + i);
preparedStatement.setInt(2, 18);
preparedStatement.addBatch();
}
preparedStatement.executeBatch();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("执行成功 : " + (endTime - startTime));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
DBUtil.close(preparedStatement);
DBUtil.close(connection);
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}






















 167
167











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








