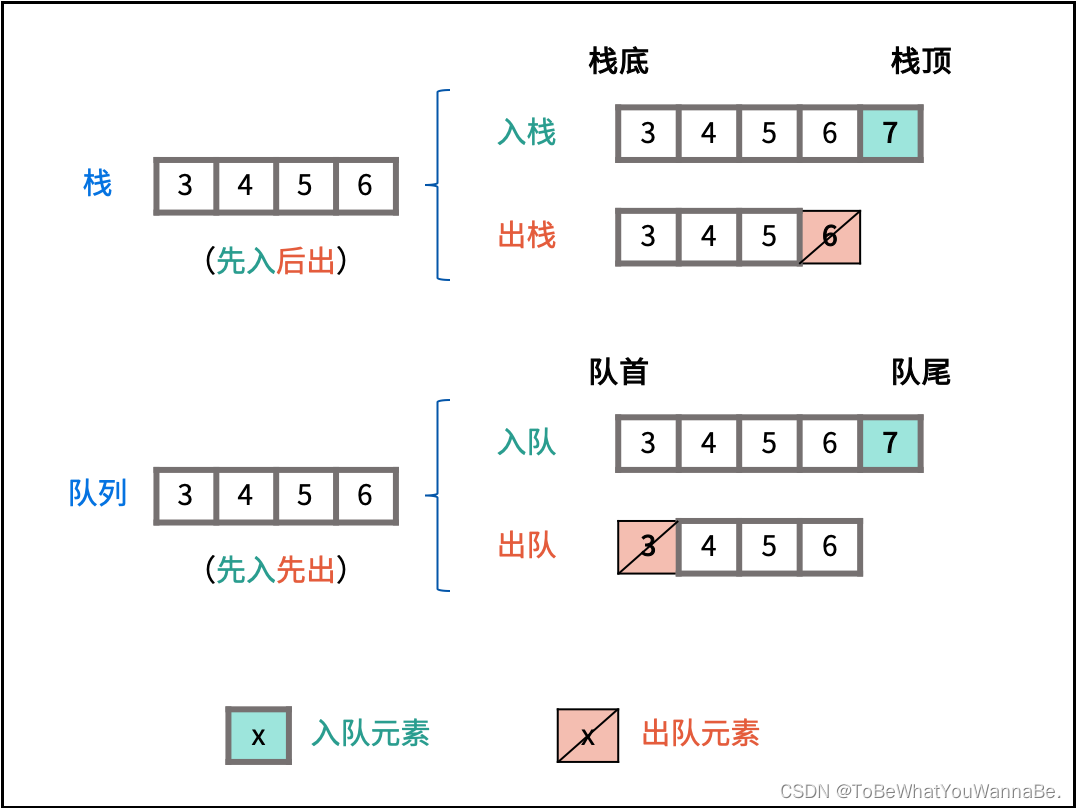
232. 用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
示例 1:
输入:
[“MyQueue”, “push”, “push”, “peek”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
解释:
MyQueue myQueue = new MyQueue();
myQueue.push(1); // queue is: [1]
myQueue.push(2); // queue is: [1, 2] (leftmost is front of the queue)
myQueue.peek(); // return 1
myQueue.pop(); // return 1, queue is [2]
myQueue.empty(); // return false
class MyQueue {
Deque<Integer> inStack;
Deque<Integer> outStack;
public MyQueue() {
inStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
outStack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
}
public void push(int x) {
inStack.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if (outStack.isEmpty()) {
in2out();
}
return outStack.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return inStack.isEmpty() && outStack.isEmpty();
}
private void in2out() {
while (!inStack.isEmpty()) {
outStack.push(inStack.pop());
}
}
}
这段代码实现了一个自定义的队列类 MyQueue,它使用两个栈(Deque 的实例,这里使用了 ArrayDeque 实现)来模拟队列的行为。队列的主要操作包括:入队(push)、出队(pop)、查看队首元素(peek)以及判断队列是否为空(empty)。下面是这个类的详细解释:
-
成员变量:
inStack: 用于存放新加入队列的元素,相当于临时存储。outStack: 用于存放待出队的元素,保证出队操作的先进先出特性。
-
构造函数:
初始化两个ArrayDeque类型的栈。 -
push(int x):
将元素x压入inStack,模拟队列的入队操作,时间复杂度 O(1)。 -
pop():
出队操作稍微复杂。首先检查outStack是否为空,如果为空,则需要将inStack中的所有元素转移到outStack中(这一步通过in2out方法完成),然后再从outStack弹出顶部元素作为出队结果,时间复杂度在最坏情况下为 O(n),但 amortized(摊还)时间复杂度接近 O(1),因为元素仅在必要时转移。 -
peek():
查看队首元素,逻辑与pop()类似,但不移除元素,只返回outStack的顶部元素或在outStack为空时通过转移元素后再返回顶部元素。 -
empty():
判断队列是否为空,只需检查两个栈都为空即可。 -
private void in2out():
这是一个辅助方法,用于将inStack中的所有元素转移到outStack,确保outStack顶部的元素是队列中的下一个出队元素,这一过程实现了从后进先出的栈结构到先进先出队列特性的转换。
总结来说,这个 MyQueue 类利用两个栈实现了标准队列的操作,虽然某些操作在最坏情况下的时间复杂度不是严格的 O(1),但在实际应用中,特别是当队列操作序列不是特别针对最坏情况设计时,其效率通常是很高的。
225. 用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的标准操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
示例:
输入:
[“MyStack”, “push”, “push”, “top”, “pop”, “empty”]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
输出:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
解释:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // 返回 2
myStack.pop(); // 返回 2
myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
这段代码实现了一个自定义的栈类 MyStack,该栈是基于两个队列(Queue 的实例,这里使用了 LinkedList 实现)来实现的。栈的主要操作包括:压栈(push)、弹栈(pop)、查看栈顶元素(top)以及判断栈是否为空(empty)。下面是这个类的详细解释:
-
成员变量:
queue1: 用于主要存储栈中的元素。queue2: 辅助队列,用于帮助实现压栈操作时的反转元素顺序。
-
构造函数:
初始化两个LinkedList类型的队列。 -
push(int x):
向栈中添加一个元素x的过程稍微复杂。首先将新元素添加到queue2,然后将queue1中的所有元素转移到queue2(这样可以保证新加入的元素在队列尾部,即栈顶位置)。之后交换两个队列的角色,使得queue1总是保持栈的状态,而queue2作为临时存储。这个操作的时间复杂度是 O(n),其中 n 是当前栈中元素的数量。 -
pop():
直接从queue1(代表栈顶)移除并返回顶部元素,时间复杂度 O(1)。 -
top():
返回queue1的顶部元素,即队列的第一个元素,时间复杂度 O(1)。 -
empty():
检查queue1是否为空来判断栈是否为空,时间复杂度 O(1)。
总结来说,这个 MyStack 类利用两个队列实现了标准栈的操作,尽管 push 操作在每次调用时都需要将元素从一个队列移动到另一个队列,导致其时间复杂度为 O(n),但在实际应用中,如果压栈操作不是非常频繁或者栈的大小相对稳定,这样的实现仍然是可行且有效的。





















 216
216

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








