带环链表 II
题目
给定一个链表,如果链表中存在环,则返回到链表中环的起始节点的值,如果没有环,返回null。
样例
给出 -21->10->4->5, tail connects to node index 1,返回10
挑战
不使用额外的空间
题解
首先通过快慢指针得到该链表是否带环,如果有环则将快慢指针进行重置,分别指向头节点和之前相遇的节点,再进行单步前进,两指针相遇的节点就是环的入口节点。
证明如下:
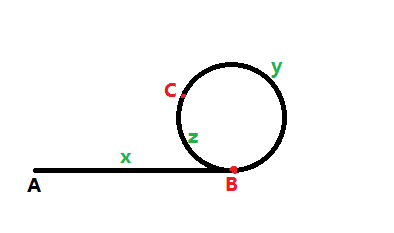
如图所示:A为头结点,B为环入口节点,C为快慢指针相遇节点
x为AB段长度,y为BC段长度,z为CB段长度。
在相遇时慢指针走过x+y,快指针走过x+y+z+y,由于快指针速度为慢指针的2倍,则有2*(x+y) = x+y+z+y =>x=z,即两指针分别从A、C两点出发,速度相同则必会在B点相遇。
/**
* Definition for ListNode.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* @param head: The first node of linked list.
* @return: The node where the cycle begins.
* if there is no cycle, return null
*/
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
ListNode enCounter = null;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode quick = head;
while (true)
{
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next;
if (slow == null || quick == null || quick.next == null)
{
return null;
}
quick = quick.next;
if (slow == quick)
{
enCounter = slow;
break;
}
}
slow = head;
quick = enCounter;
while (true)
{
if (slow == quick)
{
enCounter = slow;
break;
}
slow = slow.next;
quick = quick.next;
}
return enCounter;
}
}Last Update 2016.12.5






















 121
121

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








