常用查找算法
学习目标: 掌握常用的查找算法
算法简介:
find//查找元素find_if//按条件查找元素adjacent_find//查找相邻重复元素binary_search//二分查找法count//统计元素个数count_if//按条件统计元素个数
1 find
功能描述: 查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型: find(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
代码示例:
//查找内置数据类型
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test1()
{
cout << "查找内置数据类型" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
}
cout << "v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找是否有7这个元素 返回迭代器
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 7)/找到与否都返回迭代器
if (pos == v1.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到元素:" << *pos << endl;
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)//const修饰 防止数据被修改 引用方式 防止浅拷贝
{
if (this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age && p.m_age)
{
return true;
}
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
};
void myprint2(Person& p)
{
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << "\t年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
//查找自定义数据类型
void test2()
{
cout << "查找自定义数据类型" << endl;
vector<Person> v2;
string nameseed[] = { "刘备", "关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "曹操", "貂蝉", "西施", "杨玉环", "王昭君" };
int ageseed[] = { 39, 37, 35, 33, 31, 29, 27, 25, 23 };
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
Person p(nameseed[i], ageseed[i]);
v2.push_back(p);
}
cout << "v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myprint2);
//查找是否有pfind这个元素 返回迭代器
Person pfind("西施", 27);
vector<Person>::iterator pos = find(v2.begin(), v2.end(), pfind);
if (pos == v2.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到元素\t姓名:" << (*pos).m_name << "\t年龄:" << pos->m_age << endl;
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}

总结:
-
利用find可以在容器中找指定的元素,返回值是迭代器
-
利用find在容器中查找自定义数据类型时候,需要配合重载
operator==。具体而言,Person类中不重载的话,find不知道用Person的姓名还是年龄对比来查找
2 find_if
功能描述: 按条件查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
函数原型: find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 函数或者谓词(返回bool类型的仿函数)
代码示例:
//查找内置数据类型
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
class greatersix
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 6;
}
};
void test1()
{
cout << "查找内置数据类型" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
}
cout << "v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找是否有大于6的元素 返回迭代器
vector<int>::iterator pos = find_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greatersix());//提供谓词
if (pos == v1.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到元素:" << *pos << endl;//返回第一个符号条件的值
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}
//查找自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
};
void myprint2(Person& p)
{
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << "\t年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
class greater29
{
public:
bool operator()(Person& p)
{
return p.m_age > 29;
}
};
void test2()
{
cout << "查找自定义数据类型" << endl;
vector<Person> v2;
string nameseed[] = { "刘备", "关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "曹操", "貂蝉", "西施", "杨玉环", "王昭君" };
int ageseed[] = { 39, 37, 35, 33, 31, 29, 27, 25, 23 };
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
Person p(nameseed[i], ageseed[i]);
v2.push_back(p);
}
cout << "v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myprint2);
//查找是否有年龄小于29的元素 返回迭代器
Person pfind("西施", 27);
//自定义数据类型时,提供谓词
vector<Person>::iterator pos = find_if(v2.begin(), v2.end(), greater29());
if (pos == v2.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到元素\t姓名:" << (*pos).m_name << "\t年龄:" << pos->m_age << endl;
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}

总结: find_if按条件查找使查找更加灵活,提供的仿函数可以改变不同的策略
3 adjacent_find
功能描述: 查找相邻重复元素,查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
函数原型: adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
代码示例:
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test1()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(18);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(21);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(26);
v1.push_back(28);
cout << "查找相邻重复元素" << endl;
cout << "v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
vector<int>::iterator pos = adjacent_find(v1.begin(), v1.end());
if (pos == v1.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *pos << endl;//返回第一个符号条件的值
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.push_back(18);
v2.push_back(23);
v2.push_back(21);
v2.push_back(23);
v2.push_back(25);
v2.push_back(26);
v2.push_back(28);
cout << "查找相邻重复元素" << endl;
cout << "v2:";
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找相邻重复元素,返回相邻元素的第一个位置的迭代器
pos = adjacent_find(v2.begin(), v2.end());
if (pos == v2.end())
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *pos << endl;//返回第一个符号条件的值
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}

总结: 面试题中如果出现查找相邻重复元素,记得用STL中的adjacent_find算法
4 binary_search
功能描述: 查找指定元素是否存在,查找指定的元素,查到 返回true 否则false。在无序序列中不可用,必须在有序序列中使用
函数原型: bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 查找的元素
代码示例:
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test1()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(18);
v1.push_back(28);
v1.push_back(26);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(23);
//无序
cout << "查找指定元素26是否存在" << endl;
cout << "无序 v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找指定元素是否存在,查到 返回true 否则false
bool ret = binary_search(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 26);
if (ret)
{
cout << "找到元素!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
//有序
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
cout << "有序 v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl;
//查找指定元素是否存在,查到 返回true 否则false
ret = binary_search(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 26);
if (ret)
{
cout << "找到元素!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有找到!" << endl;
}
cout << endl << string(40, '-') << endl;
}

总结: 二分查找法查找效率很高,值得注意的是查找的容器中元素必须的有序序列
5 count
功能描述: 统计元素个数,统计元素出现次数
函数原型: count(iterator beg, iterator end, value);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// value 统计的元素
代码示例:
//内置数据类型
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test1()
{
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(18);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(21);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(26);
v1.push_back(28);
cout << "v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "统计内置数据类型" << endl;
int num = count(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 25);
cout << "25元素的个数为:" << num << endl;
cout << string(40, '-') << endl << endl;;
}
//自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
//自定义数据类型时,类中需要重载==
//如果要统计其他条件的 if的条件可以修改
bool operator==(const Person& p)//防止数据被修改
{
if (this->m_age < p.m_age)//传进来的的人的年龄 比 容器中的人的年龄大
{
return true;//可以统计
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
};
void myprint2(Person& p)
{
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << "\t年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
void test2()
{
vector<Person> v2;
string nameseed[] = { "刘备", "关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "曹操", "貂蝉", "西施", "杨玉环", "王昭君" };
int ageseed[] = { 39, 37, 35, 33, 31, 29, 27, 25, 23 };
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
Person p(nameseed[i], ageseed[i]);
v2.push_back(p);
}
cout << "v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myprint2);
cout << "\n统计自定义数据类型" << endl;
Person p("诸葛亮", 35);
int num = count(v2.begin(), v2.end(), p);//自定义数据类型时,类中需要重载==
cout << "年龄比诸葛亮小的人有 " << num << "人" << endl;
cout << string(40, '-') << endl;
}

count源码
可以看到在count源码中,进行统计次数时,还是通过传入值和迭代器遍历值进行比较。如果两值相等,则计数,count++。

总结: 统计自定义数据类型时候,需要配合重载 operator==
6 count_if
功能描述: 按条件统计元素个数,按条件统计元素出现次数
函数原型: count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred);
参数说明:
// beg 开始迭代器
// end 结束迭代器
// _Pred 谓词
代码例:
//内置数据类型
void mtprint(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
class greater25
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 25;
}
};
void test1()
{
cout << "统计内置数据类型" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(18);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(21);
v1.push_back(23);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(25);
v1.push_back(26);
v1.push_back(28);
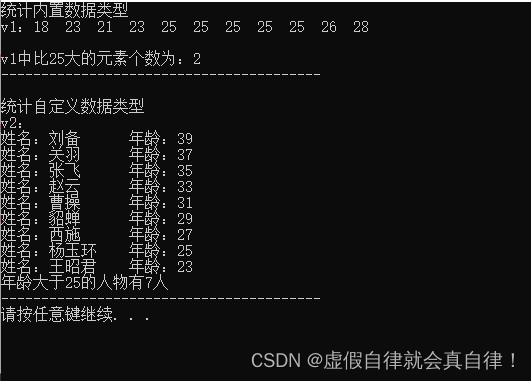
cout << "v1:";
for_each(v1.begin(), v1.end(), mtprint);
cout << endl << endl;
int num = count_if(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater25());
cout << "v1中比25大的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
cout << string(40, '-') << endl << endl;;
}
//自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_name = name;
this->m_age = age;
}
//如果要统计其他条件的 if的条件可以修改
bool operator==(const Person& p)//防止数据被修改
{
if (this->m_age < p.m_age)//传进来的的人的年龄 比 容器中的人的年龄大
{
return true;//可以统计
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_name;
int m_age;
};
void myprint2(Person& p)
{
cout << "姓名:" << p.m_name << "\t年龄:" << p.m_age << endl;
}
class AgeGreater25
{
public:
bool operator()(const Person& p)
{
if (p.m_age > 25)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
void test2()
{
cout << "自定义数据类型" << endl;
vector<Person> v2;
string nameseed[] = { "刘备", "关羽", "张飞", "赵云", "曹操", "貂蝉", "西施", "杨玉环", "王昭君" };
int ageseed[] = { 39, 37, 35, 33, 31, 29, 27, 25, 23 };
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
Person p(nameseed[i], ageseed[i]);
v2.push_back(p);
}
cout << "v2:" << endl;
for_each(v2.begin(), v2.end(), myprint2);
//查找是否有年龄大于25的人物
int num = count_if(v2.begin(), v2.end(), AgeGreater25());//提供谓词
cout << "年龄大于25的人物有" << num << "人" << endl;
cout << string(40, '-') << endl;
}
总结: 按值统计用count,按条件统计用count_if








 本文详细介绍了C++标准模板库(STL)中的几种常用查找算法,包括find、find_if、adjacent_find、binary_search、count和count_if。这些算法用于在不同条件下查找和统计元素,如按值查找、按条件查找、查找相邻重复元素、二分查找以及统计元素个数。文章提供了实例代码和解析,强调了在自定义数据类型中需重载`==`运算符以及使用谓词函数的重要性。
本文详细介绍了C++标准模板库(STL)中的几种常用查找算法,包括find、find_if、adjacent_find、binary_search、count和count_if。这些算法用于在不同条件下查找和统计元素,如按值查找、按条件查找、查找相邻重复元素、二分查找以及统计元素个数。文章提供了实例代码和解析,强调了在自定义数据类型中需重载`==`运算符以及使用谓词函数的重要性。
















 914
914

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








