目录
异常及其体系结构
在Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称为“异常”,开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是异常。
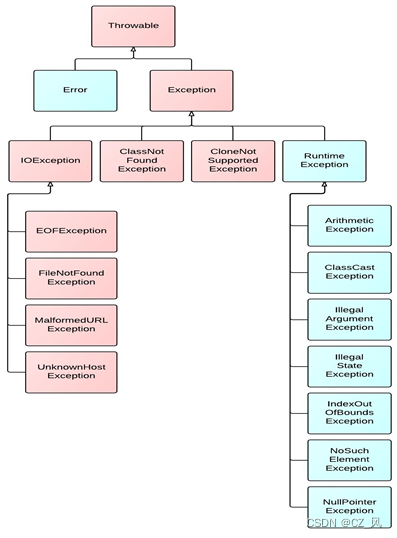
java.lang.Throwable
java.lang.Error:Java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题,一般不编写针对性的代码进行处理。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况,常见有StackOverflowError和OOM。
java.lang.Exception:可以进行异常的处理
编译时异常(checked)
IOException
FileNotFoundException
ClassNotFoundException
运行时异常(unchecked,RuntimeException)
NullPointerException
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
ClassCastException
NumberFormatException
InputMismatchException
ArithmeticException
常见异常举例
编译时异常
//编译时就会出现异常
@Test
public void test7(){
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int data = fis.read();
while(data != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
data = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
}运行时异常
NullPointException
//NullPointException
@Test
public void test1() {
int[] arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[2]);
String str = "abv";
str = null;
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
}InexOutOfBoundsException
//InexOutOfBoundsException
@Test
public void test2() {
int a[] = new int[10];
System.out.println(a[10]);
}ClassCastException
//ClassCastException
@Test
public void test3() {
Object o = new Date();
String s = (String)o;
}NumberFormatException
//NumberFormatException
@Test
public void test4() {
String str = "abc";
Integer.parseInt(str);
}InputMismatchException
//InputMismatchException
@Test
public void test5() {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scan.nextInt();
System.out.println(a);
scan.close();
}ArithmeticException
//ArithmeticException
@Test
public void test7() {
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
int c = b/a;
}Java异常处理的方式
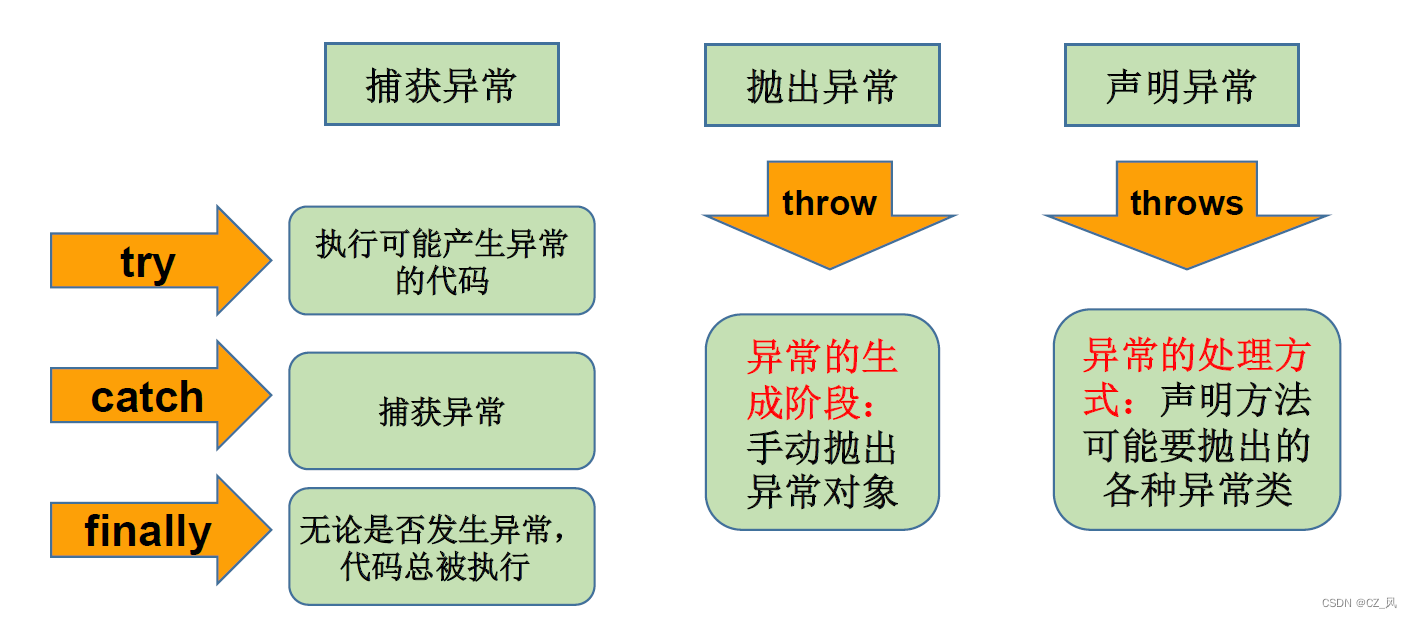
Java 程序的执行过程中如出现异常,会生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象将被提交给Java 运行时系统,这个过程称为抛出( throw)异常。
抓抛模型
过程一
"抛":程序一旦出现异常就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象并将此对象抛出。一旦抛出对象后,其后的代码就不再执行。
过程二
"抓":可以理解为异常的处理方式:① try-catch-finally ② throws + 异常类型
异常对象的产生
●系统自动生成的异常对象。
●手动的生成一个异常对象,并抛出 throw !
try-catch-finally的使用
格式:
try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
//处理异常的方式1
}catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
//处理异常的方式2
}catch(异常类型3 变量名3){
//处理异常的方式3
}
...
finally{
//一定会执行的代码
}说明:
1、finally是可选择的。
2、使用try将可能出现异常代码包装起来,在执行过程中,一旦出现异常,
就会生成一个对应异常类的对象,根据此对象的类型去catch中进行匹配。
3、一旦try中的异常对象匹配到某一个catch时,就进入catch中进行异常的处理。
处理完了就跳出当前try-catch结构(在没有写finally的情况),进行执行后面代码。
4、catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类的关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓。
catch中的异常类型如果满足子父类的关系,则要求子类一定在上。
5、常用的异常对象处理的方式:① e.getMessage() ② e.printStackTrace()
6、在try结构中声明的变量,在出了try结构后就不能再被调用了。
7、try-catch-finally结构可以嵌套。
8、finally中声明的代码是一定会被执行的。不论在 try 代码块中是否发生了异常事件, catch 语句是否执行, catch 语句是否有异常, catch 语句中是否有 return等。
9、像数据库连接、输入输出流、网络编程Socket等资源,JVM是不能自动的回收的,我们需要自己手动的进行资源的释放。此时的资源释放,就需要声明在finally中。
注意:
●使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常,使得程序在编译时不再报错,但运行时仍可能报错。
●由于运行时异常比较常见,所以我们通常不针对运行时异常使用try-catch-finally,对于编译时异常要考虑处理。
//java.lang.NumberFormatException
@Test
public void test(){
String str = "123";
str = "abc";
int num = 0;
try{
num = Integer.parseInt(str); //发生NumberFormatException的地方
System.out.println("hello-----1"); //上面语句发生异常,此语句不会执行
}catch(NumberFormatException e){
//有两个输出异常信息的方法可以任选使用,选择其中一个即可
//一:String getMessage():
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//For input string: "abc"
//二:printStackTrace():
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(NullPointerException e){
System.out.println("出现空指针异常了,不要着急...."); //不执行
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("出现异常了,不要着急...."); //不执行
}
System.out.println(num); //0
System.out.println("hello-----2");//hello-----2
}
//ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
@Test
public void testMethod(){
int num = method();
System.out.println(num);
}
public int method(){
try{
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.println(arr[10]); //产生ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException的地方
return 1; //不执行
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
e.printStackTrace();
return 2; //不执行
}finally{
System.out.println("finally块里的语句一定会被执行");//finally块里的语句一定会被执行
return 3; //3
}
}
@Test
public void test(){
try{
int a = 10;
int b = 0;
System.out.println(a / b);//产生java.lang.ArithmeticException
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("有点猛"); //有点猛
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("好猛啊!"); //好猛啊!
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
System.out.println("有点6!");
System.out.println("欸~,真的有点6!");
}
}“throws + 异常类型”的使用
1、"throws + 异常类型"写在方法的声明处。指明此方法执行时,可能会抛出异常类型
一旦当方法体执行时,出现异常,仍会在异常代码出生成一个异常类的对象,此对象
满足throws后异常类型时,就会被抛出。异常代码后续的代码就不再执行!
2、try-catch-finally:真正的将异常给处理掉了。
throws的方式只是将异常抛给方法的调用者,并没有真正将异常处理掉。
格式:
public void readFile(String file) throws FileNotFoundException{
……
//读文件的操作可能产生 FileNotFoundException 类型的异常
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream (file);
……
}
public class ThrowsTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
method2();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
// method3();
}
public static void method3(){
try {
method2();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void method2() throws IOException{
method1();
}
public static void method1() throws FileNotFoundException,IOException{
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int data = fis.read();
while(data != -1){
System.out.print((char)data);
data = fis.read();
}
fis.close();
System.out.println("老6!");
}
}开发中如何选择使用try-catch-finally 还是使用throws?
1、如果父类中被重写的方法没有throws方式处理异常,则子类重写的方法也不能使用throws,意味着如果子类重写的方法中有异常,必须使用try-catch-finally方式处理。
2、执行的方法A中,先后又调用了另外的几个方法,这几个方法是递进关系执行的。我们建这几个方法使用throws的方式进行处理。而执行的方法A可以考虑使用try-catch-finally方式进行处理。
手动抛出异常
Java 异常类对象除在程序执行过程中出现异常时由系统自动生成并抛出,也可根据需要使用人工创建并抛出(throw)。
throw 和 throws 区别
throw 表示抛出一个异常类的对象,生成异常对象的过程。声明在方法体内。
throws 属于异常处理的一种方式,声明在方法的声明处。
自定义异常类
自定义异常类的要求
1、继承于现有的异常结构,如RuntimeException、Exception。
2、通常需要提供几个重载的构造器。
3、提供全局常量serialVersionUID。
4、自定义的异常通过throw抛出。
public class MyException extends Exception{
//serialVersionUID 随便不同数值即可
static final long serialVersionUID = -7034897193246939L;
private int id;
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String msg ,int id){
super(msg);
this.id = id;
}
}public class MyExceptionTest{
public void regist(int n) throws MyException { //这里throws + 自己定义的异常类型
if (n < 0)
throw new MyException("人数不能为负数", 6);//throw 抛出异常对象
else
System.out.println("登记人数为:" + n);
}
public void manager(){
try {
regist(88888888);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.print("登记失败");
}
System.out.print("本次登记结束");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
MyExceptionTest m = new MyExceptionTest();
m.manager();
}
}//判断程序的输出结果
public class Test {
static void methodA() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法A");
throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("用方法A进入finally");
}
}
static void methodB() {
try {
System.out.println("进入方法B");
return;
}finally {
System.out.println("用方法B进入finally");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
methodA();
}catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//制造异常
}
methodB();
}
}
结果:
进入方法A
用方法A进入finally
制造异常
进入方法B
用方法B进入finally总结:






















 248
248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








