归并排序:
算法描述:
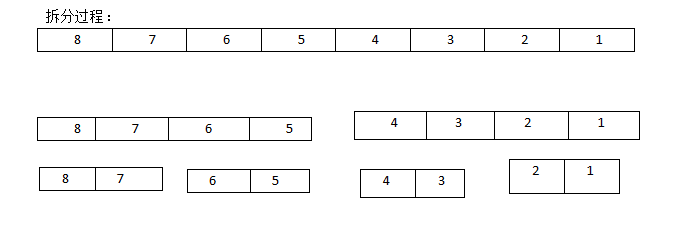
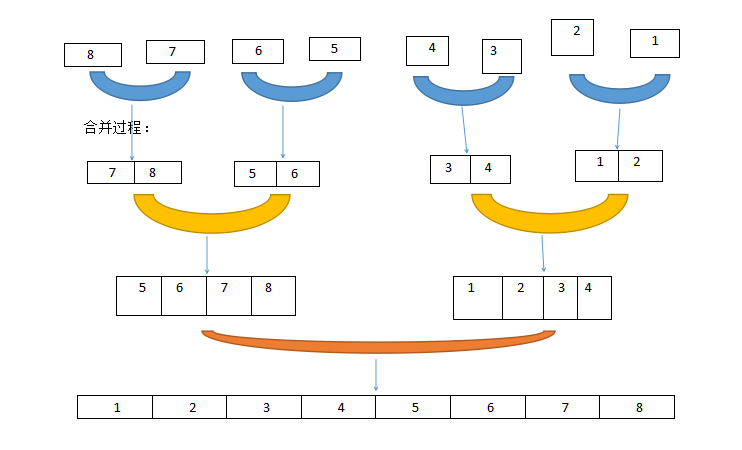
分分分 --->>> 合合合
算法分析:
需要进行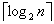
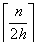
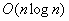
在归并的过程中需要用到辅助数组,所以空间复杂度为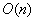
归并排序是一项稳定的排序。
算法实现:
Code:
//空间复杂度中各种各样的数组是归并排序的一大混乱点
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000000;
int num[maxn];
int T[maxn];
int temp[maxn];
void Merge(int s, int m, int t)
{
int i = s, j = m+1, k;
for(k = s ; i <= m && j <= t;)
{
if(temp[i] > temp[j])
T[k] = temp[j], j++, ++k;
else
T[k] = temp[i], i++, ++k;
}
while(i <= m)
T[k] = temp[i], i++, k++;
while(j <= t)
T[k] = temp[j], j++, k++;
for(int ii = s; ii <= t; ii++)
temp[ii] = T[ii];
return ;
}
void M_Sort(int s, int t)
{
if(s == t)
{
temp[s] = num[s]; //只有一个元素
T[s] = num[s];
}
else
{
int m = (s+t)/2; //确定中间元素的位置
M_Sort(s, m); //将num数组的[s, m]归并为有序的TR2
M_Sort(m+1, t); //将num数组的[m+1, t]归并为有序的TR2
Merge(s, m, t); //讲TR2中的[s, m] 和 [m+1]合并为TR1
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
M_Sort(1, n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(i == 1) cout << T[i];
else cout << " " << T[i];
return 0;
}






















 6014
6014

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








