数据结构——线性表:链表
1.Definition and notice
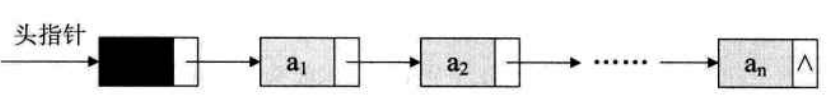
(1)每个数据ai除了存储其本身信息之外,还需要存储一个指示其直接后继信息的地址。一个元素分为数据域、指针域。
(2)头结点:链表里的第一个结点,指针域存放首元结点地址。
头指针:指向第一个结点的指针。若有头结点,则指向头结点

下图为带有头结点的链表
2.代码
(1)定义
a.别名PNODE 就是 struct node *,别名NODE就是 struct node。注意定义的方法。
b.malloc()函数的头文件为stdlib.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ERROR 0
#define OK 1
typedef struct node //typedef 用于取struct node 的别名
{
int data;
struct node *next;
}*PNODE,NODE; //别名PNODE 就是 struct node * 别名NODE就是 struct node
(2)main函数
int main()
{
PNODE init(); //链表初始化
void insertf(PNODE head, int newdata); //链表插入头插法
void insertl(PNODE head, int newdata); //链表插入尾插法
void print(PNODE head); //打印链表
void frlist(PNODE head); //释放链表
//大话数据结构
int getele(PNODE head, int i, int *e); //获取第i个结点的元素
int inserti(PNODE head, int i, int e); //单链表第i个数据插入结点
//在链表第i个位置之前插入行的数据元素e,从而e为第i个结点。
int deletei(PNODE head, int i); //删除第i个结点
PNODE head = init();
return 0;
}
(3)链表初始化函数(返回头指针head)
PNODE init()
{
PNODE head = (PNODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
(4)头插法和尾插法
a.头插法

void insertf(PNODE head, int newdata) //头插法
{
PNODE current;
current = (PNODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
current->data = newdata;
current->next = head->next;
head->next = current;
}
b.尾插法
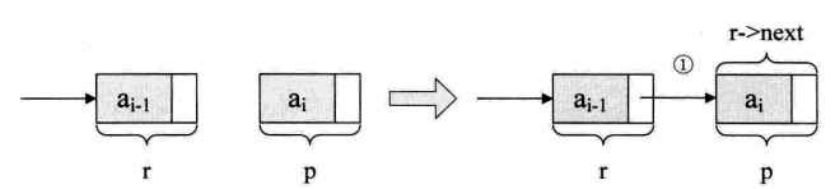
void insertl(PNODE head, int newdata)
{
PNODE p, current;
current = (PNODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
current->data = newdata;
p = head;
while (p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = current;
current->next = NULL;
}
(5)打印函数
void print(PNODE head)
{
PNODE p;
p = head->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
(6)链表释放函数
void frlist(PNODE head) //释放链表
{
PNODE p, temp;
p = head;
while (p != NULL)
{
temp = p->next;
free(p);
p = temp;
}
}
(7)获取第i个结点元素的函数
找到**a[i]**这个结点

int getele(PNODE head, int i, int *e)
{
int j = 1;
PNODE p = head->next; //p指向第一个结点,j=1。
while (p != NULL && j < i)
{
p = p->next;
j++;
} //循环结束 此时p指向第i个结点
if (p == NULL || j > i)
return ERROR;
*e = p->data;
return OK;
}
(8)链表的插入函数
在链表第i个结点之前插入行的数据元素e,从而e所在结点为第i个结点。首先要找到a[i-1]这一结点。
注意:此处函数指针p初始化时与 getele()函数不同
此处为p=head;而getele()函数中为p=head->next;
int inserti(PNODE head, int i, int e) //单链表第i个数据插入结点
{
PNODE p,current;
int j = 1;
p = head; //p指向头结点,j=1。注意此处与getele()不同
while (p != NULL && j < i)
{
p = p->next;
j++;
} //循环结束 此时p指向第a[i-1]个结点
if (p == NULL || j > i)
return ERROR;
current = (PNODE)malloc(sizeof(NODE));
current->data = e;
current->next = p->next;
p->next = current;
return OK;
}
(9)链表的结点删除函数
注意:此处if判断条件为if (p->next == NULL || j > i)
不同于inserti()函数中的if (p == NULL || j > i)

int deletei(PNODE head, int i)
{
PNODE p,current;
p = head; //此处与inserti()相同,不同于getele()
int j = 1;
while (p != NULL && j < i) //此处大话书上P65有问题
{
p = p->next;
j++;
} //循环结束 此时p指向第a[i-1]个结点
if (p->next == NULL || j > i)
//此处不同于inserti()函数,判断a[i]存在与否
return ERROR;
current = p;
p->next = p->next->next;
free(current);
return OK;
}























 446
446











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








