前言
人生如逆旅,我亦是行人。————苏轼《临江仙·送钱穆父》
一、题:
给你一个字符串 num ,表示一个大整数。如果一个整数满足下述所有条件,则认为该整数是一个 优质整数 :
- 该整数是
num的一个长度为3的 子字符串 。 - 该整数由唯一一个数字重复
3次组成。
以字符串形式返回 最大的优质整数 。如果不存在满足要求的整数,则返回一个空字符串 "" 。
注意:
- 子字符串 是字符串中的一个连续字符序列。
num或优质整数中可能存在 前导零 。
示例1:
输入:num = "6777133339"
输出:"777"
解释:num 中存在两个优质整数:"777" 和 "333" 。
"777" 是最大的那个,所以返回 "777" 。
示例2:
输入:num = "2300019"
输出:"000"
解释:"000" 是唯一一个优质整数。
示例3:
输入:num = "42352338"
输出:""
解释:不存在长度为 3 且仅由一个唯一数字组成的整数。因此,不存在优质整数。
提示:
3 <= num.length <= 1000num仅由数字(0 - 9)组成
二、分析
遍历数组,找到满足条件的答案。
- 首先得出数组的长度;
- 如果其长度小于
3,则说明无优质整数,返回空字符串 - 再定义一个字符型变量
- 遍历整个数组,后两位无需遍历,
- 出现连续三个相等的数字,则记录它的大小并与之前的比较大小判断谁更大
- 如果最后
cur仍为初始值,则说明数组没有连续重复三次的数字,则返回空字符串 - 不为初始值,则返回
3个由字符cur组成的字符串,也就是我们需要求的优质整数
三、代码编写(C++):
class Solution {
public:
string largestGoodInteger(string num) {
int n = int(num.size()); //首先得出数组的长度
if(n < 3) return ""; //如果其长度小于3,则说明无优质整数,返回空字符串
char cur = '\0'; //定义一个字符型变量
for(int i=0; i<n-2; i++) //遍历整个数组,后两位无需遍历,
{
//出现连续三个相等的数字,则记录它的大小并与之前的比较大小判断谁更大
if(num[i] == num[i+1] && num[i] == num[i+2])
{
cur = max(cur, num[i]);
}
}
//如果最后cur仍为初始值,则说明数组没有连续重复三次的数字,则返回空字符串
//不为初始值,则返回3个由字符cur组成的字符串,也就是我们需要求的优质整数
return cur == '\0' ? "" : string(3, cur);
}
};
四、string类
- 使用
string类需要包含头文件<string>,
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1;
string s2 = "c plus plus";
string s3 = s2;
string s4 (5, 's');
return 0;
}
- 变量
s1:只是定义但没有初始化,编译器会将默认值赋给s1,默认值是"",也即空字符串。 - 变量
s2:在定义的同时被初始化为"c plus plus"。与C风格的字符串不同,string的结尾没有结束标志'\0'。 - 变量
s3:在定义的时候直接用s2进行初始化,因此s3的内容也是"c plus plus"。 - 变量
s4:被初始化为由5个's'字符组成的字符串,也就是"sssss"。
- 与C风格的字符串不同,当我们需要知道字符串长度时,可以调用 string 类提供的 length() 函数。如下所示:
string s = "http://c.biancheng.net";
int len = s.length();
cout<<len<<endl;
- 结果为
22,由于string的末尾没有'\0'字符,所以length()返回的是字符串的的真实长度,而不是长度+1;
1、转换为C风格的字符串
虽然 C++ 提供了 string 类来替代C语言中的字符串,但是在实际编程中,有时候必须要使用C风格的字符串(例如打开文件时的路径),为此,string 类为我们提供了一个转换函数 c_str(),该函数能够将 string 字符串转换为C风格的字符串,并返回该字符串的 const 指针(const char*)。请看下面的代码:
string path = "D:\\demo.txt";
FIFE *fp = fopen(path.c_str(), "rt");
为了使用C语言中的 fopen() 函数打开文件,必须将 string 字符串转换为C风格的字符串。
2、string 字符串的输入输出
string 类重载了输入输出运算符,可以像对待普通变量那样对待 string 变量,也就是用 >> 进行输入,用 << 进行输出。请看下面的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
cin>>s; //输入字符串
cout<<s<<endl; //输出字符串
return 0;
}
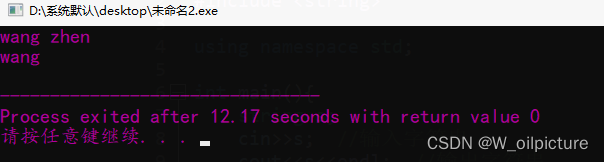
运行结果:
虽然我输入了两个由空格隔开的字符串,但是只输出了一个,这是因为输入运算符 >> 默认会忽略空格,遇到空格就认为输入结束,所以最后输入的 zhen 没有被存储到变量 s。
3、访问字符串中的字符
string 字符串也可以像C风格的字符串一样按照下标来访问其中的每一个字符。string 字符串的起始下标仍是从 0 开始。请看下面的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s = "1234567890";
for(int i=0,len=s.length(); i<len; i++){
cout<<s[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
s[5] = '5';
cout<<s<<endl;
return 0;
}
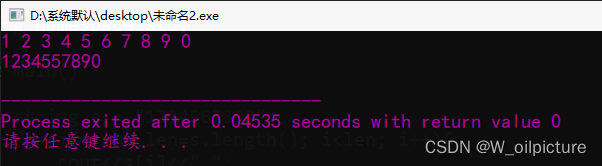
运行结果:
本例中定义了一个 string 变量 s,并赋值 “1234567890”,之后用 for 循环遍历输出每一个字符,借助下标,除了能够访问每个字符,也可以修改每个字符,s[5] = '5'; 就能将第 6 个字符修改为 ‘5’,所以 s 最后为 "1234557890"。
4、字符串的拼接
有了 string 类,我们可以使用 + 或 += 运算符来直接拼接字符串,非常方便,再也不需要使用C语言中的 strcat()、strcpy()、malloc() 等函数来拼接字符串了,再也不用担心空间不够会溢出了。
用 + 来拼接字符串时,运算符的两边可以都是 string 字符串,也可以是一个 string 字符串和一个C风格的字符串,还可以是一个 string 字符串和一个字符数组,或者是一个 string 字符串和一个单独的字符。请看下面的例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1 = "first ";
string s2 = "second ";
char *s3 = "third ";
char s4[] = "fourth ";
char ch = '@';
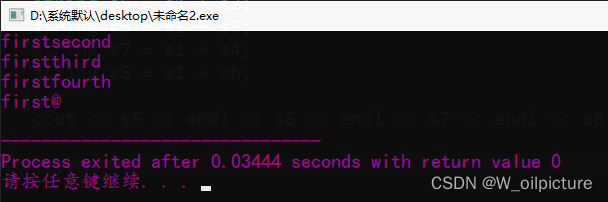
string s5 = s1 + s2;
string s6 = s1 + s3;
string s7 = s1 + s4;
string s8 = s1 + ch;
cout<<s5<<endl<<s6<<endl<<s7<<endl<<s8<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
5、字符串的增删改查
C++提供的 string 类包含若干实用的成员函数,大大方便了字符串的增加、删除、更改、查询等操作。
一、插入字符串
insert() 函数可以在 string 字符串中指定的位置插入另一个字符串,它的一种原型为:
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str);
pos:表示要插入的位置,也就是下标;str:表示要插入的字符串,它可以是string字符串,也可以是C风格的字符串。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
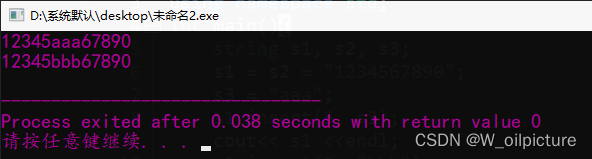
string s1, s2, s3;
s1 = s2 = "1234567890";
s3 = "aaa";
s1.insert(5, s3);
cout<< s1 <<endl;
s2.insert(5, "bbb");
cout<< s2 <<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
insert() 函数的第一个参数有越界的可能,如果越界,则会产生运行时异常.
二、删除字符串
erase() 函数可以删除 string 中的一个子字符串。它的一种原型为:
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
pos:表示要删除的子字符串的起始下标,len:表示要删除子字符串的长度。如果不指明len的话,那么直接删除从pos到字符串结束处的所有字符(此时len = str.length - pos)。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
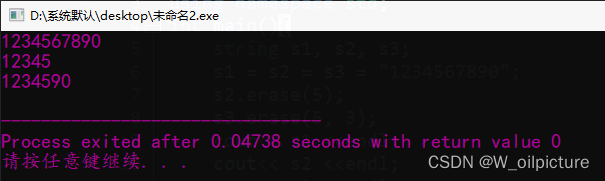
int main(){
string s1, s2, s3;
s1 = s2 = s3 = "1234567890";
s2.erase(5);
s3.erase(5, 3);
cout<< s1 <<endl;
cout<< s2 <<endl;
cout<< s3 <<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
在 pos 参数没有越界的情况下, len 参数也可能会导致要删除的子字符串越界。但实际上这种情况不会发生,erase() 函数会从以下两个值中取出最小的一个作为待删除子字符串的长度:
len的值;- 字符串长度减去的
pos的值
三、提取子字符串
substr() 函数用于从string 字符串中提取子字符串。它的一种原型为:
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
pos:表示要提取的子字符串的起始下标,len:表示要提取子字符串的长度。如果不指明len的话,那么直接删除从pos到字符串结束处的所有字符(此时len = str.length - pos)。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
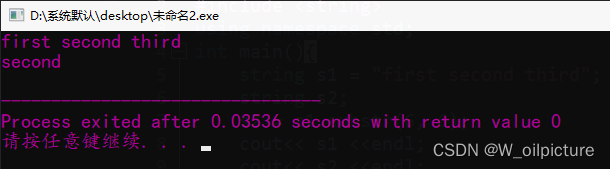
int main(){
string s1 = "first second third";
string s2;
s2 = s1.substr(6, 6);
cout<< s1 <<endl;
cout<< s2 <<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
系统对 substr() 参数的处理和 erase() 类似:
- 如果
pos越界,会抛出异常; - 如果
len越界,会提取从pos到字符串结尾处的所有字符。
四、字符串查找
1)find()函数:
find() 函数用于在 string 字符串中查找子字符串出现的位置,它其中的两种原型为:
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
- 第一个参数为 :待查找的子字符串,它可以是 string 字符串,也可以是C风格的字符串。
- 第二个参数为:开始查找的位置(下标);如果不指明,则从第0个字符开始查找。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
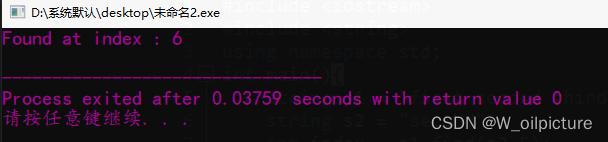
int main(){
string s1 = "first second third";
string s2 = "second";
int index = s1.find(s2,5);
if(index < s1.length())
cout<<"Found at index : "<< index <<endl;
else
cout<<"Not found"<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
find() 函数最终返回的是子字符串第一次出现在字符串中的起始下标。本例最终是在下标 6 处找到了 s2 字符串。如果没有查找到子字符串,那么会返回一个无穷大值 4294967295。
2)rfind()函数:
rfind() 和 find() 很类似,同样是在字符串中查找子字符串,不同的是 find() 函数从第二个参数开始往后查找,而 rfind() 函数则最多查找到第二个参数处,如果到了第二个参数所指定的下标还没有找到子字符串,则返回一个无穷大值 4294967295。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
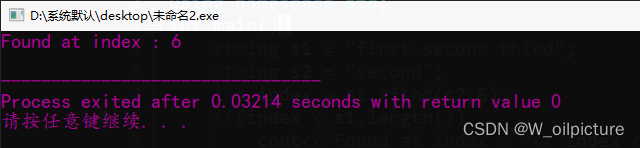
int main(){
string s1 = "first second third";
string s2 = "second";
int index = s1.rfind(s2,6);
if(index < s1.length())
cout<<"Found at index : "<< index <<endl;
else
cout<<"Not found"<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
3)find_first_of() 函数:
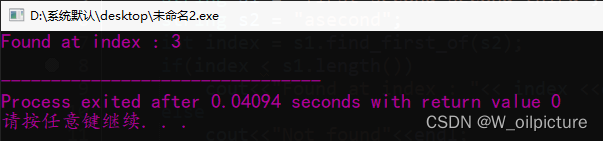
find_first_of() 函数用于查找子字符串和字符串共同具有的字符在字符串中首次出现的位置。请看下面的代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s1 = "first second second third";
string s2 = "asecond";
int index = s1.find_first_of(s2);
if(index < s1.length())
cout<<"Found at index : "<< index <<endl;
else
cout<<"Not found"<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:























 196
196











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










