一、简介
exists(subquery): 如果子查询查询的结果不为空,说明子查询有值,返回真,则执行主查询sql;如果子查询查询的结果为空,说明子查询没值,返回假,则不会执行主查询sql。
not exists(subquery): not exists和exists相反,子查询语句结果为空,则表示where条件成立,执行sql语句,否则不执行。
注意:子查询中使用 NULL 仍然返回结果集
select * from TableIn where exists(select null)
等同于: select * from TableIn
下面,以一个示例说明exists与not exists的用法,以及与in、not in的比较。
二、用法详解
【a】首先,我们先创建两个表: department部门表与employee员工表,建表语句如下:
-- Create table
create table DEPARTMENT
(
depid VARCHAR2(128) not null,
depname VARCHAR2(128)
)
tablespace TEST_TABLESPACE
pctfree 10
initrans 1
maxtrans 255
storage
(
initial 64K
next 1M
minextents 1
maxextents unlimited
);
-- Add comments to the table
comment on table DEPARTMENT
is '部门表';
-- Add comments to the columns
comment on column DEPARTMENT.depid
is '部门ID';
comment on column DEPARTMENT.depname
is '部门名称';
-- Create/Recreate primary, unique and foreign key constraints
alter table DEPARTMENT
add constraint DEP_PK_ID primary key (DEPID)
using index
tablespace TEST_TABLESPACE
pctfree 10
initrans 2
maxtrans 255
storage
(
initial 64K
next 1M
minextents 1
maxextents unlimited
);
-- Create table
create table EMPLOYEE
(
empid VARCHAR2(128) not null,
empname VARCHAR2(128),
empsalary NUMBER,
depid VARCHAR2(128)
)
tablespace TEST_TABLESPACE
pctfree 10
initrans 1
maxtrans 255
storage
(
initial 64K
next 1M
minextents 1
maxextents unlimited
);
-- Add comments to the table
comment on table EMPLOYEE
is '员工表';
-- Add comments to the columns
comment on column EMPLOYEE.empid
is '员工ID';
comment on column EMPLOYEE.empname
is '员工名称';
comment on column EMPLOYEE.empsalary
is '员工工资';
comment on column EMPLOYEE.depid
is '所属部门主键ID';
-- Create/Recreate primary, unique and foreign key constraints
alter table EMPLOYEE
add constraint PK_ID primary key (EMPID)
using index
tablespace TEST_TABLESPACE
pctfree 10
initrans 2
maxtrans 255
storage
(
initial 64K
next 1M
minextents 1
maxextents unlimited
);
alter table EMPLOYEE
add constraint FK_DEP_ID foreign key (DEPID)
references DEPARTMENT (DEPID);
表创建完成后,我们插入一些测试数据:
insert into department (DEPID, DEPNAME)
values ('001', '研发部');
insert into department (DEPID, DEPNAME)
values ('002', '人力资源部');
insert into department (DEPID, DEPNAME)
values ('003', '测试部');
insert into department (DEPID, DEPNAME)
values ('004', '市场部');
insert into employee (EMPID, EMPNAME, EMPSALARY, DEPID)
values ('01', '张三', 1000, '001');
insert into employee (EMPID, EMPNAME, EMPSALARY, DEPID)
values ('02', '李四', 2000, '002');
insert into employee (EMPID, EMPNAME, EMPSALARY, DEPID)
values ('03', '王五', 3000, '003');
insert into employee (EMPID, EMPNAME, EMPSALARY, DEPID)
values ('04', '赵六', 4000, '001');
insert into employee (EMPID, EMPNAME, EMPSALARY, DEPID)
values ('05', '田七', 5000, '002');
commit;【b】案例一:查询存在员工的部门信息
--查询存在员工的部门信息
select dep.depid, dep.depname
from department dep
where exists (select * from employee emp where emp.depid = dep.depid)
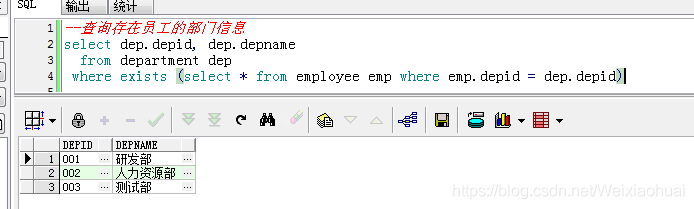
如图,我们过滤掉了市场部这个部门没有员工的数据。
以上sql使用in也可以达到相同的效果:
--查询存在员工的部门信息
select d.depid, d.depname
from department d
where d.depid in (select e.depid from employee e)
【c】案例二:查询部门平均工资不小于3000元的部门信息(未过滤没有员工的部门信息)
首先我们先查询每个部门的平均工资:
--查询每个部门的平均工资
select avg(empsalary) avgsal, e.depid, d.depname
from employee e
left join department d
on d.depid = e.depid
group by e.depid, d.depname;

需要查询平均工资不少于3000的,可以使用not exists来实现:
--查询部门平均工资不小于3000元的部门信息(未过滤没有员工的部门信息)
select *
from department de
where not exists (select em.depid
from employee em
where em.depid = de.depid
group by em.depid
having(avg(em.empsalary) < 3000))
可以看到,市场部这个部门并没有员工,但是查询结果也查询出来了。
not exists可以使用not in来达到同样的效果:
--相当于使用in:
select depa.depid, depa.depname
from department depa
where depa.depid not in
(select empl.depid
from employee empl
group by empl.depid
having(avg(empl.empsalary) < 3000)) 
如果需要过滤掉没有员工的部门,可以进行一下改造。
【d】案例三:查询部门平均工资不小于3000元的部门信息(过滤掉没有员工的部门信息)
-- 查询部门平均工资不小于3000元的部门信息(过滤掉没有员工的部门信息)
select *
from department de
where not exists (select em.depid
from employee em
where em.depid = de.depid
group by em.depid
having(avg(em.empsalary) < 3000))
and exists
(select * from employee empl where empl.depid = de.depid)在没有过滤没有员工的基础上加上exists(select * from employee empl where empl.depid = de.depid)就可以过滤了。

同样我们也可以用not in来实现:
--相当于使用in:
select depa.depid, depa.depname
from department depa
where depa.depid not in
(select empl.depid
from employee empl
group by empl.depid
having(avg(empl.empsalary) < 3000))
and depa.depid in (select emplo.depid from employee emplo)
三、exists与in效率比较
--语句一:使用exists实现
select dep.depid, dep.depname
from department dep
where exists (select * from employee emp where emp.depid = dep.depid)
--语句二:使用in实现
select d.depid, d.depname
from department d
where d.depid in (select e.depid from employee e)以上两个语句,语句二使用in的效率没有语句一使用exists的效率高。
原因分析:
【a】oracle在执行exists语句,执行的时候会先检查主查询语句,然后运行子查询知道找到匹配的第一项。
【b】oracle在执行in语句的时候,首先执行子查询,并将获取的结果存在一个有索引的临时表中,在执行子查询之前,主查询出于挂起状态,直到子查询执行完毕,存放在临时表中以后主查询才会执行,而且in查询不走索引。
【c】基于上面两点,exists是对主查询循环,所以exists适合主查询那张表数据量比较小,子查询对应表数据量大的场景;in是先执行子查询,所以in适合子查询数据量小、主查询对应表数据量大的场景。
四、总结
实际工作中,需要根据具体的需求来决定是使用exists还是in语句,本文是笔者对exists和in语句使用的一些总结,仅供大家学习参考,共同学习,共同进步!
























 1204
1204

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








