慕课选择题自己看一下。
“科技文献常识”部分考察形式为四选一选择题。
U1 Introduce of scientific literature
1.The classifications of scientific literature (科技文献)
(1)primary literature: papers that present novel scientific research, conference documents, patents, technical reports, standards(标准论文).
(2)secondary literature: review articles, books.
(3)tertiary literature: textbooks, encyclopedias, similar works intended for broad public consumption.
2.The categories of TSJ(Technical and scientific jargon, 技术和科学术语)
(1)General TSJ (much larger number)
The words that can be used in different fields with different meanings.
(2)Specific TSJ
The words that are usually restricted to given fields.
3.The purposes of using hedging language (模糊语)
出于严谨性考虑,学术写作中会使用模糊语来避免语气过于绝对。
(1)Minimize the possibility of another scholar opposing the claims.
(2)Enable the results to be reported more precisely.
(3)Enable a politeness strategy to be executed in case there may be flaw in the claims.
(4)Conform to an accepted practice in the field of academic writing.
U2 Journals
1.The purposes of a scientific journal (科技期刊)
(1)Give researchers a venue (会场) to impart their knowledge to one another.
(2)Make contributions to enriching the knowledge of all sciences.
2.The types of journal articles
(1)Original research articles (原创研究文章).
(2)Review articles (综述文章).
(3)Perspective, opinion or commentary articles (观点、意见或评论文章).
(4)Book reviews (书评).
3.The usages of journal metrics (度量标准)
(1)The evaluation of an academic journal’s impact and quality.
(2)To reflect the place of a journal within its field.
(3)To reflect the relative difficulty of an article published in that journal, and the prestige associated with it.
4.Some journal metrics (课本P13)
(1)IF/JIF (影响因子)
The (Journal) Impact Factor.
reflects the yearly average number of citations to recent articles published in that journal.
as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its fields.
(2)Eigenfactor (特征因子)
rate the importance of a scientific journal to the scientific community.
(3)h-index
measure the productivity and impact of an author
(4)Immediacy Index
the number of articles in a journal receive in a given year / the number of articles published.
indicates how quickly articles in a journal are cited.
(5)Total Cites
the total number of times that a journal has been cited by all journals in the database in the JCR(Journal Citation Reports) year.
(6)Cited Half-Life
to see if articles from a journal that were published a long time ago are still being cited.
U3 Monographs (专著)
1.The standards of scholarly monograph
(1)The author has an advanced degree (PhD, Ed.D) and/or is associated with an academic institution.
(2)The book is published by a university press, scholarly society, or other scholarly organizations.
(3)The book includes a bibliography at the end citing all of the sources that the author used in the research.
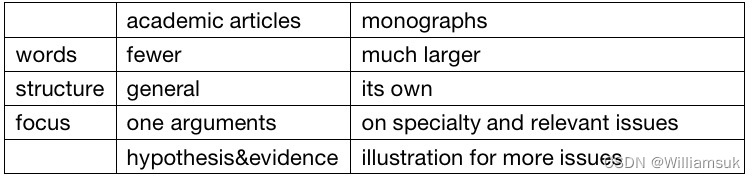
2.The differences between academic articles (学术论文) and monographs
(1)The words of monographs are much larger than academic articles.
(2)An academic article follows the general structure of a research article and focus on one arguments, while a monograph follows a structure of its own and focus on one specialty and giving thought to all relevant issues.
(3)An academic article propose a hypothesis and proves it with evidence, while a monograph conducts comprehensive and intensive illustration of more issues.
3.The features of scholarly monographs
(1)Academicality
(2)Creativity
(3)Authoritativeness
(4)Comprehensiveness
(5)Systematicness
(6)Beyond time and space
U4 Conference documents (会议文献)
1.The types of documents
(1)Documents distributed before a conference : announcements, calls for papers, instructions for authors, instructions for speakers, registration forms, invitations, preliminary printed proceedings, collections of abstracts.
(2)Documents distributed at a conference: daily schedules, conference proceedings such as conference paper abstracts, opening speeches, and closing speeches.
(3)Documents distributed after a conference: post-conference proceedings, special edition of conference documents, conference reports, transactions, and conference promotions.
2.The types of academic conferences
(1)Conference
(2)Forum
(3)Lecture
(4)Panel (专家咨询会)
(5)Seminar
(6)Symposium (专题研讨会)
(7)Workshop
U5 Graduation Papers
1.Differences between a graduation paper and a journal article. (P27)
graduation paper journal article
purpose graduate share
length much longer shorter
abstract longer, includes the structure shorter, omits the structure sometimes
Methods section explicit brief
reference more, earlier and classical research reported
details each some selective
evaluation supervisor and scholars editors
number of authors only one co-written
U6 Technical reports (技术报告)
1.Types of technical reports.
In terms of research progress:
(1)primary reports
(2)progressive reports
(3)interim reports
(4)final reports
In terms of the scope of the evaluation:
(1)top secret reports
(2)secret reports
(3)confidential reports
(4)restricted reports
(5)unclassified reports
(6)declassified reports
In terms of formality:
(1)informal reports
(2)semiformal reports
(3)formal reports
2.The series of technical reports in America
(1)AD reports
(2)PB reports
(3)NASA reports
(4)DOE reports
U7 Science news
1.Types of science news
(1)Science news stories
(2)Science newsletters
(3)Science feature stories
(4)Science news commentaries
U8 Patents (专利)
1.The duration of a patent
20 years.
2.The duration of the copyright
(1)author’s life plus 50 to 100 years
(2)the life of the last surviving joint creator plus another 70 years
(3)min{95 years from the year of first publication, 120 years from the year of creation}, works made for hire
U9 Product specifications (产品规格)
1.Features of product specifications
(1)Genuine
(2)Scientific
(3)Logical
(4)Practical
2.Types of product specifications
(1)industrial product specifications
(2)agricultural product specifications
(3)financial product specifications
(4)insurance product specifications
U10 Government publications (政府出版物)
1.American government publications
(1)GPO publications
(2)GPO monthly catalog
(3)NTIS publications
U11 Standards
1.Types of standards
In terms of applicable scope:
(1)international standards
(2)regional standards
(3)national standards
(4)professional standards
(5)institutional standards
In terms of content:
(1)Basic standards
(2)Manufacturing standards
(3)Standards of method
U12 Titles and author affiliation (标题和作者所属)
1.Types of titles
(1)Declarative titles: states the main findings or conclusions
(2)Descriptive titles: describe the subject
(3)Interrogative titles: a question
(4)Compound titles: consists of two parts
2.Author affiliation
The lead author is listed at the beginning, and the corresponding author is usually marked with a little star, such as Juan L. Acero*
different universities or institutions – corresponding makers of either letters or numbers.
U13 Abstract
1.The parts of abstract
(1)background
(2)problem
(3)methods
(4)results
(5)conclusion
2.Types of abstract
(1)Informative abstracts: a report sketching out the whole article.
(2)Indicative abstracts: help readers understand the general nature and scope.
(3)Structured abstracts: few paragraphs
(4)Graphical abstracts: pictorial and visual summary
U14 Introduction
1.The moves of introduction
(1)Establish a territory
(2)Reviewing previous related research
(3)Establish a niche
(4)Occupying the niche
U15 Methods
1.Methods Section includes:
(1)materials
(2)instruments
(3)subjects
(4)procedures
(5)data collection
(6)data analysis
2.Types of research
Based on purpose:
(1)basic research
(2)applied research
Based on methods:
(1)non-experimental research
(2)experimental research
(3)quasi-experimental research
Based on originality:
(1)primary research
(2)secondary research
3.Kinds of research require ethical approval
(1)research involving living human subjects
(2)research involving human remains, cadavers, tissues, biological fluids, embryos, etc.
(3)research that involves gathering information about human beings and organizations.
(4)research involving secondary use of data.
U16 Results
1.Features of results
(1)Be objective.
(2)Be logical.
(3)Be concise.
(4)Use non-verbal language.
(5)Use mixed tense (时态).
2.Moves of results
(1)Providing preparatory information.
(2)Describing the data in figures and tables.
(3)Reporting the results based on the data.
U17 Discussion
1.Features of discussion
(1)organized from the specific to the general.
(2)has the same point of view in the Introduction section.
(3)has opinions and comments.
2.Moves of discussion
(1)Reviewing the present study.
(2)Consolidating the results.
(3)Stating limitations and possible future research directions.
U18 Conclusion
1.Main information of Conclusion section
(1)restatement of the research question and thesis statement.
(2)summary of the main points in the articles.
(3)discussion of the significance of the research.
(4)presentation of the future of the subject.
2.Types of conclusion
(1)Thesis-oriented conclusion.
(2)Field-oriented conclusion.
U19 Acknowledgements (致谢)
1.Features of Acknowledgements
(1)Polite
(2)Brief
(3)Specific
U20 References
1.Types of reference
(1)In-text citations
(2)End references
2.Citation Styles
(1)APA style: 作者名后面跟时间,如Lumby, J(2001)
(2)MLA style: 作者名+页号,下划线标注引用
(3)IEEE styles: 数字被方括号[ ]包裹








 本文详细介绍了科技文献的不同类型,包括原始研究、综述文章和专著等,强调了学术期刊在知识传播中的作用以及度量标准如影响因子。此外,还探讨了学术论文和专著的区别,以及在学术写作中使用模糊语的目的。同时,涵盖了会议文献、毕业论文、技术报告、专利和政府出版物等多个方面。
本文详细介绍了科技文献的不同类型,包括原始研究、综述文章和专著等,强调了学术期刊在知识传播中的作用以及度量标准如影响因子。此外,还探讨了学术论文和专著的区别,以及在学术写作中使用模糊语的目的。同时,涵盖了会议文献、毕业论文、技术报告、专利和政府出版物等多个方面。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








