注解(未来的编程基于注解)
1.概述
概念:注解(也称为元数据):为我们在代码中添加信息提供了一种形式化的方法,使我们可以在稍后的某个时刻非常方便地使用这些数据。
注解在一定程度上是在把元数据与源代码文件结合在一起,而不是保存在外部文档中这一大催势之下所催生的。
注解的语法比较简单,除了@符号的使用之外,它基本与Java固有的语法一致。Java SE5内置了三种,定义在java.lang中的注解。
1.1 三种内置注解
1. @Override:表示当前的方法定义将覆盖超类中的方法。如果你不小心拼写错误,或者方法名对不上被覆盖的方法,编译器会发出错误的提示。
class Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭罗!");
}
}
class Dag extends Animal{
//@Override表示该方法是从父类中继承下来的,方法名必须与父类某方法相等
@Override
public void eat(){
System.out.println("狗吃饭");
}
}2.@Deprecated 如果程序员使用注解为它的元素,那么编译器会发出警告信息。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Animal ani = new Animal();
ani.eat();
}
}
class Animal{
//@Deprecated该方法表示为过时的方法,可以编译可以运行,但是有该方法出现的地方就会出现警告信息
@Deprecated
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭罗!");
}
}3.@SuppressWarnings 关闭不当的编译器警告信息。
2.自定义Annotation
2.1 概述
概念:定义Annotation类型时,也需要用到定义接口的interface关键字,不过需要在interface关键字的前面加一个“@”符号,即定义Annotation类型的关键字是@interface,这个关键字隐含的意思是继承自java.lang.annotation.Annotation接口。
语法:
public @interface MyAnnotation的名称{}2.2 标记注解(marker annotation):
没有元素的注解,如上MyAnnotation。
在注解中,一般都会包含一些元素以表示某些值。当分析处理注解时,程序或工具可以利用这些值。注解的元素看起来像接口的方法。唯一的区别是你可以为其指定默认值。
如下注解:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String value()default "123";
}这是一个用于类、接口、枚举,运行中加载到JVM里面有一成员,其有默认值为”123”。
参数说明:
1. 注解可用的类型有八种基本类型、String、Class、Annotation、枚举、数组。
2. Value,成员名称,如果在所定义的Annotation类型中只包含一个成员,通常将名称命名为value
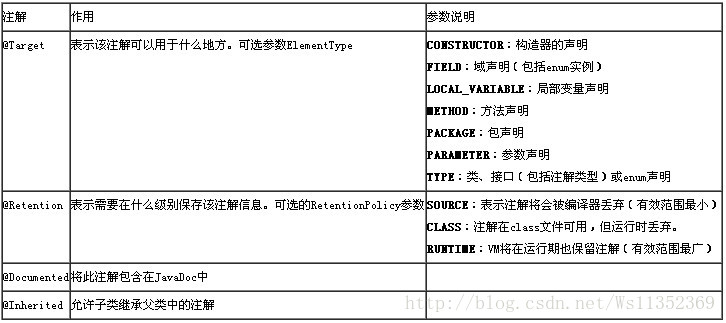
2.3 元注解(注解中的注解)
Java内置了有三种标准注解,以及四种均注解,元注解专职负责注解其他的注解。
代码实例:
定义一个用来注释构造方法的Annotation类型@Construction_Annotation,有效范围为在运行时加载到Annotation到JVM中;还有一个用来注释字段、方法和参数的的Annotation类型的@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation有效范围在运动时加载Annotion到JVM中。
@Construction_Annotation的代码
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//用于构造函数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
//在运行时加载到Annotatin到JVM中
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ConStructor_Annotation {
//定义一个有默认值的String型成员
String value() default "默认构造方法";
}@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation的代码
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//用于字段、方法和参数
@Target({ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER})
//在运行时加载Annotation到JVM中
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation {
//定义一个没有默认值的String型成员
String describe();
//定义一个有默认值的Class型成员
Class type() default void.class;
}Record的代码
public class Record {
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "编号", type = int.class)
private int id;
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "名字" , type = String.class)
private String name;
//因为其有默认值所以不需要填写任何东西
@ConStructor_Annotation
public Record(){}
public Record(
//class有默认值,故可填可不填
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "编号")
int id ,
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "名字")
String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//注释方法
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "获得编号",type = int.class)
public int getId() {
return id;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "设置编号")
public void setId(//注释方法参数
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "编号",type = int.class) int id)
{
this.id = id;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "得到名字")
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "设置名字")
public void setName(@Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation(describe = "名字", type = String.class) String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}如上可见,注解就是一种特别的注释,他会提醒用户需要做什么
3.访问Annotation信息
如果在定义Annotation类型时将@Retention设置为RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,那么在运行程序时通过反射就可以获取相关的Annotatin信息,如获取构造方法,字段和方法的Annotation信息。
3.1 访问Annotation的方法
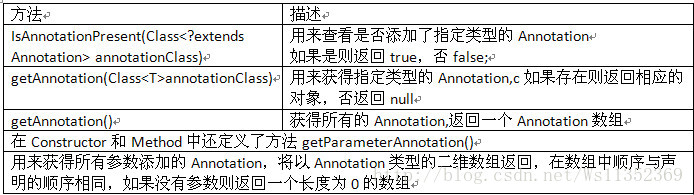
代码实例(访问上述例子的Annotation):
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Class classR = null;
Record re = new Record();
classR = re.getClass();
System.out.println("===================获得所有构造函数===================");
//获得所有构造函数
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = classR.getDeclaredConstructors();
//遍历构造函数
for (int i = 0; i < declaredConstructors.length; i++) {
Constructor constructor = declaredConstructors[i];
//查看是否具有指定类型的注解
if (constructor.isAnnotationPresent(Constructor_Annotation.class)) {
//获得指定类型的注解
Constructor_Annotation ca = (Constructor_Annotation) constructor
.getAnnotation(Constructor_Annotation.class);
// 获得注释的内容
System.out.println(ca.value());
}
//获得参数的注解
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = constructor
.getParameterAnnotations();
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations.length; j++) {
//获得指定参数注解的长度
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length;
//如果长度为0,则表示没有为该参数添加注解
if (length == 0) {
System.out.println("未添加Annotation参数");
} else {
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
//获得参数的注解
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation pa = (Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation) parameterAnnotations[j][k];
//获得参数的描述与类型
System.out.print(pa.describe() + " " + pa.type()
+ " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
System.out.println("====================获得所有字段的信息========================");
//获得所有字段
Field[]declaredFields = classR.getDeclaredFields();
//遍历字段
for(int i = 0 ; i < declaredFields.length ; i ++){
Field field = declaredFields[i];
//获得指定类型的注解
if(field.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class)){
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation fa = field.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class);
//获得参数的描述与类型
System.out.println(fa.describe() + " " + fa.type());
}
}
System.out.println("=====================获得访问方法的信息===============================");
//获得所有方法
Method [] methods = classR.getDeclaredMethods();
//遍历方法
for(int i = 0 ; i < methods.length ; i ++){
Method method = methods[i];
//查看是否具有指定类型的注解
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class)){
//获得指定类型的注解
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation ma = method.getAnnotation(Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation.class);
//获得方法的描述与返回值类型
System.out.println(ma.describe() + " " + ma.type() );
}
//获得方法的注解
Annotation [] []parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
for(int j = 0 ; j < parameterAnnotations.length ; j ++ ){
//获得指定注解的长度
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length;
//如果长度为0,则表示没有为该参数添加注解
if(length == 0){
System.out.println("未指定类型的注释");
}else{
for(int k = 0 ; k < length ; k ++){
//获得指定类型的注解
Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation pa = (Field_Method_Parameter_Annotation)parameterAnnotations[j][k];
//获得参数的描述与类型
System.out.print(pa.describe() + "\n " + pa.type());
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
输出:
===================获得所有构造函数===================
默认构造方法
有参构造函数
编号 int
名字 class java.lang.String
====================获得所有字段的信息========================
编号 int
名字 class java.lang.String
=====================获得访问方法的信息===============================
设置编号 void
编号
int
得到名字 class java.lang.String
获得编号 int
设置名字 void
名字
class java.lang.String----------- android培训、java培训、java学习型技术博客、期待与您交流! ------------






















 1946
1946

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








