前言
迭代器模式就是分离了集合对象的遍历行为,抽象出一个迭代器类来负责,这样既可以做到不暴露集合的内部结构,又可让外部代码透明地访问集合内部的数据。
迭代器模式在访问数组、集合、列表等数据时,尤其是数据库数据操作时,是非常普遍的应用,但由于它太普遍了,所以各种高级语言都对它进行了封装,所以反而给人感觉此模式本身不太常用了。
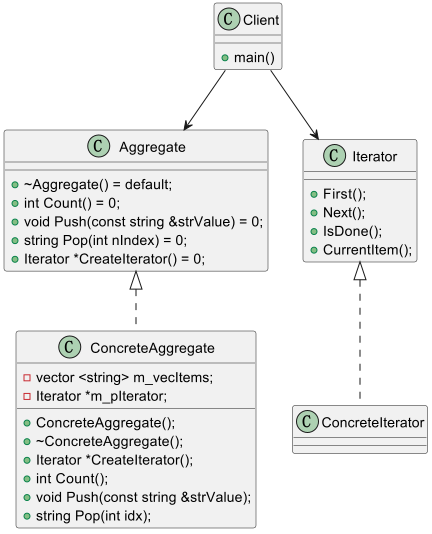
代码
Aggregate.h
#ifndef AGGREGATE_H
#define AGGREGATE_H
#include <string>
#include "Iterator.h"
using namespace std;
class Aggregate {
public:
virtual ~Aggregate() = default;
virtual int count() = 0;
virtual void push(const string &strValue) = 0;
virtual string pop(int idx) = 0;
virtual Iterator *createIterator() = 0;
};
#endif //AGGREGATE_H
ConcreteAggregate.h
#ifndef CONCRETEAGGREGATE_H
#define CONCRETEAGGREGATE_H
#include <vector>
#include "Aggregate.h"
#include "ConcreteIterator.h"
class ConcreteAggregate : public Aggregate {
public:
ConcreteAggregate();
~ConcreteAggregate() override;
Iterator *createIterator() override;
int count() override;
void push(const string &strValue) override;
string pop(int idx) override;
private:
vector <string> m_vecItems;
Iterator *m_pIterator;
};
#endif //CONCRETEAGGREGATE_H
ConcreteAggregate.cpp
#include "ConcreteAggregate.h"
ConcreteAggregate::ConcreteAggregate() : m_pIterator(nullptr) {
m_vecItems.clear();
}
ConcreteAggregate::~ConcreteAggregate() {
if (m_pIterator != nullptr) {
delete m_pIterator;
m_pIterator = nullptr;
}
}
int ConcreteAggregate::count() {
return m_vecItems.size();
}
void ConcreteAggregate::push(const string &strValue) {
m_vecItems.push_back(strValue);
}
string ConcreteAggregate::pop(int idx) {
string strRet;
if (idx < count()) {
strRet = m_vecItems[idx];
}
return strRet;
}
Iterator *ConcreteAggregate::createIterator() {
if(m_pIterator == nullptr)
{
m_pIterator = new ConcreteIterator(this);
}
return m_pIterator;
}
Iterator.h
#ifndef ITERATOR_H
#define ITERATOR_H
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Iterator {
public:
Iterator() = default;
virtual ~Iterator() = default;
virtual string first() = 0;
virtual string next() = 0;
virtual string getCurr() = 0;
virtual bool isEnd() = 0;
};
#endif //ITERATOR_H
ConcreteIterator.h
#ifndef CONCRETEITERATOR_H
#define CONCRETEITERATOR_H
#include "Iterator.h"
#include "Aggregate.h"
class ConcreteIterator : public Iterator {
public:
explicit ConcreteIterator(Aggregate *pAggregate);
string first() override;
string next() override;
string getCurr() override;
bool isEnd() override;
private:
Aggregate *m_Aggregate;
int m_nCurrent;
};
#endif //CONCRETEITERATOR_H
ConcreteIterator.cpp
#include "ConcreteIterator.h"
ConcreteIterator::ConcreteIterator(Aggregate *pAggregate) : m_nCurrent(0), Iterator() {
m_Aggregate = pAggregate;
}
string ConcreteIterator::first() {
return m_Aggregate->pop(0);
}
string ConcreteIterator::next() {
string strRet;
m_nCurrent++;
if (m_nCurrent < m_Aggregate->count()) {
strRet = m_Aggregate->pop(m_nCurrent);
}
return strRet;
}
string ConcreteIterator::getCurr() {
return m_Aggregate->pop(m_nCurrent);
}
bool ConcreteIterator::isEnd() {
return (m_nCurrent >= m_Aggregate->count());
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "iterator.h"
#include "ConcreteAggregate.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
auto *pName = new ConcreteAggregate();
pName->push("hello");
pName->push("word");
pName->push("cue");
Iterator *iter = pName->createIterator();
if (iter != nullptr) {
string strItem = iter->first();
while (!iter->isEnd()) {
cout << iter->getCurr() << " is ok" << endl;
iter->next();
}
}
return 0;
}





















 424
424











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








