第一题
请使用工厂模式、构造函数模式,原型模式和组合模式,分别创建对象student,其属性有id,name,class,age,hobbies,方法showHobbies()和addHobbies()。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
//工厂模式
function createStudent(id,name,classNo,age,hobbies){
let obj = new Object();
obj.id = id;
obj.name = name;
obj.class = classNo;
obj.age = age;
obj.hobbies = hobbies;
obj.showHobbies = function(){
console.log(this.hobbies);
};
obj.addHobbies = function(newHobbies){
this.hobbies = [...this.hobbies,...newHobbies];
};
return obj;
}
let student = createStudent("190350203","张三","1908013",21,["吃饭","睡觉"]);
console.log("姓名:" + student.name + " 学号:" + student.id);
student.showHobbies();
student.addHobbies(["编程","看电影"]);
student.showHobbies();
//构造函数模式
function Student2(id,name,classNo,age,hobbies){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.class = classNo;
this.age = age;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
this.showHobbies = function(){
console.log(this.hobbies);
};
this.addHobbies = function(newHobbies){
this.hobbies = [...this.hobbies,...newHobbies];
};
}
let student2 = new Student2("190350204","李四","1908011",20,["打游戏","听音乐"]);
console.log("姓名:" + student2.name + " 学号:" + student2.id);
student2.showHobbies();
student2.addHobbies(["跑步"]);
student2.showHobbies();
//原型模式
function Student3(){}
Student3.prototype = {
construct : Student3,
id : "190350205",
name : "王五",
class : "1908012",
hobbies : ["跳舞"],
showHobbies: function(){
console.log(this.hobbies);
},
addHobbies: function(newHobbies){
this.hobbies = [...this.hobbies,...newHobbies];
}
}
let student3 = new Student3();
console.log("姓名:" + student3.name + " 学号:" + student3.id);
student3.showHobbies();
student3.addHobbies(["跑步"]);
student3.showHobbies();
//组合模式
function Student4(id,name,classNo,age,hobbies){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.class = classNo;
this.age = age;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
Student4.prototype = {
construct : Student4,
showHobbies: function(){
console.log(this.hobbies);
},
addHobbies: function(newHobbies){
this.hobbies = [...this.hobbies,...newHobbies];
}
}
let student4 = new Student4("190350206","赵六","1908013",22,["唱歌"]);
console.log("姓名:" + student4.name + " 学号:" + student4.id);
student4.showHobbies();
student4.addHobbies(["跑步"]);
student4.showHobbies();
</script>
</body>
</html>第二题
应用构造函数创建一个自定义对象,通过自定义对象生成指定行数、列数、宽度和高度的表格。开发步骤提示:
(1)定义构造函数Table(),首先在函数中应用this关键字初始化对象中的属性,然后可以应用prototype属性为对象添加属性和方法。
(2)创建不同的对象实例并调用对象中方法生成表格。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box"></div>
<div id="box2"></div>
<script>
function Table(row, col, width, height) {
this.row = row; //行数
this.col = col; //列数
this.width = width; //宽
this.height = height; //高
}
Table.prototype.generate = function() {
let row = this.row;
let col = this.col;
let width = this.width;
let height = this.height;
let html = '<table border="1" cellspacing="0" width="' + width + '" height="' + height + '">'
for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {
html += '<tr>';
for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {
html += '<td></td>';
}
html += '</tr>';
}
html += "<br>"
return html;
}
let box = document.getElementById('box');
let table1 = new Table(4, 4, 200, 100);
box.innerHTML = table1.generate();
let box2 = document.getElementById('box2');
let table2 = new Table(6, 5, 200, 300);
box2.innerHTML = table2.generate();
</script>
</body>
</html>第三题
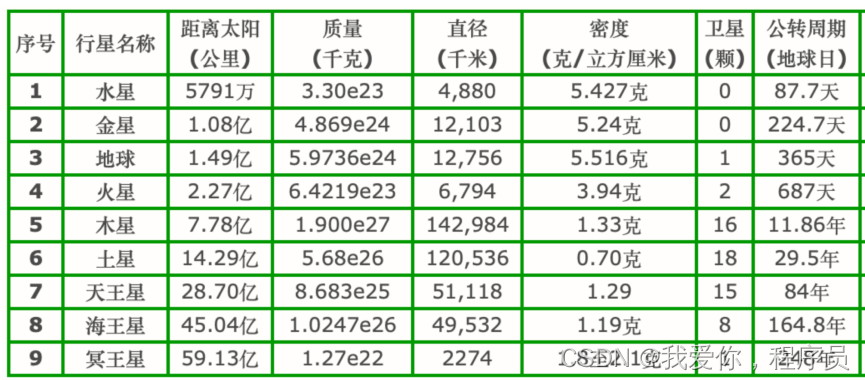
根据后续表格中九大行星的数据,为每个行星设计对应的属性,设计2个方法:
1.显示每个行星的数据
2.比较任意两个行星的任意两个属性之间的倍数。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function Planet(name, disToSun, quality, diameter, density, numOfSatellite, revolutionPeriod) {
this.name = name; //行星名称
this.disToSun = disToSun; //距离太阳(万公里)
this.quality = quality; //质量(千克)
this.diameter = diameter; //直径(千米)
this.density = density; //密度(克/立方厘米)
this.numOfSatellite = numOfSatellite; //卫星数量
this.revolutionPeriod = revolutionPeriod; //公转周期(地球日)
}
Planet.prototype.showData = function() {
console.log("行星名称:" + this.name + "\n距离太阳(公里):"+this.disToSun + "\n质量(千克):"+this.quality
+ "\n直径(千米):" + this.diameter + "\n密度(克/立方厘米):" + this.density + "\n卫星数量:"+this.numOfSatellite
+ "\n公转周期(地球日):"+this.revolutionPeriod+"\n");
}
//anotherPlanet表示要比较的另一个planet对象,attr表示要比较的属性
Planet.prototype.compare = function(anotherPlanet, attr) {
//先判断对象实例中有没有attr这个属性,name属性无法比较
if(this.hasOwnProperty(attr) && attr != "name") {
return this[attr] / anotherPlanet[attr];
}
return false;
}
let mercury = new Planet("水星",5791*1e4,3.30e23,4880,5.427,0,87.7);
let venus = new Planet("金星",1.08*1e8,4.869e24,12103,5.24,0,224.7);
mercury.showData(); //显示水星数据
venus.showData(); //显示金星数据
console.log("水星/金星的直径之比:" + mercury.compare(venus,"diameter").toFixed(2));
console.log("金星/水星的密度之比:" + venus.compare(mercury,"density").toFixed(2))
</script>
</body>
</html>






















 779
779











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










