问题及代码:
问题描述:定义顺序栈存储结构,实现其基本运算,并完成测试。
输入描述:无。
程序输出:测试内容。
sqstack.h 代码:
#define MaxSize 100
typedef char ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top; //栈指针
} SqStack; //顺序栈类型定义
void InitStack(SqStack *&s); //初始化栈
void DestroyStack(SqStack *&s); //销毁栈
bool StackEmpty(SqStack *s); //栈是否为空
int StackLength(SqStack *s); //返回栈中元素个数——栈长度
bool Push(SqStack *&s,ElemType e); //入栈
bool Pop(SqStack *&s,ElemType &e); //出栈
bool GetTop(SqStack *s,ElemType &e); //取栈顶数据元素
void DispStack(SqStack *s); //输出栈
sqstack.cpp代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
void InitStack(SqStack *&s)
{
s=(SqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SqStack));
s->top=-1;
}
void DestroyStack(SqStack *&s)
{
free(s);
}
int StackLength(SqStack *s) //返回栈中元素个数——栈长度
{
return(s->top+1);
}
bool StackEmpty(SqStack *s)
{
return(s->top==-1);
}
bool Push(SqStack *&s,ElemType e)
{
if (s->top==MaxSize-1) //栈满的情况,即栈上溢出
return false;
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=e;
return true;
}
bool Pop(SqStack *&s,ElemType &e)
{
if (s->top==-1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
bool GetTop(SqStack *s,ElemType &e)
{
if (s->top==-1) //栈为空的情况,即栈下溢出
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
return true;
}
void DispStack(SqStack *s) //输出栈
{
int i;
for (i=s->top;i>=0;i--)
printf("%c ",s->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
int main()
{
ElemType e;
SqStack *s;
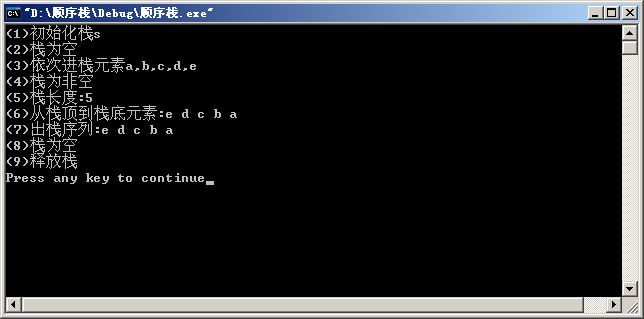
printf("(1)初始化栈s\n");
InitStack(s);
printf("(2)栈为%s\n",(StackEmpty(s)?"空":"非空"));
printf("(3)依次进栈元素a,b,c,d,e\n");
Push(s,'a');
Push(s,'b');
Push(s,'c');
Push(s,'d');
Push(s,'e');
printf("(4)栈为%s\n",(StackEmpty(s)?"空":"非空"));
printf("(5)栈长度:%d\n",StackLength(s));
printf("(6)从栈顶到栈底元素:");DispStack(s);
printf("(7)出栈序列:");
while (!StackEmpty(s))
{
Pop(s,e);
printf("%c ",e);
}
printf("\n");
printf("(8)栈为%s\n",(StackEmpty(s)?"空":"非空"));
printf("(9)释放栈\n");
DestroyStack(s);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
知识点总结:
栈的建立,释放,进栈出栈及栈的输出。
学习心得:
栈与线性表有着异曲同工之妙,无论是顺序表还是链表都跟栈有着密不可分的关系。所以学好线性表是基础。























 649
649

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










