转载用于收藏学习,尊重原创
原文链接
https://blog.csdn.net/July_whj/article/details/124087435
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「July_whj」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/July_whj/article/details/124087435
一、相关术语
1.1、Index/Key/DataPage
索引、键、数据页分别是什么?
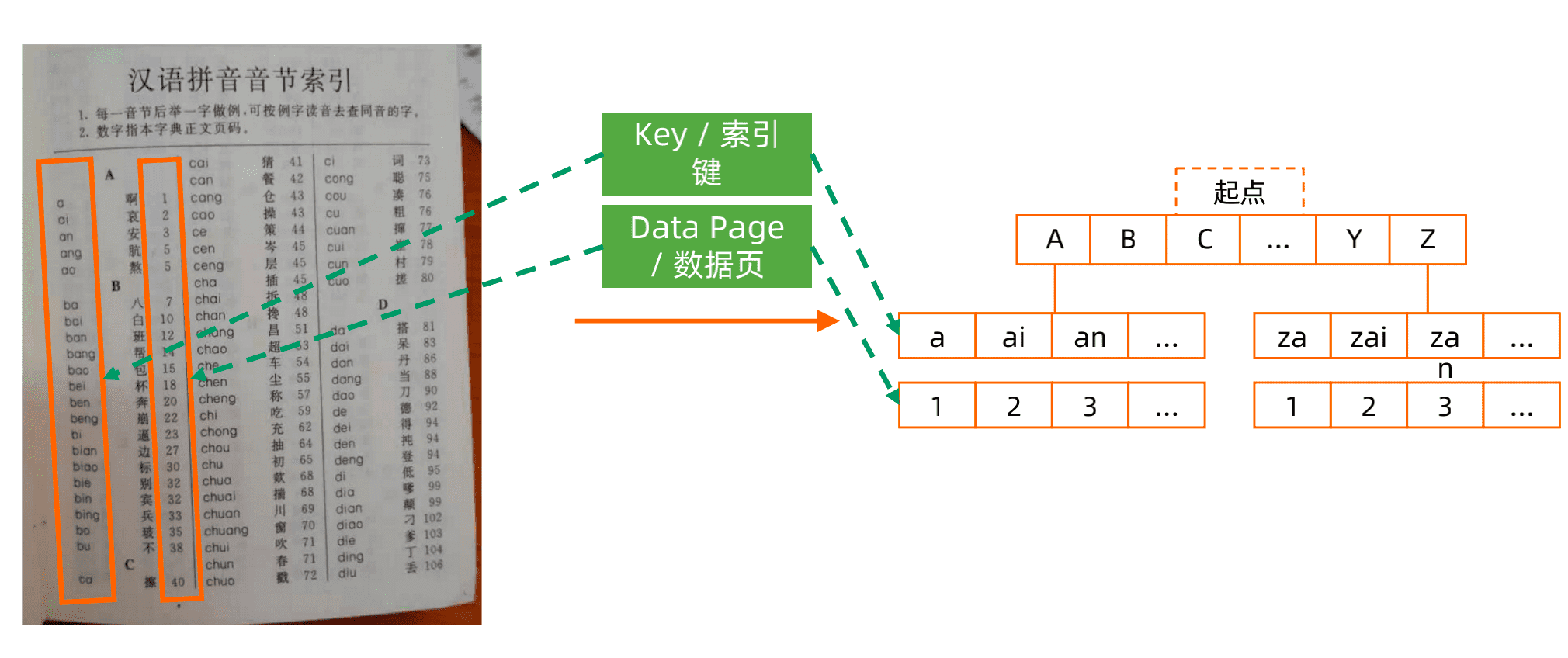
什么是索引
Covered Query,覆盖查询
如果所有需要的字段都在索引中,不需要额外的字段,就可以不再需要从数据页加载数据,这就是查询覆盖。
db.human.createIndex({firstName: 1, lastName: 1, gender: 1, age: 1})
IXSCAN/COLLSCAN
索引扫描/集合扫描(全表扫描)
Query Shape
查询形态,即查询条件:不同的查询条件对索引的影响是不同的,比如等值查询和范围查询。
Index Prefix
索引前缀:
db.human.createIndex({firstName: 1, lastName: 1, gender: 1, age: 1})
以上索引的全部前缀包括:
-
{firstName:
1}
-
{firstName:
1, lastName:
1}
-
{firstName:
1, lastName:
1, gender:
1}
所有索引前缀都可以被该索引覆盖,没有必要针对这些查询建立额外的索引;
Selectivity
过滤性:
在一个有10000条记录的集合中:
- 满足 gender= F 的记录有4000 条
- 满足 city=LA 的记录有 100 条
- 满足 ln=‘parker’ 的记录有 10 条
条件 ln 能过滤掉最多的数据,city 其次,gender 最弱。所以 ln 的过 滤性(selectivity)大于 city 大于 gender。
二、B树结构
索引背后是 B-树。要正确使用索引,必须先了解 B-树的工作原理。
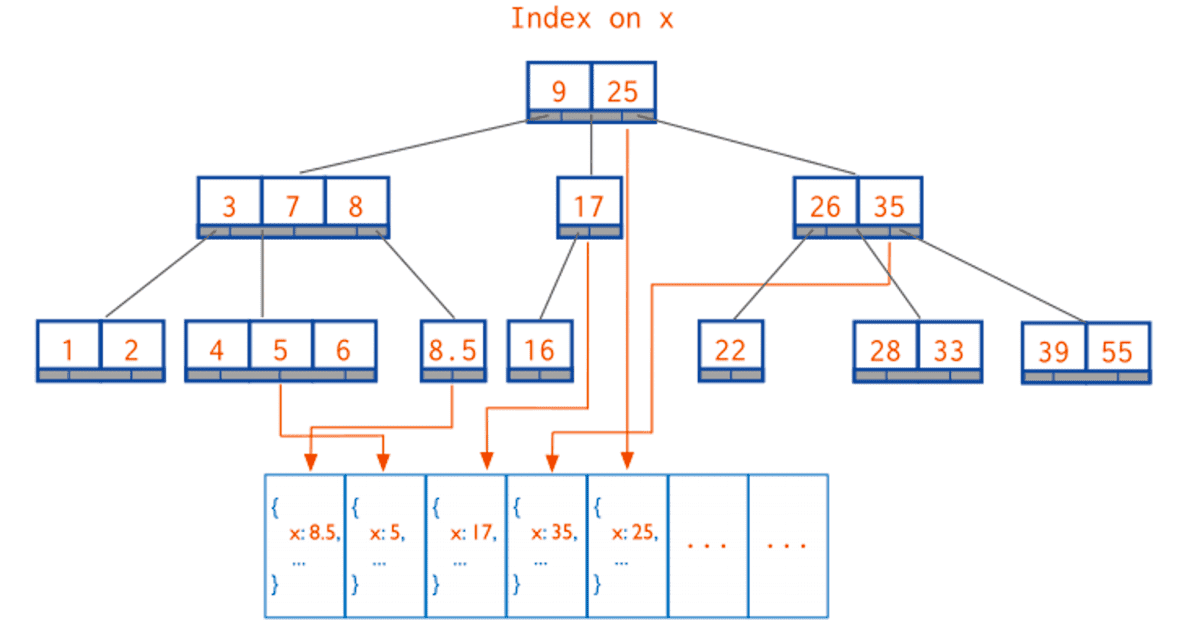
B- 树: 基于B树,但是子节点数量可以超过2个。
由于 B树/B-树的工作过程过于复杂,但本质上它是一个有序的数据结构。我们用数组来理解它。假设索引为{a: 1}(a 升序):
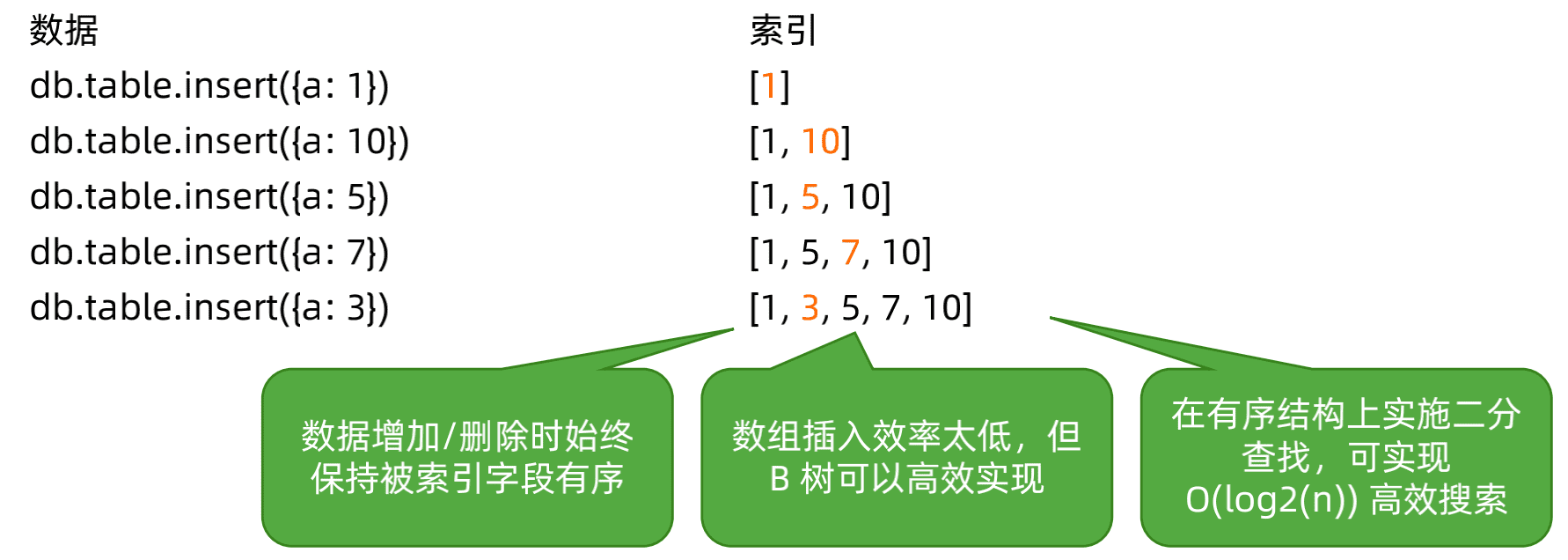
三、索引执行计划
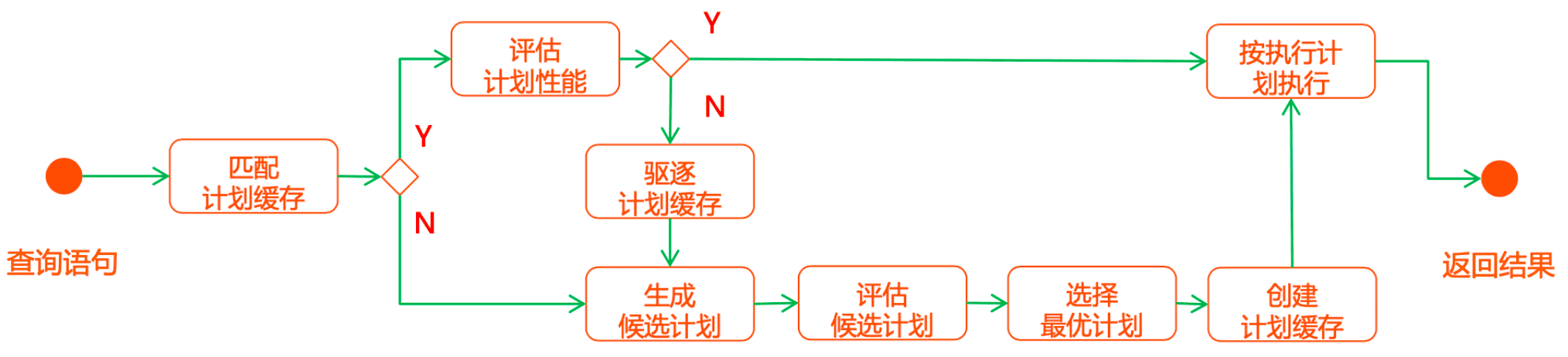
假设集合有两个索引
-
{city: 1}
-
{last_name:1 }
查询:
db.members.find({ city: “LA”, last_name: “parker”})
问题:用哪个索引?
两个线程同时尝试两个索引看哪个索引跑的比较快就选谁。
3.1、explain()
-
-- 写入10000条文档
-
for (var i=
1;i<
100000; i++)
-
db.col.
insert({name:i, age:i,
-
date:new Date() }
-
)
-
-- 查询
-
db.col.
find({name:
1111}).explain(
true)
查看执行计划:
-
"executionStats" :
-
{
"executionSuccess" :
true,
-
"nReturned" :
1,
//返回数据条数
-
"executionTimeMillis" :
58,
//执行时间
-
"totalKeysExamined" :
0,
//使用索引数
-
"totalDocsExamined" :
99999,
//扫描文档数
-
"executionStages" : {
-
"stage" :
"COLLSCAN",
-
"filter" : {
"name" : {
"$eq" :
1111}},
-
"nReturned" :
1,
-
"executionTimeMillisEstimate" :
53,
-
"works" :
100001,
-
"advanced" :
1,
-
"needTime" :
99999,
-
"needYield" :
0,
-
"saveState" :
783,
-
"restoreState" :
783,
-
"isEOF" :
1,
-
"invalidates" :
0,
-
"direction" :
"forward",
-
"docsExamined" :
99999
- 创建name索引
db.col.createIndex({name:1})
在查看执行计划:
-
"executionStats" : {
-
"executionSuccess" :
true,
-
"nReturned" :
1,
//返回数据条数
-
"executionTimeMillis" :
3,
//执行时间
-
"totalKeysExamined" :
1,
//使用索引数
-
"totalDocsExamined" :
1,
//扫描数据条数
-
"executionStages" : {
-
"stage" :
"FETCH",
-
"nReturned" :
1,
-
"executionTimeMillisEstimate" :
0,
-
"docsExamined" :
1,
"alreadyHasObj" :
0,
-
"inputStage" : {
-
"stage" :
"IXSCAN",
-
"nReturned" :
1,
-
"executionTimeMillisEstimate" :
0,
-
"works" :
2,
-
"advanced" :
1,
-
… }
我们可以看到,使用索引后,性能极大的提升。
四、MongoDB 索引类型
- 单键索引
- 组合索引
- 多值索引
- 地理位置索引
- 全文索引
- TTL索引
- 部分索引
- 哈希索引
4.1、组合索引 – Compound Index
db.members.find({ gender: “F”, age: {$gte: 18}}).sort(“join_date:1”)
-
{ gender:
1, age:
1, join_date:
1 }
-
{ gender:
1, join_date:
1, age:
1 }
-
{ join_date:
1, gender:
1, age:
1 }
-
{ join_date:
1, age:
1, gender:
1 }
-
{ age:
1, join_date:
1, gender:
1}
-
{ age:
1, gender:
1, join_date:
1}
-
这么多候选的,用哪一个?
组合索引的最佳方式:ESR原则
- 精确(Equal)匹配的字段放最前面
- 排序(Sort)条件放中间
- 范围(Range)匹配的字段放最后面
同样适用: ES, ER;
4.1.1、组合索引工作模式: 精确匹配
db.test.createIndex({a: 1, b: 1, c: 1})
我们查询:
-
db
.test
.find({
-
a:
2,
-
b:
2,
-
c:
1
-
})

4.1.2、组合索引工作模式: 范围查询
db.test.createIndex({a: 1, b: 1, c: 1})
我们查询:
-
db.test.find({
-
a:
2,
-
b: {
$gte:
2,
$lte:
3},
-
c:
1
-
})
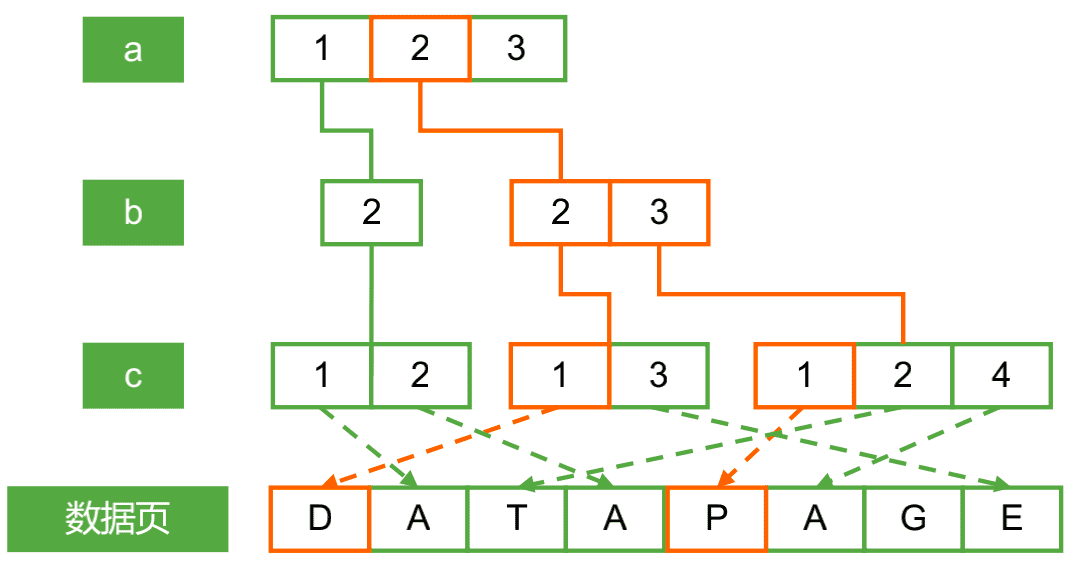
范围组合查询: 索引字段顺序的影响:
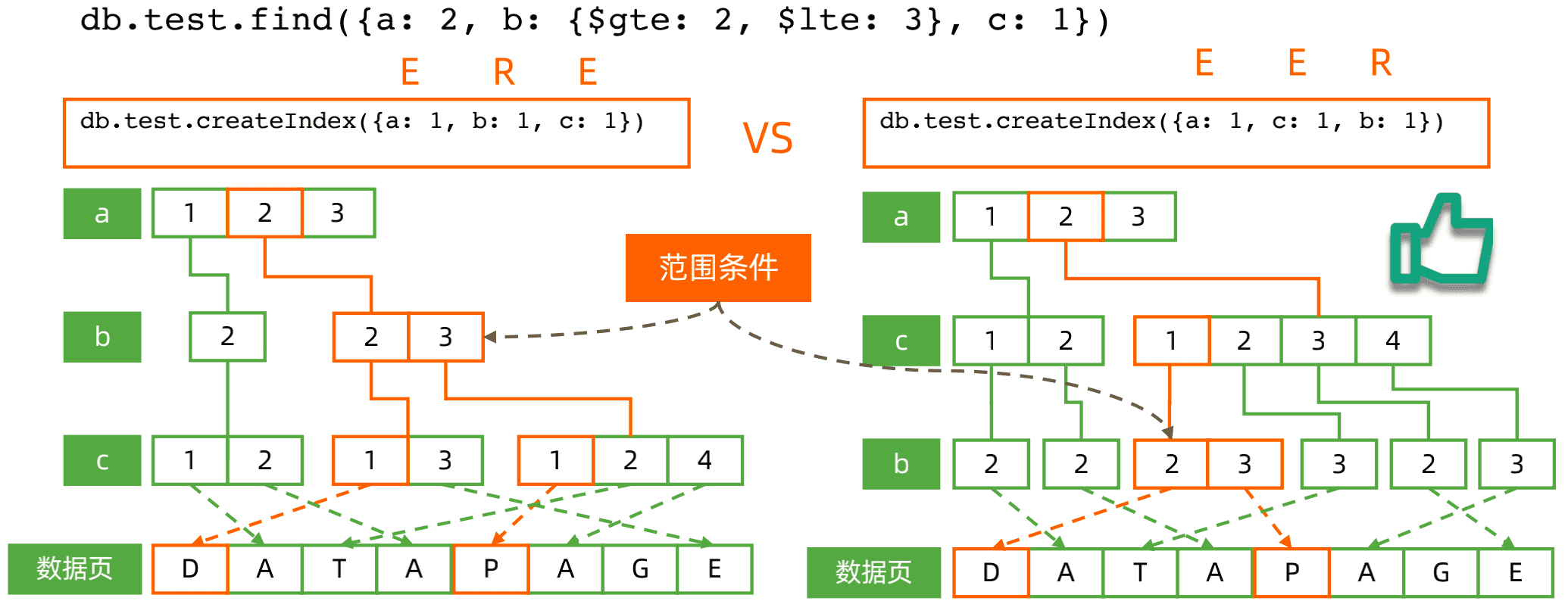
这里我们应该遵循ESR原则,先进行等值字段创建索引。在进行范围字段索引创建。
范围+排序组合查询: 索引字段顺序的影响
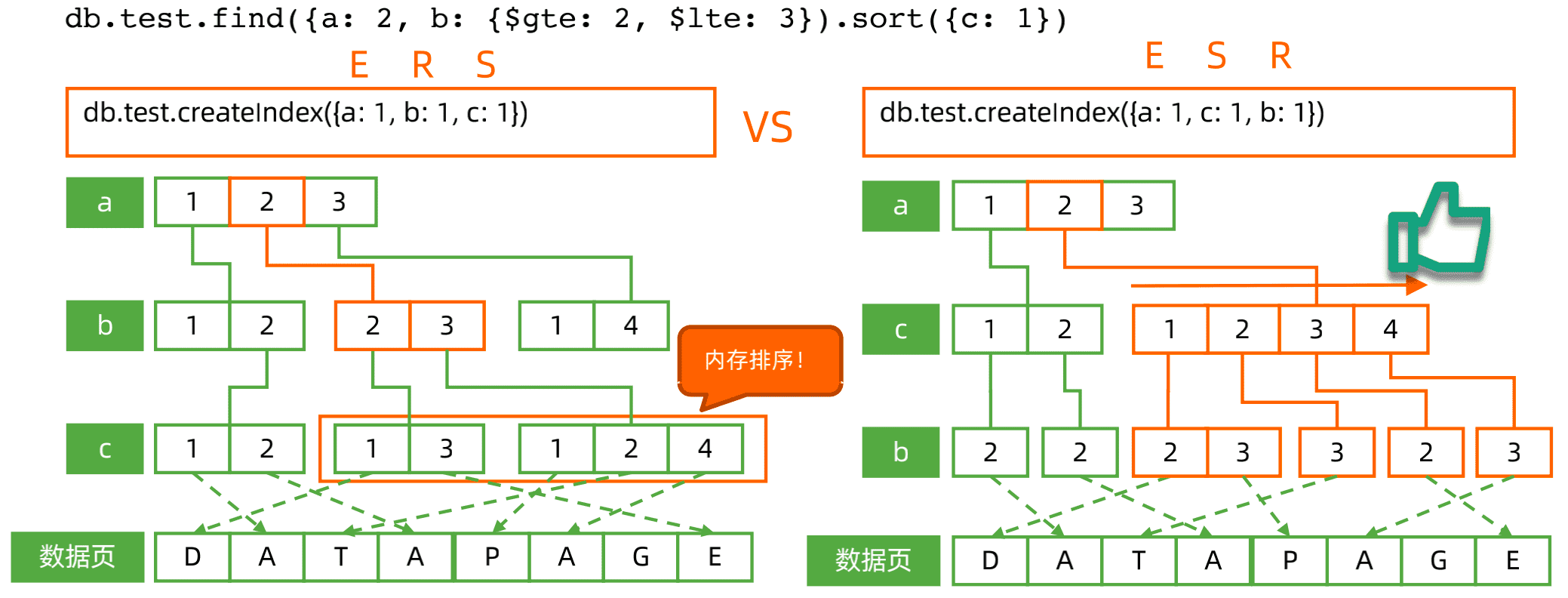
这里ERS方式使用了内存排序,而内存排序是非常消耗性能的,需要将数据从磁盘加载到内存中,在内存中进行排序操作。而将字段C放在第二位,B-树本身已经对C进行了排序,可以直接查询使用。
4.2、地理位置索引
创建索引:
-
db
.geo_col
.createIndex(
-
{ location: “
2d”} ,
-
{ min:-
20, max:
20 , bits:
10},
-
{collation:
-
{locale:
"simple"}
-
}
-
)
查询:
-
db.geo_col.find(
-
{ location :
-
{
$geoWithin :
-
{
$box : [ [
1,
1 ] , [
3,
3 ] ] } } }
-
)
4.3、全文索引
全文索引可以对某些字段创建索引,在查询时,可以自动检索增加字段的索引信息。
-
db.<collection_name>.insert(
-
{ _
id:
1, content: “This morning I had a cup of
-
coffee.”, about: “beverage”, keywords: [
-
“coffee” ] } ,
-
{ _
id:
2, content:
"Who doesn't like cake?",
-
about:
"food", keywords: [
"cake",
"food",
-
"dessert" ] },
-
{ _
id:
3, content:
"Why need coffee?", about:
-
”food
", keywords: [ ”drink",
"food" ] }
-
)
创建索引:
-
db.<collection_name>
.createIndex(
-
{‘
content’ :
"text" }
-
)
查询:
-
db.<collection_name>.find(
-
{
$text :
-
{
$search :
"cup coffee like" }
-
} )
-
db.<collection_name>.find(
-
{
$text :
-
{
$search :
"a cup of coffee" }
-
} )
我们可以直接使用"test"进行查询操作,如果在创建索引时,增加了content、about、keywords,则分别会在这三个字段中查询。
排序操作:
-
db.<collection_name>.find(
-
{
$text : {
$search : ”coffee
"} },
-
{ textScore: { $meta : "textScore
" }}
-
).sort({ textScore: { $meta: "textScore
" }} )
-
4.4、部分索引
创建部分索引:
-
db.
<collection_name>.createIndex(
-
{‘a’: 1 },
-
{ partialFilterExpression:
-
{a:
-
{$gte:5}
-
}
-
)
创建 部分索引可以针对部分数据进行索引创建,如a大于5的数据进行索引创建。
现实场景中:如统计今年订单量,那么去年订单就可以不创建索引,可以节省深大的存储空间。
4.5、其他索引技巧
- 后台创建索引
- db.member.createIndex( { city: 1}, {background: true} )
使用background:true进行后台索引创建,创建索引是比较耗时操作。
- 对BI / 报表专用节点单独创建索引
- 该从节点priority设为0
- 关闭该从节点
- 以单机模式启动
- 添加索引(分析用)
- 关闭该从节点,以副本集模式启动





















 991
991











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








