Android通知系统源码解析
1. 概述
Android 通知系统是应用与系统UI交互的重要系统,方便应用告知用户有新的通知或正在运行的后台程序,用户可通过通知面板直接或间接与应用交互,并可以随时跳转。
本文基于Android P的代码,只讲述发送通知和SystemUI注册流程,与取消通知流程类似不再赘述,可自行查看源码。
2. 流程图
2.1. 发送通知流程图
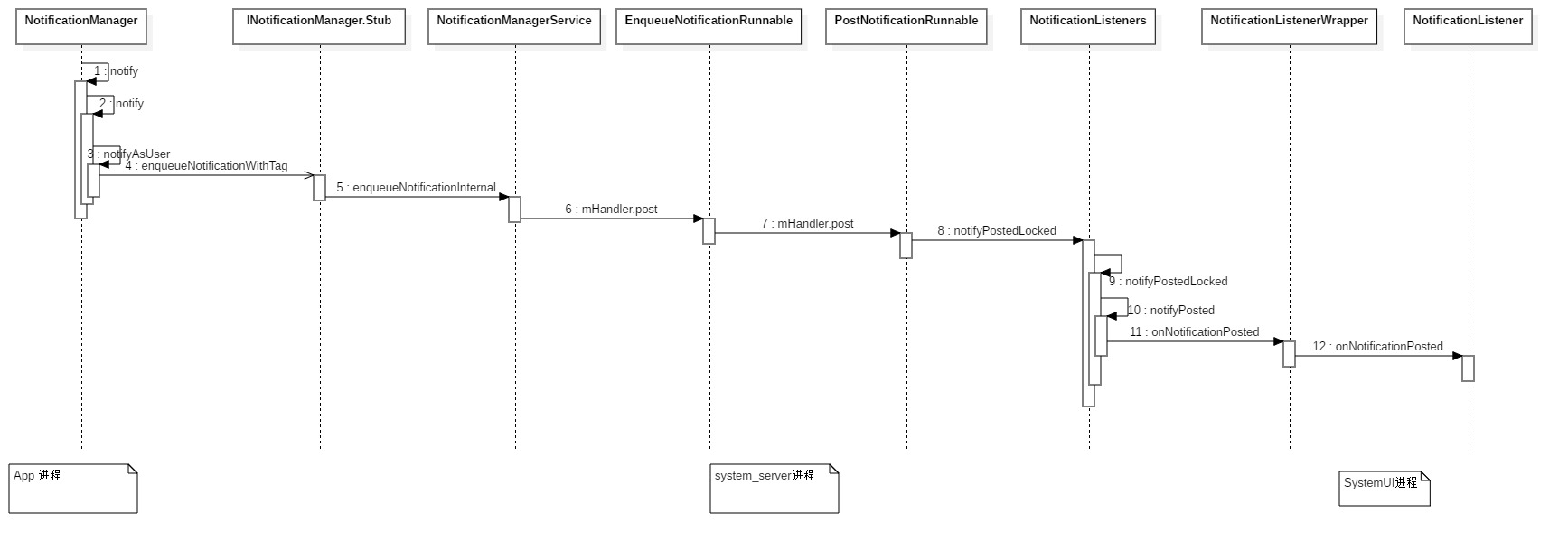
3. 源码解析
整个通知系统主要涉及到三个进程,分别是:
- APP进程:负责更新、创建、发送或取消通知;
- SystemServer进程:负责管理(添加、取消、控制等)通知,类似通知的管理中心;
- SystemUI进程:负责显示通知,并保持与用户的交互;
3.1. 使用通知–APP进程
3.1.1. 创建通知:
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(this, MainActivity.class);
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NO_USER_ACTION);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(MainActivity.this,
0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_CANCEL_CURRENT);
Notification.Builder builder = new Notification.Builder(MainActivity.this, channelId)
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setContentTitle("Test Title")
.setContentText("Test Content")
.setTicker("Test Ticker")
.setAutoCancel(true)
.setContentIntent(pendingIntent)
.setVisibility(Notification.VISIBILITY_PUBLIC);
Notification notification = builder.build();
3.1.2. 发送(更新)通知:
NotificationManager nm = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
nm.notify(0, notification);
3.1.3. 取消通知:
NotificationManager nm = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
nm.cancel(0);
// 或取消全部通知
// nm.cancelAll();
3.1.4. 创建通知源码解析:
-
构建一个Notification.Builder 对象,然后初始化Notification部分字段。典型的建造者模式,将构建复杂对象的操作分解成一步步简单的操作。
Notification.Builder
public Builder(Context context, String channelId) { this(context, (Notification) null); mN.mChannelId = channelId; } public Builder(Context context, Notification toAdopt) { .... if (toAdopt == null) { mN = new Notification(); if (context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.N) { mN.extras.putBoolean(EXTRA_SHOW_WHEN, true); } mN.priority = PRIORITY_DEFAULT; mN.visibility = VISIBILITY_PRIVATE; } ... } -
通过Notification.Builder 建造并封装好Notification对象,然后返回。发现Android 5.0 之后,构建Notification的时候,不初始化和携带contentView、bigContentView等RemoteView(处理应用自定义RemoteView);
保留问题1: 为什么呢?什么时候去加载RemoteView?
在下面SystemUI侧的源码分析中会讲到这点。原因我认为是,Notification需要跨进程被传输,携带过多数据会降低性能。Notification.java
public Notification build() { // first, add any extras from the calling code if (mUserExtras != null) { mN.extras = getAllExtras(); } mN.creationTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); // lazy stuff from mContext; see comment in Builder(Context, Notification) Notification.addFieldsFromContext(mContext, mN); buildUnstyled(); // 初始化mStyle内容,在这里可以发现,可以通过setStyle()接口为Notification设置不同的style,比如我们最常见的BigPictureStyle,以及播放器MediaStyle等等,可自行去查询相关接口 if (mStyle != null) { mStyle.reduceImageSizes(mContext); mStyle.purgeResources(); mStyle.validate(mContext); mStyle.buildStyled(mN); } mN.reduceImageSizes(mContext); // Android 5.0 之后,构建Notification的时候,不初始化和携带contentView、bigContentView等RemoteView if (mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.N && (useExistingRemoteView())) { if (mN.contentView == null) { mN.contentView = createContentView(); mN.extras.putInt(EXTRA_REBUILD_CONTENT_VIEW_ACTION_COUNT, mN.contentView.getSequenceNumber()); } if (mN.bigContentView == null) { mN.bigContentView = createBigContentView(); if (mN.bigContentView != null) { mN.extras.putInt(EXTRA_REBUILD_BIG_CONTENT_VIEW_ACTION_COUNT,mN.bigContentView.getSequenceNumber()); } } if (mN.headsUpContentView == null) { mN.headsUpContentView = createHeadsUpContentView(); if (mN.headsUpContentView != null) { mN.extras.putInt(EXTRA_REBUILD_HEADS_UP_CONTENT_VIEW_ACTION_COUNT,mN.headsUpContentView.getSequenceNumber()); } } } if ((mN.defaults & DEFAULT_LIGHTS) != 0) { mN.flags |= FLAG_SHOW_LIGHTS; } mN.allPendingIntents = null; return mN; }
3.2. 管理通知–SystemServer进程
3.2.1. 发送通知:
-
应用调用Notification.notify()接口发送通知,最终会进入system_server进程,调用NotificationManagerService的enqueueNotificationWithTag()。
NotificationManager.java
public void notify(int id, Notification notification){ notify(null, id, notification); } public void notify(String tag, int id, Notification notification){ notifyAsUser(tag, id, notification, mContext.getUser()); } /** * @hide */ public void notifyAsUser(String tag, int id, Notification notification, UserHandle user){ INotificationManager service = getService(); String pkg = mContext.getPackageName(); // Fix the notification as best we can. Notification.addFieldsFromContext(mContext, notification); ... fixLegacySmallIcon(notification, pkg); // Android 5.0之后必须要设置small icon 否则抛异常 if (mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion > Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP_MR1) { if (notification.getSmallIcon() == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid notification (no valid small icon): "+ notification); } } if (localLOGV) Log.v(TAG, pkg + ": notify(" + id + ", " + notification + ")"); notification.reduceImageSizes(mContext); ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE); boolean isLowRam = am.isLowRamDevice(); final Notification copy = Builder.maybeCloneStrippedForDelivery(notification, isLowRam, mContext); try { service.enqueueNotificationWithTag(pkg, mContext.getOpPackageName(), tag, id, copy, user.getIdentifier()); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } }
3.2.2. Service处理和推送通知:
-
最终通过mHandler执行EnqueueNotificationRunnable。
NotificationManagerService.java
@Override public void enqueueNotificationWithTag(String pkg, String opPkg, String tag, int id, Notification notification, int userId) throws RemoteException { enqueueNotificationInternal(pkg, opPkg, Binder.getCallingUid(), Binder.getCallingPid(), tag, id, notification, userId); } void enqueueNotificationInternal(final String pkg, final String opPkg, final int callingUid, final int callingPid, final String tag, final int id, final Notification notification, int incomingUserId) { ... // 检查发送通知的App是不是同一个App或系统App checkCallerIsSystemOrSameApp(pkg); // The system can post notifications for any package, let us resolve that. final int notificationUid = resolveNotificationUid(opPkg, callingUid, userId); ..... // setup local book-keeping String channelId = notification.getChannelId(); ... // 在Android 9.0上如果没有创建channel,则无法发送通知 final NotificationChannel channel = mRankingHelper.getNotificationChannel(pkg, notificationUid, channelId, false /* includeDeleted */); if (channel == null) { final String noChannelStr = "No Channel found for " + "pkg=" + pkg + ", channelId=" + channelId + ", id=" + id + ", tag=" + tag + ", opPkg=" + opPkg + ", callingUid=" + callingUid + ", userId=" + userId + ", incomingUserId=" + incomingUserId + ", notificationUid=" + notificationUid + ", notification=" + notification; Log.e(TAG, noChannelStr); boolean appNotificationsOff = mRankingHelper.getImportance(pkg, notificationUid) == NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_NONE; if (!appNotificationsOff) { doChannelWarningToast("Developer warning for package \"" + pkg + "\"\n" + "Failed to post notification on channel \"" + channelId + "\"\n" + "See log for more details"); } return; } // 将通知信息封装到StatusBarNotification对象 final StatusBarNotification n = new StatusBarNotification( pkg, opPkg, id, tag, notificationUid, callingPid, notification, user, null, System.currentTimeMillis()); // 然后再次创建NotificationRecord对象,该对象仅仅在system_server进程中流通 final NotificationRecord r = new NotificationRecord(getContext(), n, channel); r.setIsAppImportanceLocked(mRankingHelper.getIsAppImportanceLocked(pkg, callingUid)); ... // 通知发送速率的检查、黑名单的检查、通知上限的检查,每个应用当前的通知数量最多为50个 if (!checkDisqualifyingFeatures(userId, notificationUid, id, tag, r, r.sbn.getOverrideGroupKey() != null)) { return; } ... mHandler.post(new EnqueueNotificationRunnable(userId, r)); } -
EnqueueNotificationRunnable最终又通过Handler 执行 PostNotificationRunnable进行最后的推送通知。
NotificationManagerService.EnqueueNotificationRunnable
protected class EnqueueNotificationRunnable implements Runnable { ... @Override public void run() { synchronized (mNotificationLock) { mEnqueuedNotifications.add(r); scheduleTimeoutLocked(r); final StatusBarNotification n = r.sbn; if (DBG) Slog.d(TAG, "EnqueueNotificationRunnable.run for: " + n.getKey()); // 获取旧的NotificationRecord NotificationRecord old = mNotificationsByKey.get(n.getKey()); if (old != null) { // Retain ranking information from previous record r.copyRankingInformation(old); } final int callingUid = n.getUid(); final int callingPid = n.getInitialPid(); final Notification notification = n.getNotification(); final String pkg = n.getPackageName(); final int id = n.getId(); final String tag = n.getTag(); ..... // This conditional is a dirty hack to limit the logging done on // behalf of the download manager without affecting other apps. if (!pkg.equals("com.android.providers.downloads") || Log.isLoggable("DownloadManager", Log.VERBOSE)) { int enqueueStatus = EVENTLOG_ENQUEUE_STATUS_NEW; if (old != null) { enqueueStatus = EVENTLOG_ENQUEUE_STATUS_UPDATE; } // 打印Event Log,一般在进行通知的问题分析过程中,可通过该LOG查看当前通知的信息,判断当前通知是否发送成功; EventLogTags.writeNotificationEnqueue(callingUid, callingPid, pkg, id, tag, userId, notification.toString(), enqueueStatus); } // 更新NotificationRecord内容,RankingHelper管理了通知的开关、channel维护,比如横幅通知是否开启,在此处更新; mRankingHelper.extractSignals(r); // tell the assistant service about the notification if (mAssistants.isEnabled()) { mAssistants.onNotificationEnqueued(r); mHandler.postDelayed(new PostNotificationRunnable(r.getKey()), DELAY_FOR_ASSISTANT_TIME); } else { // Post 通知出去 mHandler.post(new PostNotificationRunnable(r.getKey())); } } } } -
推送通知最后又交由NotificationListeners mListeners处理,通过类名可以判断出NotificationListeners应该维护了通知的监听者,那么我们可以猜测SystemUI的注册类应该有该Listerners维护。
NotificationManagerService.PostNotificationRunnable
protected class PostNotificationRunnable implements Runnable { .... @Override public void run() { synchronized (mNotificationLock) { try { NotificationRecord r = null; int N = mEnqueuedNotifications.size(); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { final NotificationRecord enqueued = mEnqueuedNotifications.get(i); if (Objects.equals(key, enqueued.getKey())) { r = enqueued; break; } } .... NotificationRecord old = mNotificationsByKey.get(key); final StatusBarNotification n = r.sbn; final Notification notification = n.getNotification(); // 通知列表mNotificationList查看是否存在该通知 int index = indexOfNotificationLocked(n.getKey()); if (index < 0) { mNotificationList.add(r); mUsageStats.registerPostedByApp(r); r.setInterruptive(isVisuallyInterruptive(null, r)); } else { old = mNotificationList.get(index); mNotificationList.set(index, r); mUsageStats.registerUpdatedByApp(r, old); // Make sure we don't lose the foreground service state. notification.flags |= old.getNotification().flags & FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE; r.isUpdate = true; r.setTextChanged(isVisuallyInterruptive(old, r)); } // 更新通知列表 mNotificationsByKey.put(n.getKey(), r); // 再一次确认前台通知的标签没有被清除掉 // Ensure if this is a foreground service that the proper additional // flags are set. if ((notification.flags & FLAG_FOREGROUND_SERVICE) != 0) { notification.flags |= Notification.FLAG_ONGOING_EVENT | Notification.FLAG_NO_CLEAR; } applyZenModeLocked(r); // 对通知列表进行排序 mRankingHelper.sort(mNotificationList); if (notification.getSmallIcon() != null) { StatusBarNotification oldSbn = (old != null) ? old.sbn : null; // 关键步骤:将通知推送出去,让NotificationListeners:mListeners处理 mListeners.notifyPostedLocked(r, old); if (oldSbn == null || !Objects.equals(oldSbn.getGroup(), n.getGroup())) { mHandler.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { mGroupHelper.onNotificationPosted( n, hasAutoGroupSummaryLocked(n)); } }); } } else { ........ } if (!r.isHidden()) { // 处理该通知,主要是是否发声,震动,Led灯 buzzBeepBlinkLocked(r); } maybeRecordInterruptionLocked(r); } finally { int N = mEnqueuedNotifications.size(); for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { final NotificationRecord enqueued = mEnqueuedNotifications.get(i); if (Objects.equals(key, enqueued.getKey())) { mEnqueuedNotifications.remove(i); break; } } } } } } -
NotificationListeners 的notifyPosted中将通知推送至SystemUI中显示,在该方法中listener数据类型是NotificationListenerWrapper的代理对象,NotificationListenerWrapper在SystemUI进程,在此处listener是client, NotificationListenerWrapper是server。
保留问题2: listener是什么时候成为SystemUI进程处理通知的代理类?NotificationManagerService.NotificationListeners
public class NotificationListeners extends ManagedServices { public void notifyPostedLocked(NotificationRecord r, NotificationRecord old) { notifyPostedLocked(r, old, true); } private void notifyPostedLocked(NotificationRecord r, NotificationRecord old, boolean notifyAllListeners) { // Lazily initialized snapshots of the notification. StatusBarNotification sbn = r.sbn; StatusBarNotification oldSbn = (old != null) ? old.sbn : null; TrimCache trimCache = new TrimCache(sbn); // 遍历所有ManagedServiceInfo for (final ManagedServiceInfo info : getServices()) { .... // 如果该通知变得不可见,则移除老的通知 // This notification became invisible -> remove the old one. if (oldSbnVisible && !sbnVisible) { final StatusBarNotification oldSbnLightClone = oldSbn.cloneLight(); mHandler.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { notifyRemoved(info, oldSbnLightClone, update, null, REASON_USER_STOPPED); } }); continue; } // 推送通知 mHandler.post(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { notifyPosted(info, sbnToPost, update); } }); } } private void notifyPosted(final ManagedServiceInfo info, final StatusBarNotification sbn, NotificationRankingUpdate rankingUpdate) { // listener数据类型是NotificationListenerWrapper的代理对象,NotificationListenerWrapper在SystemUI进程,在此处listener是client, NotificationListenerWrapper是server final INotificationListener listener = (INotificationListener) info.service; StatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder = new StatusBarNotificationHolder(sbn); try { // 跨进程调用,进入SystemUI进程 listener.onNotificationPosted(sbnHolder, rankingUpdate); } catch (RemoteException ex) { Log.e(TAG, "unable to notify listener (posted): " + listener, ex); } } }
3.3. 展示通知–SystemUI进程
首先我们来解决上面留下的保留问题2,SystemUI是怎么接收和处理通知的。
3.3.1. 注册监听
-
SystemUI进程在起来的时候,会执行StatusBar.start()方法,start()方法里面会执行mNotificationListener.setUpWithPresenter()在注册监听,其中mNotificationListener是NotificationListener类型,然后我们来看看NotificationListener类。
StatusBar.java
@Override public void start() { // Set up the initial notification state. mNotificationListener.setUpWithPresenter(this, mEntryManager); } -
NotificationListener类继承于NotificationListenerWithPlugins,而NotificationListenerWithPlugins又继承于NotificationListenerService,同时也看到非常熟悉的方法,比如onNotificationPosted 等等。
注册最终会调到NotificationListenerService.registerAsSystemService()方法;NotificationListener.java
public class NotificationListener extends NotificationListenerWithPlugins { private static final String TAG = "NotificationListener"; // Dependencies: private final NotificationRemoteInputManager mRemoteInputManager = Dependency.get(NotificationRemoteInputManager.class); private final Context mContext; protected NotificationPresenter mPresenter; protected NotificationEntryManager mEntryManager; public NotificationListener(Context context) { mContext = context; } @Override public void onListenerConnected() { if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onListenerConnected"); onPluginConnected(); final StatusBarNotification[] notifications = getActiveNotifications(); if (notifications == null) { Log.w(TAG, "onListenerConnected unable to get active notifications."); return; } final RankingMap currentRanking = getCurrentRanking(); mPresenter.getHandler().post(() -> { for (StatusBarNotification sbn : notifications) { mEntryManager.addNotification(sbn, currentRanking); } }); } // 接收通知,然后交由mEntryManager进行处理 @Override public void onNotificationPosted(final StatusBarNotification sbn, final RankingMap rankingMap) { if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onNotificationPosted: " + sbn); if (sbn != null && !onPluginNotificationPosted(sbn, rankingMap)) { mPresenter.getHandler().post(() -> { processForRemoteInput(sbn.getNotification(), mContext); String key = sbn.getKey(); mEntryManager.removeKeyKeptForRemoteInput(key); boolean isUpdate = mEntryManager.getNotificationData().get(key) != null; // In case we don't allow child notifications, we ignore children of // notifications that have a summary, since` we're not going to show them // anyway. This is true also when the summary is canceled, // because children are automatically canceled by NoMan in that case. if (!ENABLE_CHILD_NOTIFICATIONS && mPresenter.getGroupManager().isChildInGroupWithSummary(sbn)) { if (DEBUG) { Log.d(TAG, "Ignoring group child due to existing summary: " + sbn); } // Remove existing notification to avoid stale data. if (isUpdate) { mEntryManager.removeNotification(key, rankingMap); } else { mEntryManager.getNotificationData() .updateRanking(rankingMap); } return; } if (isUpdate) { mEntryManager.updateNotification(sbn, rankingMap); } else { mEntryManager.addNotification(sbn, rankingMap); } }); } } // 通知移除的回调,同样交由mEntryManager进行处理 @Override public void onNotificationRemoved(StatusBarNotification sbn, final RankingMap rankingMap) { if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onNotificationRemoved: " + sbn); if (sbn != null && !onPluginNotificationRemoved(sbn, rankingMap)) { final String key = sbn.getKey(); mPresenter.getHandler().post(() -> { mEntryManager.removeNotification(key, rankingMap); }); } } @Override public void onNotificationRankingUpdate(final RankingMap rankingMap) { if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onRankingUpdate"); if (rankingMap != null) { RankingMap r = onPluginRankingUpdate(rankingMap); mPresenter.getHandler().post(() -> { mEntryManager.updateNotificationRanking(r); }); } } // 注册回调 public void setUpWithPresenter(NotificationPresenter presenter, NotificationEntryManager entryManager) { mPresenter = presenter; mEntryManager = entryManager; try { registerAsSystemService(mContext, new ComponentName(mContext.getPackageName(), getClass().getCanonicalName()), UserHandle.USER_ALL); } catch (RemoteException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Unable to register notification listener", e); } } } -
创建NotificationListenerWrapper实例,NotificationListenerWrapper类就是上面所述的server端,然后将mWrapper对象通过NotificationManagerService传递出去;再来看看NotificationManagerService 的 registerListener 方法
NotificationListenerService.java
public void registerAsSystemService(Context context, ComponentName componentName, int currentUser) throws RemoteException { if (mWrapper == null) { mWrapper = new NotificationListenerWrapper(); } mSystemContext = context; INotificationManager noMan = getNotificationInterface(); mHandler = new MyHandler(context.getMainLooper()); mCurrentUser = currentUser; noMan.registerListener(mWrapper, componentName, currentUser); } protected class NotificationListenerWrapper extends INotificationListener.Stub { @Override public void onNotificationPosted(IStatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder, NotificationRankingUpdate update) { StatusBarNotification sbn; ... // protect subclass from concurrent modifications of (@link mNotificationKeys}. synchronized (mLock) { applyUpdateLocked(update); if (sbn != null) { SomeArgs args = SomeArgs.obtain(); args.arg1 = sbn; args.arg2 = mRankingMap; // 发送通知,mHandler处理MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_POSTED事件时,会调用自身的onNotificationPosted 方法,即NotificationListener 重写的onNotificationPosted 方法; mHandler.obtainMessage(MyHandler.MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_POSTED, args).sendToTarget(); } else { // still pass along the ranking map, it may contain other information mHandler.obtainMessage(MyHandler.MSG_ON_NOTIFICATION_RANKING_UPDATE, mRankingMap).sendToTarget(); } } } @Override public void onNotificationRemoved(IStatusBarNotificationHolder sbnHolder, NotificationRankingUpdate update, NotificationStats stats, int reason) { ........ } @Override public void onListenerConnected(NotificationRankingUpdate update) { ..... } @Override public void onNotificationRankingUpdate(NotificationRankingUpdate update) throws RemoteException { ..... } @Override public void onListenerHintsChanged(int hints) throws RemoteException { mHandler.obtainMessage(MyHandler.MSG_ON_LISTENER_HINTS_CHANGED, hints, 0).sendToTarget(); } ..... } -
mListeners 会将INotificationListener封装到ManagedServices.ManagedServiceInfo ,看到这里一切就明了。
NotificationManagerService.java
public void registerListener(final INotificationListener listener, final ComponentName component, final int userid) { enforceSystemOrSystemUI("INotificationManager.registerListener"); mListeners.registerService(listener, component, userid); } -
保留问题1
SystemUI什么时候去创建RemoteView,SystemUI里面有个创建通知视图的类NotificationInflater,在类里面会根据传递过来的StatusBarNotification 数据在自己进程端构建RemoteView。
这是非常聪明的做法,对于标准通知视图,根本不用携带着在进程间通信流转,非常浪费资源甚至造成卡顿。NotificationInflater.java
// 重建通知的RemoteView private static InflationProgress createRemoteViews(int reInflateFlags, Notification.Builder builder, boolean isLowPriority, boolean isChildInGroup, boolean usesIncreasedHeight, boolean usesIncreasedHeadsUpHeight, boolean redactAmbient, Context packageContext) { InflationProgress result = new InflationProgress(); isLowPriority = isLowPriority && !isChildInGroup; if ((reInflateFlags & FLAG_REINFLATE_CONTENT_VIEW) != 0) { result.newContentView = createContentView(builder, isLowPriority, usesIncreasedHeight); } if ((reInflateFlags & FLAG_REINFLATE_EXPANDED_VIEW) != 0) { result.newExpandedView = createExpandedView(builder, isLowPriority); } if ((reInflateFlags & FLAG_REINFLATE_HEADS_UP_VIEW) != 0) { result.newHeadsUpView = builder.createHeadsUpContentView(usesIncreasedHeadsUpHeight); } if ((reInflateFlags & FLAG_REINFLATE_PUBLIC_VIEW) != 0) { result.newPublicView = builder.makePublicContentView(); } if ((reInflateFlags & FLAG_REINFLATE_AMBIENT_VIEW) != 0) { result.newAmbientView = redactAmbient ? builder.makePublicAmbientNotification() : builder.makeAmbientNotification(); } result.packageContext = packageContext; result.headsUpStatusBarText = builder.getHeadsUpStatusBarText(false /* showingPublic */); result.headsUpStatusBarTextPublic = builder.getHeadsUpStatusBarText( true /* showingPublic */); return result; } // 最终也是调用Notification.Builder来创建 private static RemoteViews createContentView(Notification.Builder builder, boolean isLowPriority, boolean useLarge) { if (isLowPriority) { return builder.makeLowPriorityContentView(false /* useRegularSubtext */); } return builder.createContentView(useLarge); }
4. 小结
- Notification系统用了典型的建造者模式;
- 针对标准视图样式,使用了传参的方式在SystemUI进程创建RemoteView,提高跨进程通讯的效率;






















 1376
1376











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








