一、OGNL
1、OGNL概述
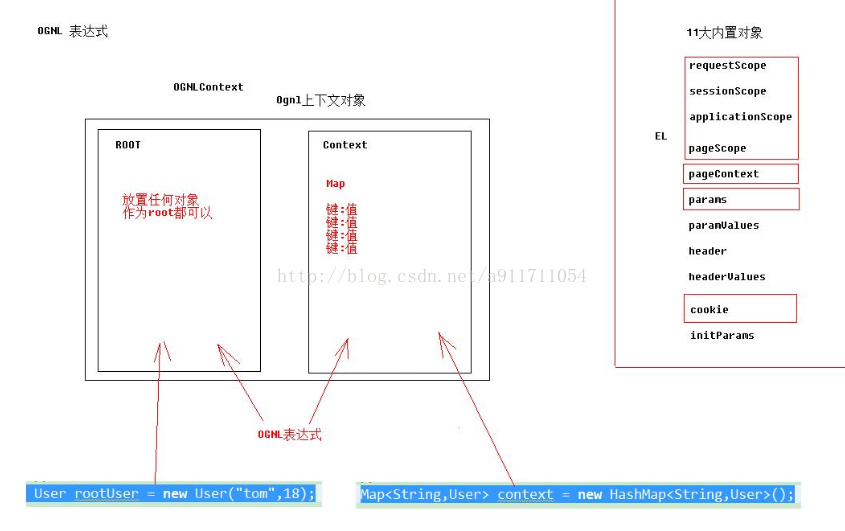
OGNL是Object-Graph Navigation Language的缩写,它是一种功能强大的表达式语言,通过它简单一致的表达式语法,可以存取对象的任意属性,调用对象的方法,遍历整个对象的结构图,实现字段类型转化等功能。它使用相同的表达式去存取对象的属性。

${user.addr.name}这种写法就叫对象视图导航,OGNL不仅仅可以视图导航,支持比EL更加丰富的功能
2、OGNL准备工作
(1)导包,struts2已经自带,无需重复导
(2)代码准备
@Test
//准备工作
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
//将rootUser作为root部分
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
//将context这个Map作为Context部分
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL
Ognl.getValue("", oc, oc.getRoot());
}3、OGNL基本语法
package com.sh.a_ognl;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.sh.bean.User;
import ognl.Ognl;
import ognl.OgnlContext;
//展示OGNL语法
public class Demo {
@Test
//准备工作
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map
context = new HashMap
();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
//将rootUser作为root部分
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
//将context这个Map作为Context部分
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL
Ognl.getValue("", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
@Test
//基本语法演示
//取出root中的属性值
public void fun2() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map
context = new HashMap
();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//书写OGNL
//取出root中user对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
}
@Test
//基本语法演示
//取出context中的属性值
public void fun3() throws Exception{
//准备ONGLContext
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map
context = new HashMap
(); context.put("user1", new User("jack",18)); context.put("user2", new User("rose",22)); OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext(); oc.setRoot(rootUser); oc.setValues(context); //书写OGNL //取出root中user对象的name属性 String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot()); Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user1.age", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name+":"+age); } @Test //基本语法演示 //为属性赋值 public void fun4() throws Exception{ //准备ONGLContext //准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom",18); //准备Context Map
context = new HashMap
(); context.put("user1", new User("jack",18)); context.put("user2", new User("rose",22)); OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext(); oc.setRoot(rootUser); oc.setValues(context); //书写OGNL Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc,oc.getRoot()); String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='麦客子'", oc,oc.getRoot()); String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1); } @Test //基本语法演示 //调用方法 public void fun5() throws Exception{ //准备ONGLContext //准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom",18); //准备Context Map
context = new HashMap
(); context.put("user1", new User("jack",18)); context.put("user2", new User("rose",22)); OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext(); oc.setRoot(rootUser); oc.setValues(context); //书写OGNL Ognl.getValue("setName('孙悟空')", oc, oc.getRoot()); String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('猪八戒'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1); } @Test //基本语法演示 //调用静态方法 public void fun6() throws Exception{ //准备ONGLContext //准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom",18); //准备Context Map
context = new HashMap
(); context.put("user1", new User("jack",18)); context.put("user2", new User("rose",22)); OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext(); oc.setRoot(rootUser); oc.setValues(context); //书写OGNL String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@com.sh.a_ognl.HahaUtils@echo('hello java')", oc, oc.getRoot()); /*double name1 = (double) Ognl.getValue("@ java.lang.Math@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());*/ double name1 = (double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); System.out.println(name1); } @Test //基本语法演示 //ognl创建对象list|map public void fun7() throws Exception{ //准备ONGLContext //准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom",18); //准备Context Map
context = new HashMap
(); context.put("user1", new User("jack",18)); context.put("user2", new User("rose",22)); OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext(); oc.setRoot(rootUser); oc.setValues(context); //书写OGNL //创建list Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'宝钗','黛玉','晴雯'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot()); String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'宝钗','黛玉','晴雯'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot()); String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'宝钗','黛玉','晴雯'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(size); System.out.println(name); System.out.println(name2); //创建map Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'宝钗','age':'18'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot()); String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'宝钗','age':'18'}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot()); Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'宝钗','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot()); System.out.println(size2); System.out.println(name3); System.out.println(age); } }
二、Struts2与OGNL表达式的结合
1、结合原理
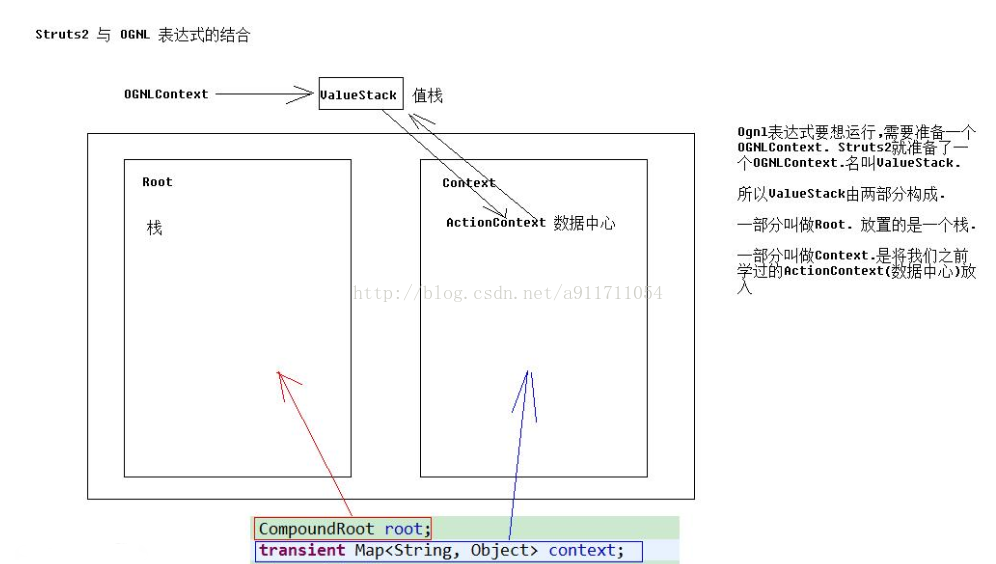
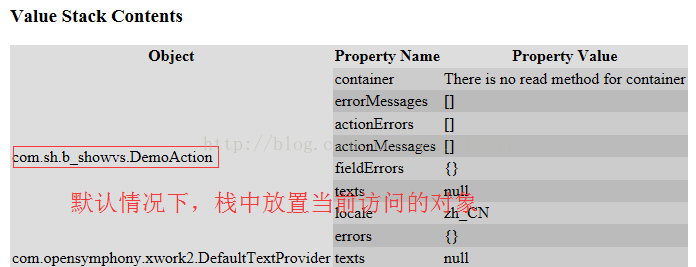
查看值栈两部分内容
Root
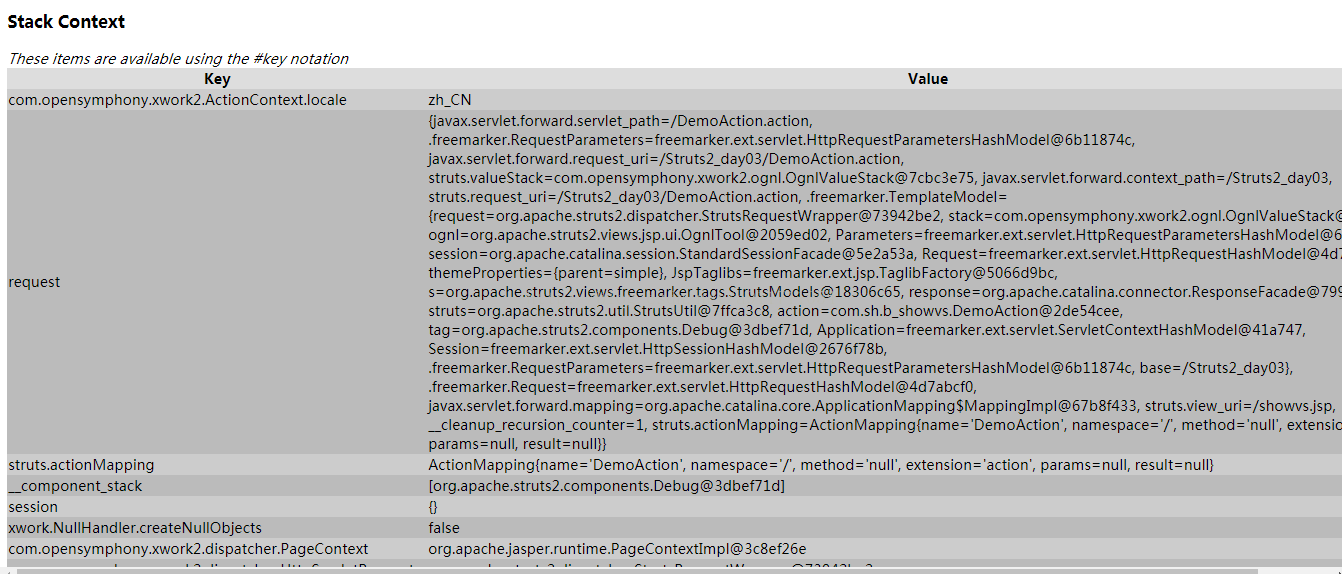
Context

2、栈的原理
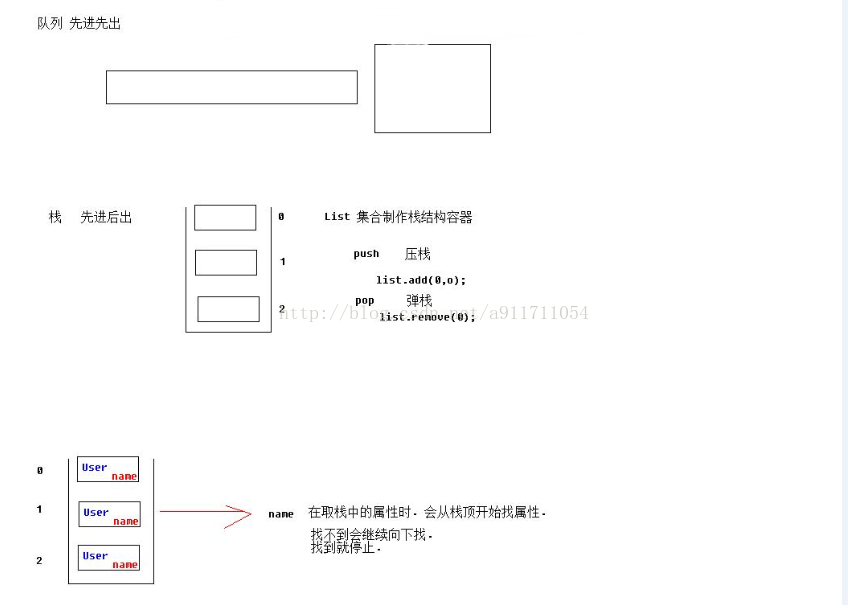
3、浅尝值栈

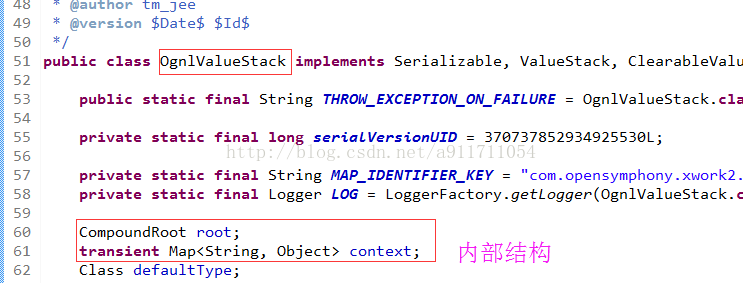
(1)值栈的内部结构
在ValueStack的实现类OngValueStack中包含两部分,分别是值栈和Map

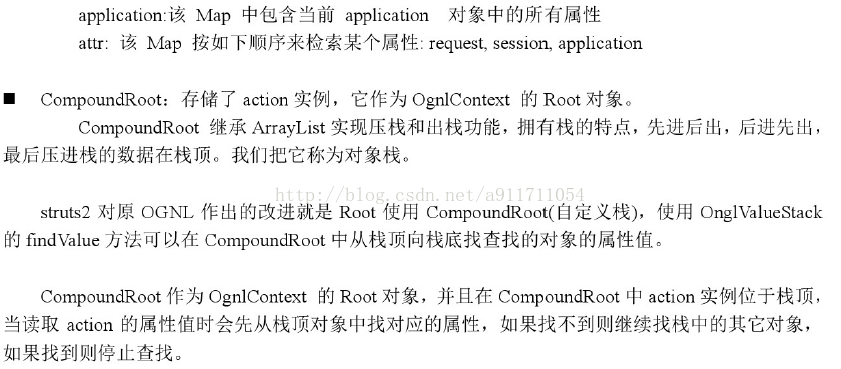
(2)ActionContext与ValueStrack的关系



4、Struts2与OGNL结合体现
(1)参数接收
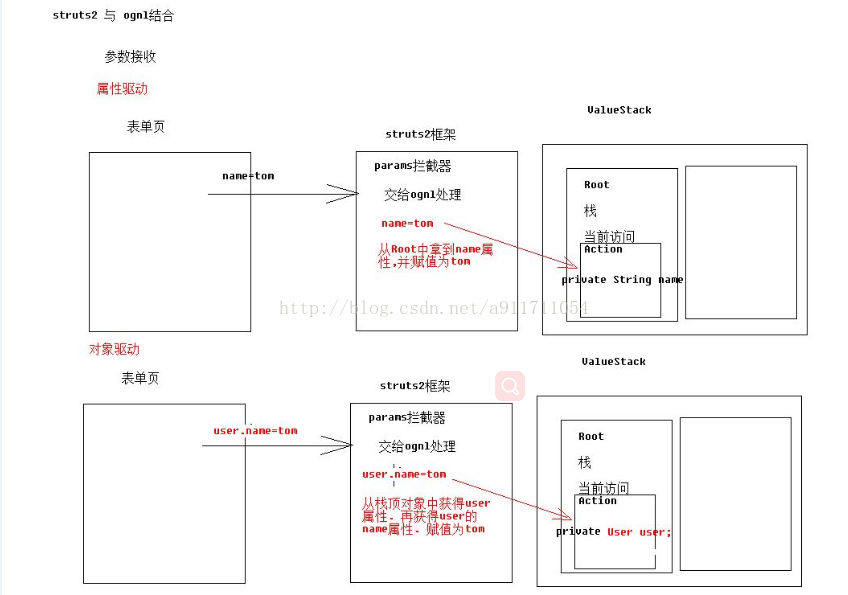
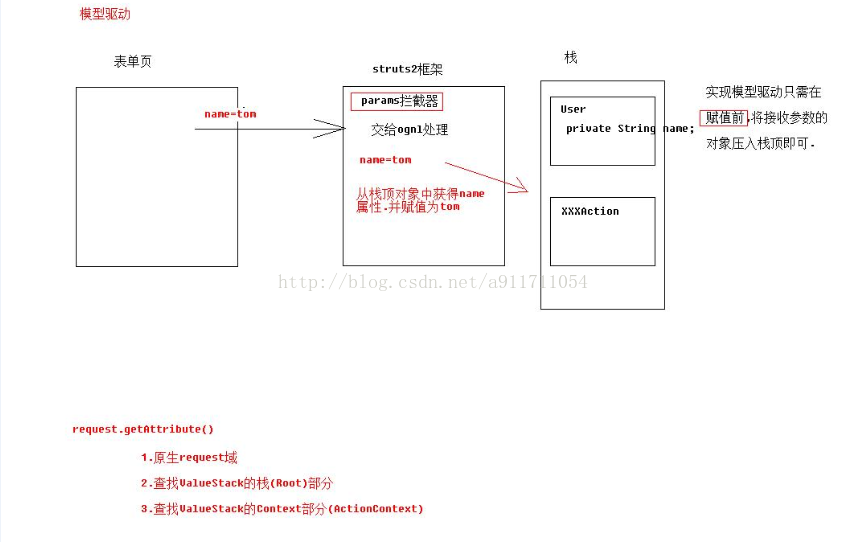
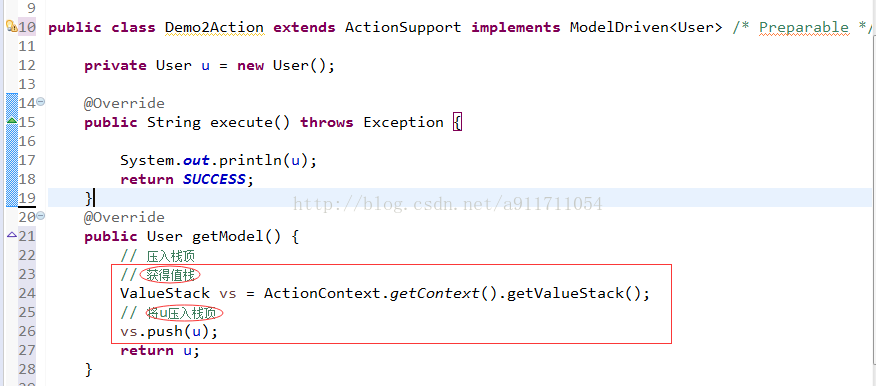
获得值栈的2种方式:


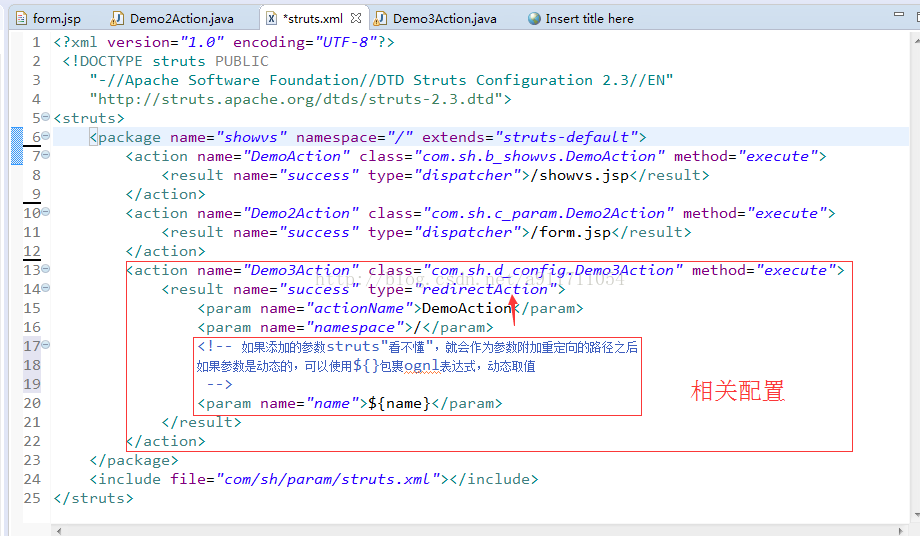
(2)配置文件中
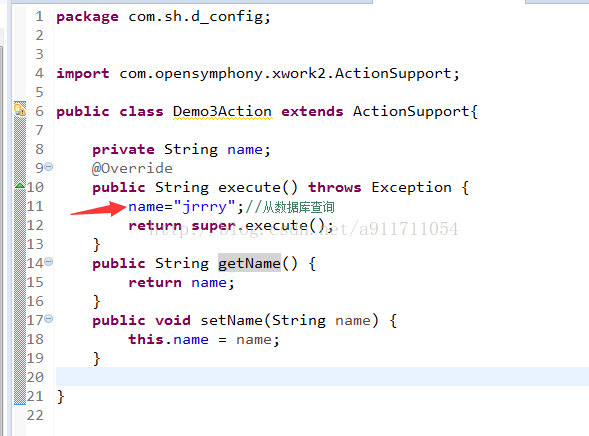
配置文件:
(3)Struts2标签
详见【SSH】Struts2学习(四)
参考源码:https://github.com/AmazeLee/Struts2.git
























 464
464

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










