线程
 继承Thread类
继承Thread类
public class TestThread1 {
public static void main(String args[]){
Thread t = new MyThread(100);
t.start();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
private int n;;
public MyThread( int n ){
super();
this.n=n;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
System.out.print (" " + i);
}
}
}向Thread构造方法传递Runnable对象
public class TestThread2 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyTask mytask = new MyTask(10);
Thread thread = new Thread(mytask);
thread.start();
//thread.setDaemon(true);
for(int i=0; i<6; i++) {
System.out.println("Main--" + i);
try{
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch( InterruptedException e ){}
}
}
}
class MyTask implements Runnable {
private int n;
public MyTask(int n){
this.n = n;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.println(" " + i);
try{
Thread.sleep(500);
}catch( InterruptedException e ){}
}
}
}
public class TestThread4Anonymous {
public static void main(String args[]) {
new Thread(){
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
System.out.println(i);
}
}.start();
new Thread( ( ) -> {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
System.out.println(" "+ i);
} ).start();
}
}多线程程序示例
import java.util.*;
import java.text.*;
public class TestThread3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Counter c1 = new Counter(1);
Thread t1 = new Thread(c1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(c1);
Thread t3 = new Thread(c1);
Counter c2 = new Counter(2);
Thread t4 = new Thread(c2);
Thread t5 = new Thread(c2);
Thread t6 = new Thread(c2);
TimeDisplay timer = new TimeDisplay();
Thread t7 = new Thread(timer);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
t6.start();
t7.start();
}
}
class Counter implements Runnable {
int id;
Counter(int id){
this.id = id;
}
public void run() {
int i=0;
while( i++<=10 ){
System.out.println("ID: " + id + " No. " + i);
try{ Thread.sleep(10); } catch( InterruptedException e ){}
}
}
}
class TimeDisplay implements Runnable {
public void run(){
int i=0;
while( i++<=3 ){
System.out.println(
new SimpleDateFormat().format( new Date()));
try{ Thread.sleep(40); } catch( InterruptedException e ){}
}
}
}
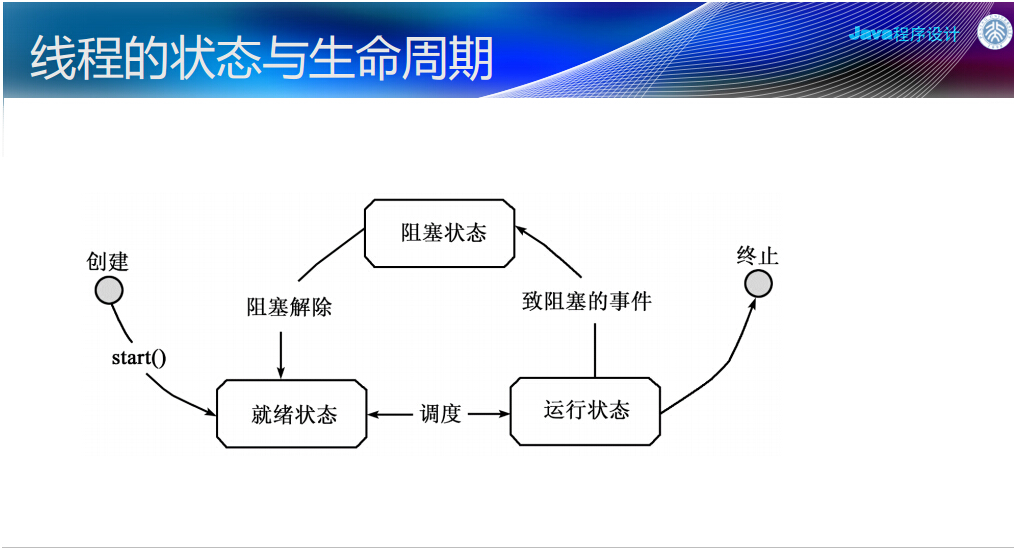



同时运行的线程需要共享数据,有时会造成混乱。所以必须考虑线程的同步问题。
synchronized用来表示不允许其它线程中途插入。
wait()是让线程暂停运行,进入等待;notify()让线程继续运行
但是多线程可能造成线程的死锁。即线程一直处于等待状态。



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








