反射
类类型Class的使用
类类型Class的实例获取方式有一下三种
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
String result =
"Hello ReflectionText.."
;
System.out.println(result);
Class userClass1 = User.
class
;
Class userClass2 =
new
User().getClass();
try
{
Class userClass3 = Class
.forName(
"idea.analyzesystem.reflection.User"
);
System.out.println(userClass1);
System.out.println(userClass2);
System.out.println(userClass3);
}
catch
(ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
我们可以通过类类型创建类实例对象(这里newInstance要求该类必须拥有无参构造函数)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
try
{
User user = User.
class
.newInstance();
System.out.println(user);
}
catch
(InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch
(IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
动态加载类
类的加载方式分为动态加载和静态加载,而上面提到的Class.format(“”)方法不仅是获取类类型Class,还表示动态加载。而编译时为静态加载,运行时为动态加载,下面再注解使用中还会提到,这里不做过多说明了。
获取方法信息
首先我们可以通过class获取类的名称,名称可以包含包名可以不包含。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
System.out.println(User.
class
.getSimpleName());
System.out.println(User.
class
.getName());
}
// .................输出结果................
User
idea.analyzesystem.reflection.User
|
获取一个类的所有public方法以及他的父类的所有public方法可以通过getMethods获取
|
1
2
|
Class cls = User.
class
;
Method[] methods = cls.getMethods();
|
如果我们想要获取自己类内部定义的其他private、 protected方法怎么办呢?可以采取以下方法(该方法不管访问权限,只要是方法都会被获取)
|
1
|
Method[] allSelfMethods = cls.getDeclaredMethods();
|
获取方法的名字通过getName得到
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
for
(Method method: methods){
System.out.println(method.getName());
}
//.....下面输出User的结果................
setLevel
setAge
getNickName
getLevel
getUserName
getAge
getPassword
getEmail
setGender
getIdCard
setIdCard
|
有时候我们需要反射得到返回值判断具体类型,可以通过method.getReturnType()方法得到。方法有无参函数和有参数的函数,我们可以通过method.getParameterTypes()方法获取方法的所有参数对应的类类型集合。
获取成员变量构造函数信息
通过反射获取定义的成员变量的相关信息可以通过getFields获取所有public定义的成员变量,getDeclaredFields呢则是获取所有定义的成员变量(field.getType获取成员变量类型),下面是相关代码块实例和输出结果对比
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
Class cls = User.
class
;
Field[] fieldspublic = cls.getFields();
for
(Field field : fieldspublic){
System.out.println(field.getName());
}
System.out.println(
"********************"
);
Field[] fields = cls.getDeclaredFields();
for
(Field field : fields){
System.out.println(field.getName());
}
}
//............输出结果................
a
test
********************
a
test
uid
userName
password
|
获取构造函数的名字以及参数列表可以通过cls.getConstructors()获取所有的public修饰的构造函数,cls.getDeclaredConstructors()则可以获取所有关键词修饰的构造函数。
方法反射的基本操作
我们可以通过Class获取到Method,再通过Method调用invoke方法操作对象的方法。下面请看实例代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
User user =
new
User();
user.setNickName(
"hello"
);
User user2 =
new
User();
user2.setNickName(
"world"
);
Class cls = user.getClass();
try
{
Method method = cls.getDeclaredMethod(
"setNickName"
, String.
class
);
method.invoke(user,
"idea"
);
System.out.println(user.getNickName());
System.out.println(user2.getNickName());
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
通过反射修改User对象的setNickName,下面是测试结果
|
1
2
|
idea
world
|
invoke方法的返回值根据方法的返回值判断,void返回null,其他的默认object类型,我们可以根据自己需求强转类型。
通过反射了解集合泛型的本质
反射的操作都是编译后的操作,编译后的泛型是去泛型化的操作。这里通过ArrayList相关操作来论证这一观点。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
ArrayList list =
new
ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<User> userList=
new
ArrayList<>();
userList.add(
new
User());
System.out.println(list.getClass()==userList.getClass());
}
//..........输出结果..........
true
|
我们在同个反射的方式调用,为userList的方式添加不同于User对象的类型,是可以添加成功的,下面是相关测试代码块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public
static
void
main(String[] arg0) {
ArrayList list =
new
ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<User> userList=
new
ArrayList<>();
userList.add(
new
User());
System.out.println(list.getClass()==userList.getClass());
try
{
Method method = userList.getClass().getMethod(
"add"
, Object.
class
);
method.invoke(userList,
"Test ArrayList add other type data"
);
System.out.println(userList.toString());
}
catch
(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
输出结果
|
1
2
3
4
|
true
[User [uid=
null
, userName=
null
, password=
null
, age=
0
,
gender=
null
, idCard=
null
, level=
0
, nickName=
null
, Email=
null
],
Test ArrayList add other type data]
|
事实证明我们是可以往List里面添加任何类型的!这里用这么多篇幅来理解反射不是闲的蛋疼的事,在下面的真主注解埋下铺垫,这里不过多透露了,如想知道更多请往下接着看..
注解
概述
如果你不用注解,请不要@me 。说个最简单的例子,Android中通过findViewById得到控件,这是一件繁琐的事情,重复着这些代码好累,使用注解可以把他简单化,注解框架有xtuils、butterknife等,也许你在项目中只希望用到 Inject View这个功能,又或者你想知道这个实现的原理是怎样的。本文主要是解决这两个问题,实现一个最简单的ViewInject.
Java中的常见注解
我们的Activity重写父类的onCreate方法如下(@Override注解表示重写父类方法)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public
class
MainActivity
extends
AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
|
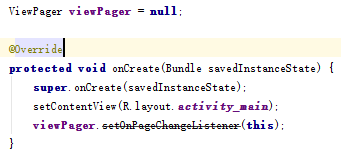
下面在看一幅图
setOnPageChangListener方法在某个版本后过时了( @Deprecated标记某个方法过时)
|
1
2
3
4
|
@Deprecated
public
void
setOnPageChangeListener(OnPageChangeListener listener) {
mOnPageChangeListener = listener;
}
|
过时方法会有警告提示,我们可以在方法/类名上面添加忽略警告的注解,警告提示就不会再存在了(@SuppressWarnings(“Deprecated”)),我们Android开发很多时候如果是因为版本问题忽略警告需要注意版本的兼容性
注解的分类
注解按照运行机制来分类可以分为三大类
- 源码注解
- 编译时注解
- 运行时注解
源码注解表示注解只在源码存在,编译成class就不存在了,编译时注解编译成class还存在,编译时存在。运行时注解表示在运行阶段还会起作用。(元注解是注解的注解,稍后再提一下)
自定义注解
下面通过一个自定义注解来帮助认知自定义注解的要素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
@Target
(ElementType.FIELD)
@Inherited
@TargetApi
(
14
)
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public
@interface
ViewInject{
int
id();
int
[] ids();
int
age()
default
18
;
}
|
@interface 表示一个注解定义,注解的方法必须是无参数的,如果有返回值可以默认返回值,如果注解的方法只有一个用value()表示,注解类型支持基本类型、String、Class、Annotation、Enumeration.@Target表示注解的作用域,可以是方法或类、字段上面。@Retention注解的生命周期控制。@Inherited表示允许被继承,@Documented描述注解信息,@TargetApi指定Anddroid开发中的Api可以使用的最低等级。注解使用可以没有成员,我们称之为表示注解。
Xutils注解剖析
通过上面反射相关的了解,我们知道可以通过反射获取类函数变量,并可以执行变量赋值、方法调用。cls.isAnnotationPresent(xx.class)用于判断是否存在指定的注解类型。Method同样支持这个方法,具体用法在我们接下来的xutils viewUtils注解模块来详细了解。下面先看看Xutils使用的注解代码块。(当然实际开发ViewUtils.inject初始化方法都放在基类,实现类Activity都可以不用重写onCreate方法)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
@ContentView
(R.layout.activity_splash)
public
class
MainActivity
extends
Activity{
@ViewInject
(R.id.button_login)
private
TextView textView;
@Override
protected
void
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super
.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
ViewUtils.inject(
this
);
}
@OnClick
(R.id.button_login)
public
void
onClick(View v){
}
@OnClick
({R.id.button_login,R.id.searchView})
public
void
onClicks(View v){
}
}
|
ViewUtils.inject(this);方法在做解析操作,我们先来看看这些注解定义:ContentView
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package
com.lidroid.xutils.view.annotation;
import
java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import
java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import
java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import
java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target
(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public
@interface
ContentView {
int
value();
}
|
在我们inject方法调用后解析类名上面的注解是这样的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
@SuppressWarnings
(
"ConstantConditions"
)
private
static
void
injectObject(Object handler, ViewFinder finder) {
Class<?> handlerType = handler.getClass();
// 判断是否存在ContentView注解,如果存在,理解通过注入的方式setContentView(int)
ContentView contentView = handlerType.getAnnotation(ContentView.
class
);
if
(contentView !=
null
) {
try
{
Method setContentViewMethod = handlerType.getMethod(
"setContentView"
,
int
.
class
);
setContentViewMethod.invoke(handler, contentView.value());
}
catch
(Throwable e) {
LogUtils.e(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
|
下面再来看onClick的注解实现,首先有个定义EventBase注解作用于注解
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
/**
* Author: wyouflf
* Date: 13-9-9
* Time: 下午12:43
*/
@Target
(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public
@interface
EventBase {
Class<?> listenerType();
String listenerSetter();
String methodName();
}
|
OnClick注解定义如下(指定了设置OnClickListener的方法名字以及回调方法名称,支持注解多个控件,这里的value表示view的id值)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/**
* Author: wyouflf
* Date: 13-8-16
* Time: 下午2:27
*/
@Target
(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@EventBase
(
listenerType = View.OnClickListener.
class
,
listenerSetter =
"setOnClickListener"
,
methodName =
"onClick"
)
public
@interface
OnClick {
int
[] value();
int
[] parentId()
default
0
;
}
|
解析这些方法注解在ViewUtils源码块如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
// inject event
Method[] methods = handlerType.getDeclaredMethods();
//获取所有方法
if
(methods !=
null
&& methods.length >
0
) {
//方法不为空
for
(Method method : methods) {
Annotation[] annotations = method.getDeclaredAnnotations();
//获取所有的方法上面的注解
if
(annotations !=
null
&& annotations.length >
0
) {
for
(Annotation annotation : annotations) {
Class<?> annType = annotation.annotationType();
if
(annType.getAnnotation(EventBase.
class
) !=
null
) {
//如果存在EventBase注解
method.setAccessible(
true
);
try
{
// ProGuard:-keep class * extent java.lang.annotation.Annotation { *; }
//如果使用了注解要添加混淆规则,保证注解不能被混淆
//下面开始为EventListenerManager添加监听事件,EventBase注解了添加事件的方法名称以及回调方法名称
Method valueMethod = annType.getDeclaredMethod(
"value"
);
Method parentIdMethod =
null
;
try
{
parentIdMethod = annType.getDeclaredMethod(
"parentId"
);
}
catch
(Throwable e) {
}
Object values = valueMethod.invoke(annotation);
Object parentIds = parentIdMethod ==
null
?
null
: parentIdMethod.invoke(annotation);
int
parentIdsLen = parentIds ==
null
?
0
: Array.getLength(parentIds);
int
len = Array.getLength(values);
for
(
int
i =
0
; i < len; i++) {
ViewInjectInfo info =
new
ViewInjectInfo();
info.value = Array.get(values, i);
info.parentId = parentIdsLen > i ? (Integer) Array.get(parentIds, i) :
0
;
EventListenerManager.addEventMethod(finder, info, annotation, handler, method);
}
}
catch
(Throwable e) {
LogUtils.e(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
inject方法的调用变量赋值这块,关于ViewInject注解定义如下(不得不说注解value只支持单个控件,个人觉得支持批量注解控件多好的,可以减少很多代码,如果你有兴趣可以尝试修改它):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
package
com.lidroid.xutils.view.annotation;
import
java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import
java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import
java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import
java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target
(ElementType.FIELD)
//作用在字段上面
//运行时任然有效,如果改为class 或者编译时就会有问题了,findById找不到
//变量为空引用时抛出空指针异常,如果混淆了注解,也会导致找不到控件
@Retention
(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public
@interface
ViewInject {
int
value();
/* parent view id */
int
parentId()
default
0
;
}
|
注解变量的解析在ViewUtils的实现如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
private
static
void
injectObject(Object handler, ViewFinder finder) {
//...................略...................
Field[] fields = handlerType.getDeclaredFields();
//查找出所有控件变量
if
(fields !=
null
&& fields.length >
0
) {
for
(Field field : fields) {
//控件变量注解找到后通过finder提供的findById获取控件实例
ViewInject viewInject = field.getAnnotation(ViewInject.
class
);
if
(viewInject !=
null
) {
try
{
View view = finder.findViewById(viewInject.value(), viewInject.parentId());
//打开权限然后用反射赋值
if
(view !=
null
) {
field.setAccessible(
true
);
field.set(handler, view);
}
}
catch
(Throwable e) {
//如果用ViewInject注解了但是找不到视图的话直接抛出了运行时异常
LogUtils.e(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
else
{
//..............略过其他注解解析................
}
}
}
}
|
小结
通过反射和注解的系统的学习了解,我们可以把我们的代码玩的更好了,再也不用愁看不懂别人写的注解代码了,根据慕课视频还get到一点,我们应用开发的数据缓存是家常便饭,我们可以通过注解的方式创建数据库表,注解的方式实现增删改sqlite的表数据,虽然我们当前使用的多数为第三方的sqlite相关的开源库,我们遇到注解如此的实现还是可以去了解一下的,xutils的db模块可以参考,尽管xutils目前已经不再维护有了xutils3.0,我们不能否定xutils是一个非常不错的开源项目。
参考资料
视频资料:http://www.imooc.com/video/3738,http://www.imooc.com/learn/456
Xutils源码层注解解析推荐:http://blog.csdn.net/drkcore/article/details/50922448
转载请注明:Android开发中文站 » Android开发之反射与注解






















 551
551

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








