【mybatis源码】 mybatis底层源码分析
注:其他一些源码解读,如果有需要,可以参考:
- 【Spring源码】 后置处理器BeanPostProcessor底层原理分析
- 【spring源码】spring声明式事务底层源码分析
- 【spring源码】ApplicationListener事件监听底层原理
- 【spring源码】AOP底层源码分析
- 【spring源码】spring IOC容器底层源码分析
- 【SpringMVC源码】SpringMVC核心DispatcherServlet底层源码分析
1.测试用例
- 我们用一个测试来当做入口
- Demo:
- 配置类:
/**
* 注解集成mybatis
*
* @author wangjie
* @version V1.0
* @date 2020/1/20
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(value="com.code.mvc.dao")
public class DaoConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("password");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false");
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource());
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
return sessionFactory.getObject();
}
}
- Mapper:
/**
* 源码分析测试类
* 1.纯注解集成
* 2.测试数据库连接
*
* @author wangjie
* @version V1.0
* @date 2020/1/20
*/
public interface UserDao {
@Insert(value="insert into t_user(name, nick) values (#{name}, #{nick})")
int add(User person);
@Delete(value="delete from t_user where id=#{id}")
int delete(long id);
@Update(value="update t_user set name=#{name}, nick=#{nick} where id=#{id}")
void update(User person);
@Select(value="select * from t_user where id=#{id}")
User select(long id);
}
- 测试用例:
/**
* mybatis测试
*
* @author wangjie
* @version V1.0
* @date 2020/1/20
*/
public class Mybatis_Test {
/**
* 1,初始化IOC容器
* 2,获取SqlSessionFactory对象
* 3,获取SqlSession对象:返回一个DefaultSqlSesion对象,包含Excutor和Configuration
* 4,获取接口的代理对象:MapperProxy
* 5,执行增删改查
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DaoConfig.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = applicationContext.getBean(SqlSessionFactory.class);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
User select = userDao.select(1);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(select));
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
applicationContext.close();
}
}
- 运行结果:
一月 20, 2020 8:27:53 下午 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@19e1023e: startup date [Mon Jan 20 20:27:53 CST 2020]; root of context hierarchy
{"id":1,"name":"wj","nick":"jj"}
一月 20, 2020 8:27:56 下午 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@19e1023e: startup date [Mon Jan 20 20:27:53 CST 2020]; root of context hierarchy
Process finished with exit code 0
2.开撸源码
- 我们从上面的测试用例Mybatis_Test 入手。
/**
* 1,初始化IOC容器
* 2,获取SqlSessionFactory对象
* 3,获取SqlSession对象:返回一个DefaultSqlSesion对象,包含Excutor和Configuration
* 4,获取接口的代理对象:MapperProxy
* 5,执行增删改查
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DaoConfig.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = applicationContext.getBean(SqlSessionFactory.class);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
User select = userDao.select(1);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(select));
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
applicationContext.close();
}
}
- 第一步初始化IOC容器,这里对springIOC的初始化不做过多介绍,有兴趣的可见:
- 【spring源码】spring IOC容器底层源码分析
- 我们从第二步开始看:
2.1 SqlSessionFactory对象的创建与获取
- 测试用例中的SqlSessionFactory对象是从IOC容器中获取到的。
- 而往上翻会发现SqlSessionFactory是在配置文类DaoConfig 中注入容器的。
- 我们直接注入点看SqlSessionFactory的创建
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
return sessionFactory.getObject();
}
- 我们看一下SqlSessionFactoryBean这个类:
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {}
- 它实现了FactoryBean,InitializingBean和ApplicationListener。
- InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它有个afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候都会执行该方法。
- FactoryBean接口:可以让我们自定义Bean的创建过程,可以用它的getObject() 方法获得自定义创建的bean。
- ApplicationListener接口:注册事件事件监听
- 这些接口在spring的源码中应用很广泛,也很重要,但今天重点不是这些,有兴趣的可以自己去多做些了解。
- 回过头,我们再这里看sessionFactory.getObject()这个方法,就是重写FactoryBean接口中的getObject() 方法实现的:
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
- getObject() 方法中重点也是调用了afterPropertiesSet()方法
- afterPropertiesSet()方法,实现 InitializingBean接口重写的方法,现在看来重点就在这个方法了:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//dataSource不为空,我们在配置类中有注入
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
//sqlSessionFactoryBuilder,它是SqlSessionFactoryBean 成员变量private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
- 先判断了dataSource和sqlSessionFactoryBuilder 不为空
- 然后 this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
String[] typeAliasPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeAliasesPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Stream.of(typeAliasPackageArray).forEach(packageToScan -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(packageToScan,
typeAliasesSuperType == null ? Object.class : typeAliasesSuperType);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for aliases");
});
}
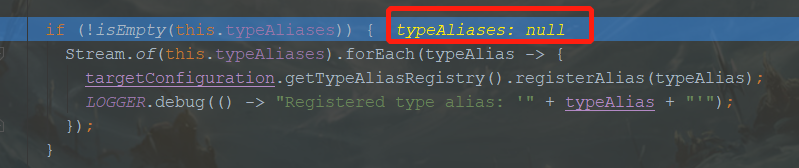
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach(plugin -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
});
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
String[] typeHandlersPackageArray = tokenizeToStringArray(this.typeHandlersPackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Stream.of(typeHandlersPackageArray).forEach(packageToScan -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(packageToScan);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Scanned package: '" + packageToScan + "' for type handlers");
});
}
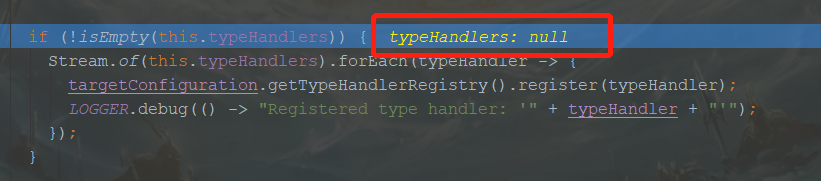
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach(typeHandler -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
});
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {//fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
targetConfiguration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.cache).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::addCache);
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment,
this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory,
this.dataSource));
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
- 对于这个方法的解读,我在网上找到一张时序图,可以参考一下:

- 这张图描述的以xml形式来集成mybatis时创建sqlSessionFactory的过程,我们是用注解,整个过程不用解析xml,相对来说会简单些。
- 下面是我Debug时的一些截图
- this.configuration : null


- 要创建配置类Configuration,但this.configuration和this.configLocation都是空,所以使用了默认配置targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
public Configuration() {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
- 再往下一路为null


… - 直到:
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
- 这里创建了一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
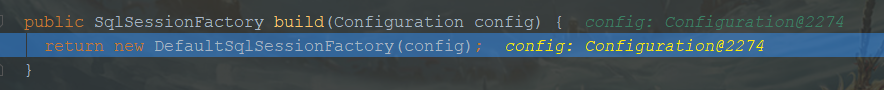
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
- 这里这个配置类Configuration就是上面那个默认配置,最后返回。
- 注意,这个Configuration中有个字段:
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
- 这个字段是用来存放所有增删改查标签详细详细的,如果是通过xml配置,走到这步时,所有的xml中的sql详细都会被解析放到每一个MappedStatement中最后放在这个Map里
public final class MappedStatement {
private String resource;
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private Integer fetchSize;
private Integer timeout;
private StatementType statementType;
private ResultSetType resultSetType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
private Cache cache;
private ParameterMap parameterMap;
private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;
private boolean flushCacheRequired;
private boolean useCache;
private boolean resultOrdered;
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
private String[] keyProperties;
private String[] keyColumns;
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
private String databaseId;
private Log statementLog;
private LanguageDriver lang;
private String[] resultSets;
...}
- 看这些字段名大家如果熟悉mybatis xml配置的话应该会眼熟。
- 而如果是用无xml纯注解的方式来集成mybatis,那此时这个Map里就会暂时为null。
- 我们在创建SqlSessionFactory方法最后返回前打个断点:

- 刚创建完SqlSessionFactory,configuration 中的mappedStatements =0.
- 直到运行到后面,sql执行时,会刷新,这时候:

- 这里先把图贴出来,后面会细讲。
2.2 获取SqlSession对象
- 得到SqlSessionFactory,返回

- 获取SqlSession对象,要通过sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
- 我们得到的SqlSessionFactory是DefaultSqlSessionFactory,我们 打开它的openSession()方法
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取环境变量
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//从环境变量里拿到事务Factory
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建执行器Executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//返回
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
- 注释已经很清楚了,这里我们看一下Executor ,mybatis四大接口之一:
public interface Executor {
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null;
// 更新
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
// 查询,先查缓存,再查数据库
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
// 查询
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException;
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException;
// 事务提交
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 事务回滚
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException;
// 创建缓存的键对象
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
// 缓存中是否有这个查询的结果
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
// 清空缓存
void clearLocalCache();
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType);
Transaction getTransaction();
void close(boolean forceRollback);
boolean isClosed();
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
- 这里创建Executor ,我们到configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType)里面看看
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据ExecutorType创建不同的executor
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//如果有开启二级缓存,就 executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
- 首先根据ExecutorType创建不同的executor
- 默认protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
- 所以我们这里会走new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
- 然后如果有开启二级缓存,就创建CachingExecutor
- 创建完executor ,回过头会根据executor 和configuration创建DefaultSqlSession返回

public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
- 下面是我从网上找到的时序图,可以参考一下:

2.3 获取接口的代理对象:MapperProxy
- 获取SqlSession对象后,再从SqlSession中拿到指定mapper接口的代理实现类MapperProxy
- 这个代理实现类MapperProxy又是怎么实现的呢
- 这里我们简单聊一下,因为要真的细聊容易走歪,刹不住车。
- 首先,我们Demo里这些Mapper接口注入的类都是由Spring进行管理的,所以我们可以先从spring的角度看一下这些bean是什么时候注入进去的。
- 我们稍稍扒一下源码,就是配置类中的@MapperScan(value=“com.code.mvc.dao”)注释
- 看名字就知道这个注释是来处理mappedr的
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@Repeatable(MapperScans.class)
public @interface MapperScan {}
- 这个注释,主要干活的是@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
- @Import的注解,spring源码中一般用来往容器里塞自定义的bean
- MapperScannerRegistrar,看名字简单易懂,mapper扫描注册。
- MapperScannerRegistrar里面我们不细聊,要不容易歪楼,源码阅读每个接口都有它特定的功能,每一步代码的实现都依赖于这些功能,真要讲清楚来龙去脉,你要细聊完全就会刹不住车,所以我们这里只点到为止。
- MapperScannerRegistrar,mapper扫描注册,它会根据你写的包名来扫描,然后把扫描到的接口用代理的方式实现,然后把实现的bean注入到spring容器里
- 当然,MapperScannerRegistrar里面点进去有几行代码涉及到后面,还是要扒一下的
//映射器接口是bean的原始类
//但是,bean的实际类是MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59
//注意,这里的BeanClass是生成Bean实例的工厂,不是Bean本身。
// FactoryBean是一种特殊的Bean,其返回的对象不是指定类的一个实例,
// 其返回的是该工厂Bean的getObject方法所返回的对象。
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());
- definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass())设置Mapper接口的class对象或是类的全限定名为MapperFactoryBean(可以理解为实现是MapperFactoryBean)。
- 下面看下MapperFactoryBean的源码
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
public MapperFactoryBean() {
//intentionally empty
}
public MapperFactoryBean(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
//主要看这个方法
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
@Override
public Class<T> getObjectType() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
public void setMapperInterface(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public void setAddToConfig(boolean addToConfig) {
this.addToConfig = addToConfig;
}
public boolean isAddToConfig() {
return addToConfig;
}
}
- MapperFactoryBean继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport并实现了Spring中的FactoryBean
- 因为实现了FactoryBean接口所以MapperFactoryBean是一个FactoryBean,所以请记住这个方法:
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
- 我们点进去getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface)
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
- 记住这个方法,下面有用。
- 这个时候我们再回过头看测试案例的代码(我说过聊多了会歪楼)
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DaoConfig.class);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = applicationContext.getBean(SqlSessionFactory.class);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try{
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
User select = userDao.select(1);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(select));
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
applicationContext.close();
}
- UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);这行,我们跟进去
/**
* 什么都不做,直接去configuration中找
*/
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
- 看到没有,熟悉不,上面MapperFactoryBean的getObject() 方法,又回到这里了,这里就是获取mapper代理的入口,spring底层也是从这里进去的。
- 我们继续。
- SqlSession调用了Configuration.getMapper(type, this);, 接下来就看看Configuration:
/**
* 我也不要,你找mapperRegistry去要
* @param type
* @param sqlSession
* @return
*/
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
- Configuration也不要,接着甩给了MapperRegistry, 那咱看看MapperRegistry
/**
* 我不做谁做
* @param type
* @param sqlSession
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//重点,其实还是MapperProxyFactory去做
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//关键在这儿
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
- 最终交给MapperProxyFactory去做了。咱们看看源码:
**
*
* @param mapperProxy
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//动态代理我们写的dao接口
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
- 终于到了这里,拿到代理类,再一路返回,这步结束,贴上网上找的图,加深一下对这步的理解:

2.4 执行增删改查
- 拿到了代理对象MapperProxy,执行增删改查
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
User select = userDao.select(1);
- Debug调试,直接进入MapperProxy的invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//判断方法是不是Object的方法,是的话跳过
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//缓存
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//不是Object的方法,执行
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
- 看mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args)
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional() &&
(result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
- 这个方法简单明了,根据方法类型选择不同的执行方式
- debug跟下去,到了result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);这行,我们继续:
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
- 重点:this.selectList(statement, parameter);
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
- MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);这行代码,还记得我们之前说过的MappedStatement,里存放着mapper里每个方法,每个sql的所有信息,其初始默认是空,但在这里,调用的时候,会在里面刷新,最后:
//
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
//这个就相当于刷新了MappedStatements
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
- debug截图

- 获取到MappedStatement ,继续执行executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//获取sql语句的详细信息
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
//缓存key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
- query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
//判断缓存是否为空
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
//没有就查
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
- delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//查看本地缓存是否有数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
- queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//查到放缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
- list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建mybatis四大接口之一StatementHandler 的对象
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//参数预处理
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//查询
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
- 创建mybatis四大接口之一StatementHandler 的对象
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
- 这里默认创建PreparedStatementHandler
- 拿到PreparedStatementHandler,回过头再继续看 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
//拿到一个链接
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
//预编译
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
//调用parameterHandler进行参数预编译
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
- mybatis第三个四大接口之一parameterHandler参数预编译出场
- 参数预编译后一路返回,到最后一个调用handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
ps.execute();
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
- 执行查询,最后用四大接口最后一个resultSetHandler进行结果处理,最后一路返回。
- 自此,查询结束
- 最后贴上最后这个查询过程的总结图:


3.总结

- 【完】

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








