HashMap
Entry
Java中最常用的两种数据结构是数组和模拟指针(引用),几乎所有的数据结构都可以用这两种结构实现,HashMap也是如此,事实上,HashMap是一个链表散列,它的数据结构如下:
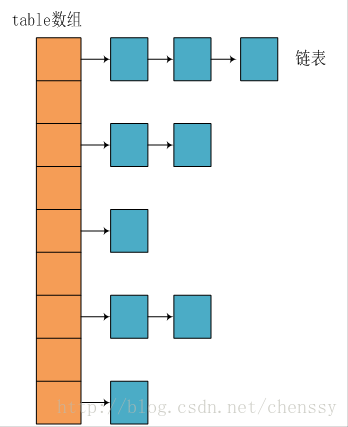
每次新建一个HashMap时,都会初始化一个table数组,table数组的元素为Entry节点,可以成为桶,桶的内部元素如下:
table = new Entry[capacity]
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash;
}HashMap的构造函数HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor),这里提及两个参数:初始容量和加载因子,容量代表哈希表中桶的数量,加载因子是哈希表在其容量自动增加之前可以达到多满的一种尺度,系统默认初始容量16,加载因子0.75
put(K,V)和get(K)
HashMap中最重要的两个函数put(K,V)和get(K),下述代码(1)(2)处是HashMap的精华处
public V put(K key, V value) {
//当key为null,调用putForNullKey方法,保存null与table第一个位置中,这是HashMap允许为null的原因
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//计算key的hash值
int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); ------(1)
//计算key hash 值在 table 数组中的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); ------(2)
//从i出开始迭代 e,找到 key 保存的位置
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判断该条链上是否有hash值相同的(key相同)
//若存在相同,则直接覆盖value,返回旧value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value; //旧值 = 新值
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue; //返回旧值
}
}
//修改次数增加1
modCount++;
//将key、value添加至i位置处
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}我们知道Object类判断相等与否的两个方法hashCode和equals,几个规定: 1、在Java程序执行期间,对同一对象多次执行hashCode(),必须返回相同的整数。2、如果根据equals(Object)方法,两个对象相同,那么对两个对象调用hashCode()也应该返回相同整数结果
static int hash(int h)
{
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
static int indexFor(int h, int length)
{
return h & (length-1);
} 执行put方法,HashMap的数据结构可能发生以下三种结果:

情形3是最少发生的,哈希码发生碰撞属于小概率事件。当不同的对象hashCode发生碰撞时,HashMap通过单链表来解决,将新元素加入链表表头,通过next指向原有的元素。单链表在Java中的实现就是对象的引用(复合),如下所示:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//获取bucketIndex处的Entry
Entry<K, V> e = table[bucketIndex];
//将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entry
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, e);
//若HashMap中元素的个数超过极限了,则容量扩大两倍
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}对HashMap而已,get方法就比较容易了,通过key的hash值找到在table数组中的索引处的Entry,然后返回该key对应的value
public V get(Object key) {
// 若为null,调用getForNullKey方法返回相对应的value
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
// 根据该 key 的 hashCode 值计算它的 hash 码
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
// 取出 table 数组中指定索引处的值
for (Entry<K, V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//若搜索的key与查找的key相同,则返回相对应的value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}HashMap Sample
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Employee> staff = new HashMap<String, Employee>();
staff.put("101", new Employee("Amy"));
staff.put("102", new Employee("Bob"));
staff.put("103", new Employee("Gray"));
staff.put("104", new Employee("France"));
System.out.println(staff);
staff.remove("103");
System.out.println(staff);
staff.put("105", new Employee("Harry"));
System.out.println(staff);
System.out.println(staff.get("101"));
for (Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry : staff.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Employee value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key=" + key + ", value=" + value);
}
Set<String> keys = staff.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.println(key);
}
Collection<Employee> values = staff.values();
for (Employee value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Employee>> iterator = staff.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry = iterator.next();
String key = entry.getKey();
Employee value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key=" + key + ", value=" + value);
}
Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry = staff.entrySet().iterator().next();
System.out.println("key=" + entry.getKey() + ", value=" + entry.getValue());
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String n) {
name = n;
salary = 0;
}
public String toString() {
return "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}HashSet
基于HashMap实现,内部通过HashMap来保存元素,只关心key值,成员变量及add方法如下:
// 使用 HashMap 的 key 保存 HashSet 中所有元素
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// 定义一个虚拟的 Object 对象作为 HashMap 的 value
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
// 将指定元素放入 HashSet 中,也就是将该元素作为 key 放入 HashMap
public boolean add(E e)
{
return map.put(e, PRESENT) == null;
}LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的一个子类,它保留元素插入的顺序,这也是与HashMap的不同之处,它维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表,此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,该迭代顺序可以是插入顺序或者是访问顺序(调用get方法),LinkedHashMap重新定义了Entry,增加了上一个元素before和下一个元素after的引用,从而在哈希表基础上构成了双向链接列表,成员变量如下:
//true表示按照访问顺序迭代,false时表示按照插入顺序(默认)
private final boolean accessOrder;
/**
* 双向链表的表头元素。
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
/**
* LinkedHashMap的Entry元素。
* 继承HashMap的Entry元素,又保存了其上一个元素before和下一个元素after的引用。
*/
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
……
}LinkedHashMap结构及操作流程如下:

LinkedHashMap并未重写父类HashMap的put方法,而是重写了父类HashMap的put方法调用的子方法void recordAccess(HashMap m),void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex)和void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex),提供了自己特有的双向链接列表的实现。 LinkedHashMap定义了排序模式accessOrder,该属性为boolean型变量,对于访问顺序,为true;对于插入顺序,则为false。按照访问模式保存元素,这种映射非常适合LRU(Least Recently Used),LinkedHashMap提供了removeEldestEntry()方法实现删除元素规则,默认返回false,即永远不删除最旧元素。
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 调用create方法,将新元素以双向链表的的形式加入到映射中。
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// 删除最近最少使用元素的策略定义
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
// 调用元素的addBrefore方法,将元素加入到哈希、双向链接列表。
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}LinkedHashMap Sample
public class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Employee> staff = new MyLinkedHashMap<String, Employee>(16, (float)0.75, true);
staff.put("101", new Employee("Amy"));
staff.put("102", new Employee("Bob"));
staff.put("103", new Employee("Gray"));
staff.put("104", new Employee("France"));
System.out.println(staff);
staff.remove("103");
System.out.println(staff);
staff.put("105", new Employee("Harry"));
System.out.println(staff);
//按照访问顺序排序,最新被访问的被放在队尾
Employee e = staff.get("101");
e = staff.get("101");
e = staff.get("104");
System.out.println(staff);
for (Map.Entry<String, Employee> entry : staff.entrySet()) {
String key = entry.getKey();
Employee value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key=" + key + ", value=" + value);
}
Set<String> keys = staff.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.println(key);
}
//通过控制removeEldestEntry返回值,LinkedHashMap会自动删除最不常用的
staff.put("106", new Employee("Tom"));
staff.put("107", new Employee("David"));
Collection<Employee> values = staff.values();
for (Employee value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
class MyLinkedHashMap<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap<K,V> {
private static final int MAX_ENTRIES = 5;
public MyLinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor, accessOrder);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return size() > MAX_ENTRIES;
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String n) {
name = n;
salary = 0;
}
public String toString() {
return "[name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}参考链接:
1. http://blog.csdn.net/chenssy/article/details/18323767
2. http://alex09.iteye.com/blog/539545
3. http://blog.csdn.net/ghsau/article/details/16843543
4. http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26864892-id-3167656.html
5. http://www.cnblogs.com/children/archive/2012/10/02/2710624.html
6. http://blog.csdn.net/hsuxu/article/details/7454212






















 1184
1184











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








