Horizontal Pod Autoscaling:pod的水平自动伸缩。这是k8s自带的模块。
pod占用cpu比率到达一定的阀值,会触发伸缩机制。
replication controller 副本控制器 pod的副本数
deployment controller 节点控制器。部署pod
hpa控制副本的数量以及控制部署pod.
hpa控制副本的数量以及控制部署pod.
1、hpa基于kube-controll-manager服务,周期性的检测pod的cpu使用率默认30秒
2、hpa和replication controller,deployment controller,都属于k8s的资源对象。通过跟踪分析副本控制器和deployment的pod的负载变化,针对性地调整目标pod的副本数。
阀值:正常情况下,pod的副本数,以及达到阀值之后,pod的扩容最大数量。
3、metrics-server 部署到集群中,对外提供度量的数据。
pod的副本数扩缩容有两种方式:
1、手动方式,修改控制器的副本数
kubectl scale deployment nginx1 --replicas=5
修改yaml文件,apply-f部署更新
2、自动扩缩容hpa
hpa的监控的是cpu。
HPA的部署运用
//在所有 Node 节点上传 metrics-server.tar 镜像包到 /opt 目录
cd /opt/
docker load -i metrics-server.tar
#在主master节点上执行
kubectl apply -f components.yaml
vim components.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-admin: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-edit: "true"
rbac.authorization.k8s.io/aggregate-to-view: "true"
name: system:aggregated-metrics-reader
rules:
- apiGroups:
- metrics.k8s.io
resources:
- pods
- nodes
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods
- nodes
- nodes/stats
- namespaces
- configmaps
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server-auth-reader
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: extension-apiserver-authentication-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server:system:auth-delegator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:auth-delegator
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: system:metrics-server
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:metrics-server
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: https
selector:
k8s-app: metrics-server
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
spec:
containers:
- args:
- --cert-dir=/tmp
- --secure-port=4443
- --kubelet-preferred-address-types=InternalIP
- --kubelet-use-node-status-port
- --kubelet-insecure-tls
image: registry.cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/dotbalo/metrics-server:v0.4.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /livez
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
periodSeconds: 10
name: metrics-server
ports:
- containerPort: 4443
name: https
protocol: TCP
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /readyz
port: https
scheme: HTTPS
periodSeconds: 10
securityContext:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-dir
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
priorityClassName: system-cluster-critical
serviceAccountName: metrics-server
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: tmp-dir
---
apiVersion: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: APIService
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: metrics-server
name: v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
spec:
group: metrics.k8s.io
groupPriorityMinimum: 100
insecureSkipTLSVerify: true
service:
name: metrics-server
namespace: kube-system
version: v1beta1
versionPriority: 100
#部署完毕后,可以通过命令来监视pod的资源占用
kubectl top pods
kubectl top nodes
HPA伸缩的测试演示
创建一个用于测试的pod资源
kubectl create deployment hpa-deploy --image=nginx:1.14 --replicas=3 -o yaml >hpa-test.yaml
vim hpa-test.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: hpa-deploy
name: hpa-deploy
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hpa-deploy
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: hpa-deploy
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx:latest
name: nginx-hpa
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 200m
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: hpa-deploy
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: hpa-deploy
创建HPA控制器,进行资源的限制,伸缩管理
使用 kubectl autoscale 命令创建 HPA 控制器,设置 cpu 负载阈值为请求资源的 50%,指定最少负载节点数量为 1 个,最大负载节点数量为 10 个
kubectl autoscale deployment hpa-deploy --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
进入其中一个pod容器仲,进行死循环模拟
kubectl exec -it hpa-deploy-5dfd5cf57b-7f4ls bash
while ture
> do
> echo this is hpa test
> done
开启另一个终端,进行hpa监视:
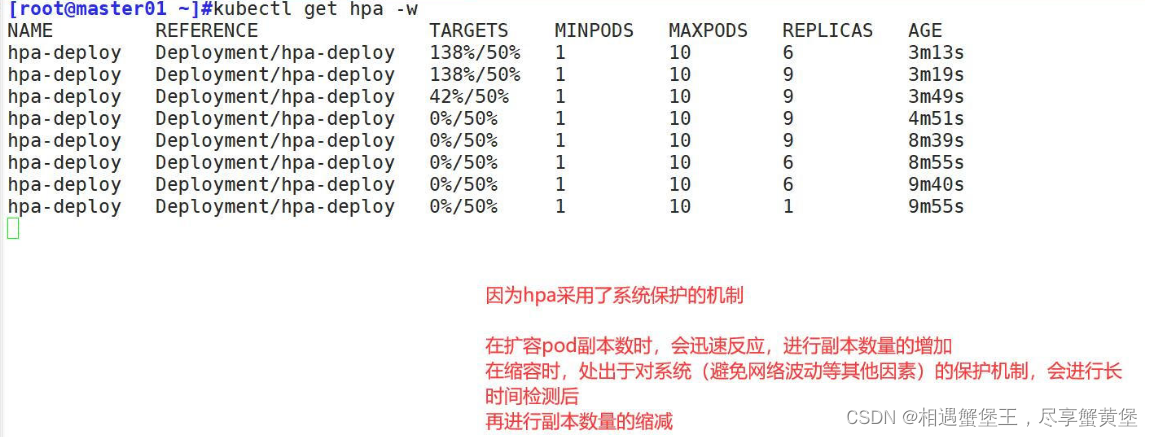
HPA 扩容的时候,负载节点数量上升速度会比较快;但回收的时候,负载节点数量下降速度会比较慢
防止在业务高峰期时因为网络波动等原因的场景下,如果回收策略比较积极的话,K8S集群可能会认为访问流量变小而快速收缩负载节点数量,而仅剩的负载节点又承受不了高负载的压力导致崩溃,从而影响业务。
1、定义pod的时候必须要有资源限制,否则HPA无法进行监控
2、扩容是即时的,只要超过阀值会立刻扩容,不是立刻扩容到最大副本数。他会在最小值和最大值波动。如果扩容的数量满足了需求,不会在扩容
3、缩容是缓慢的。如果业务的峰值较高,回收的策略太积极的话,可能会产生业务的崩溃。缩容的速度是比较慢的。周期性的获取数据,缩容的机制问题。
命名空间的资源限制
命名空间资源限制的配置字段:ResourceQuota
kubectl explain ResourceQuota
计算资源的配额限制
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota #使用 ResourceQuota 资源类型
metadata:
name: compute-resources
namespace: spark-cluster #指定命令空间
spec:
hard:
pods: "20" #设置 Pod 数量最大值
requests.cpu: "2"
requests.memory: 1Gi
limits.cpu: "4"
limits.memory: 2Gi
以上述为例,为已创建的命名空间sapark-cluster进行计算资源限制。首先限制在该命名空间最大的pod数量为20个,预留cpu和最大限制cpu分别为两个与四个。预留内存和最大限制内存分别为2GI和4GI.
配置对象数量配额限制
apiVersion: v1
kind: ResourceQuota
metadata:
name: object-counts
namespace: spark-cluster
spec:
hard:
configmaps: "10"
persistentvolumeclaims: "4" #设置 pvc 数量最大值
replicationcontrollers: "20" #设置 rc 数量最大值
secrets: "10"
services: "10"
services.loadbalancers: "2"
上述为例,该配置是对namespace中所存在的资源对象进行限制。
如果Pod没有设置requests和limits,则会使用当前命名空间的最大资源;如果命名空间也没设置,则会使用集群的最大资源。
K8S 会根据 limits 限制 Pod 使用资源,当内存超过 limits 时 cgruops 会触发 OOM(内存溢出)。
这里就需要创建 LimitRange 资源来设置 Pod 或其中的 Container 能够使用资源的最大默认值:
apiVersion: v1
kind: LimitRange #使用 LimitRange 资源类型
metadata:
name: mem-limit-range
namespace: test #可以给指定的 namespace 增加一个资源限制
spec:
limits:
- default: #default 即 limit 的值
memory: 512Mi
cpu: 500m
defaultRequest: #defaultRequest 即 request 的值
memory: 256Mi
cpu: 100m
type: Container #类型支持 Container、Pod、PVC





















 826
826











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








