Mybatis 源码解析 - 配置、启动加载介绍了mybatis的配置与加载过程,熟悉了mybatis的配置之后,可以大概了解mybatis的概念模型,接下来我们看一下具体的执行过程是什么样子。
一般在使用mybatis的时候,会在DAO层设计一个*Mapper的接口,然后会有与之对应的*Mapper.xml文件,其namespace为接口class的全限定名,而里面的insert* | update* | delete* | select*这些操作标签对应接口里面的方法。
我们在Mapper接口打断点,然后执行到断点的时候,如下图所示:
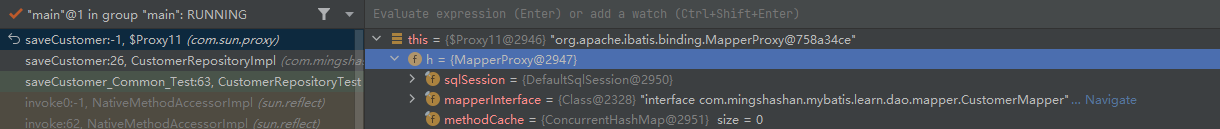
可以看到此时的Mapper接口对应的是
org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy@758a34ce
这明显是一个由MapperProxy派生出来的代理类。
Mapper代理
Mapper接口本身并没有实现类,但是执行到这里我们可以看到是MapperProxy的类定义:
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
}
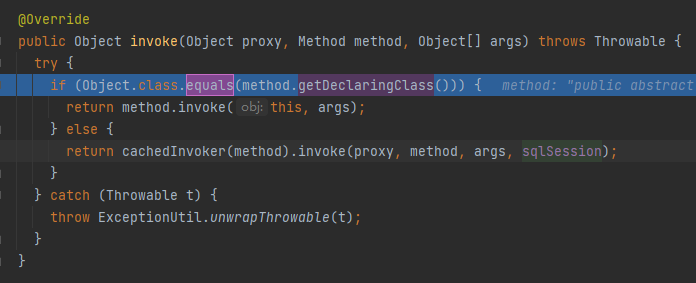
很明显,这是一个基于JDK动态代理实现的代理类,真正执行Mapper里面所定义方法的是MapperProxy的invoke方法。进入到MapperProxy的invoke方法里面
代理模式可以参考:代理模式(Proxy Pattern)
回顾Mapper的加载
再来回顾一下解析加载的过程,在Mybatis解析过程中会把所有能扫描到的Mappers放到MapperRegistr这个容器里面,其简单过程由前面的Mybatis 源码解析 - 配置、启动加载可以知道,在XMLMapperBuilder的bindMapperForNamespace会调用Configuration的addMapper,然后再调用到MapperRegistry.addMapper的方法,即:
XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace
-->
Configuration#addMapper
-->
MapperRegistry#addMapper
addMapper方法也很简单,会把新的Mapper加入到MapperRegistry里面的knownMappers
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
其value是Mapper代理的工厂,通过MapperProxyFactory来生产MapperProxy。
public class MapperRegistry {
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
// 添加新的Mapper到knowMappers这个容器里面
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 是不是是接口
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 是否已经添加过(只能加一次)
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 这里注意value
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 即必须要在parser.parse()方法之前加入到knownMappers里面
// 否则会被parser自动重试。
// MapperAnnotationBuilder处理注解模式的Mapper
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
MapperProxy的生成与调用
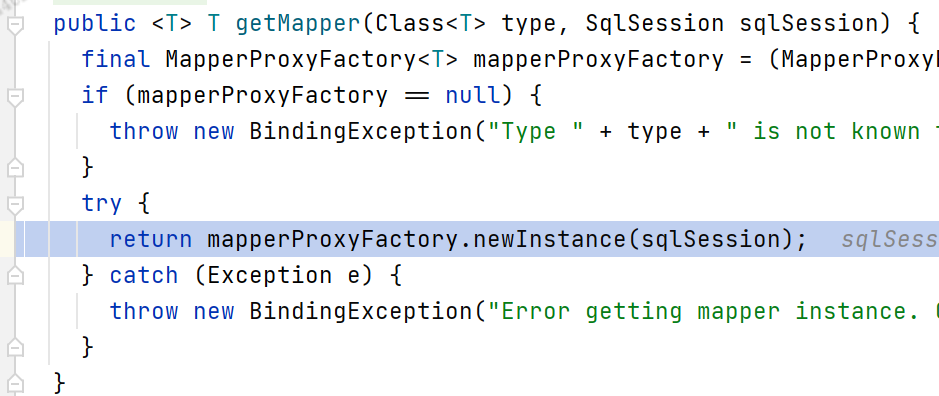
要从MapperRegistory容器里面中,以Mapper接口的class元信息为key,获取对应的Mapper代理类,但是容器里面实际存的是MapperProxyFactory实例。所以:
// 从knownsMappers里面获取MapperProxyFactory实例
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// 调用MapperProxyFactory工厂的newInstance方法生成MapperProxy
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
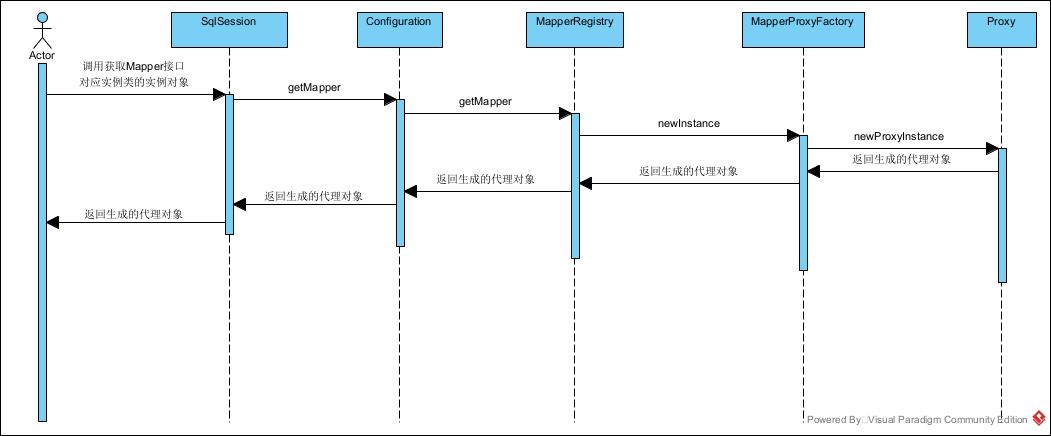
其调试的执行过程见下面图例。
DefaultSqlSession
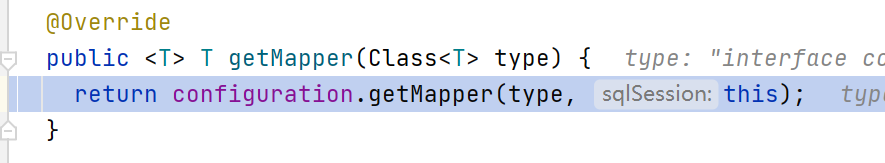
Configuration
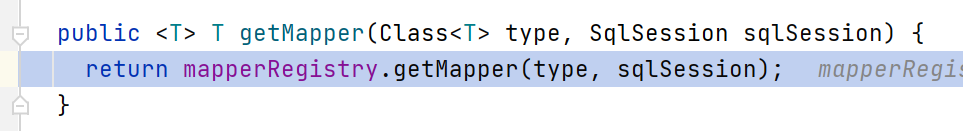
MapperRegistry
MapperProxyFactory

最终会调用java.lang.reflect.Proxy#newProxyInstance来生成代理类。
大概时序图如下所示:
再接着看MapperProxy的invoke方法。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 先判断,如果是Object类的方法走这个分支
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 走下面的分支
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
// 如果是default方法(Java8以后接口的default方法)因为多数情况不是default,所以会走下面的分支
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
// privateLookupIn = MethodHandles.class.getMethod("privateLookupIn", Class.class, MethodHandles.Lookup.class);
// privateLookupIn是Java9之后新增加的,在MethodHandlers里面
// Returns a lookup object with full capabilities to emulate all supported bytecode behaviors
// 主要功能是返回一个具有完整功能的lookup object来模拟所有支持的字节码行为
// 这里判断如果privateLookupInMethod为空,则走getMethodHandleJava8
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// new一个PlainMethodInvoker
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
}
代码里面可以看到,又会调用到MapperMethod。
MapperMethod(Mapper方法的执行类)
可以看到会创建一个MapperMethod,将其放入到MapperMethodInvoker里面,再由MapperMethodInvoker去调用MapperMethod的execute方法。
在new MapperMethod过程中会创建SqlCommand和MethodSignature
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
新建SqlCommand时,会根据mapperInterface与method的名字,拼接成
类全限定名 + . + 方法名的字符串,刚好和Mapper.xml里面namespace+.+id对应。
这样,可以从在启动解析阶段放到Configuration的org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#mappedStatements

找到对应的MappedStatement,其内容如下:
resource = "mapper/CustomerMapper.xml"
configuration = {Configuration@3351}
id = "com.mingshashan.mybatis.learn.dao.mapper.CustomerMapper.saveCustomer"
fetchSize = null
timeout = null
statementType = {StatementType@3578} "PREPARED"
resultSetType = {ResultSetType@3473} "DEFAULT"
sqlSource = {RawSqlSource@3579}
cache = {LoggingCache@3580}
parameterMap = {ParameterMap@3581}
resultMaps = {Collections$UnmodifiableRandomAccessList@3582} size = 0
flushCacheRequired = true
useCache = false
resultOrdered = false
sqlCommandType = {SqlCommandType@3583} "INSERT"
keyGenerator = {NoKeyGenerator@3584}
keyProperties = null
keyColumns = null
hasNestedResultMaps = false
databaseId = null
statementLog = {Jdk14LoggingImpl@3585}
lang = {XMLLanguageDriver@3586}
resultSets = null
然后将MappedStatement#id赋值给SqlCommand#name
将MappedStatement#sqlCommandType赋值给SqlCommand#type
接下来是构造方法签名MethodSignature对象其主要属下如下:
public static class MethodSignature {
private final boolean returnsMany;
private final boolean returnsMap;
private final boolean returnsVoid;
private final boolean returnsCursor;
private final boolean returnsOptional;
private final Class<?> returnType;
private final String mapKey;
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
}
构造好PlainMethodInvoker后,就会通过invoke方法去调用MapperMethod的execute方法。
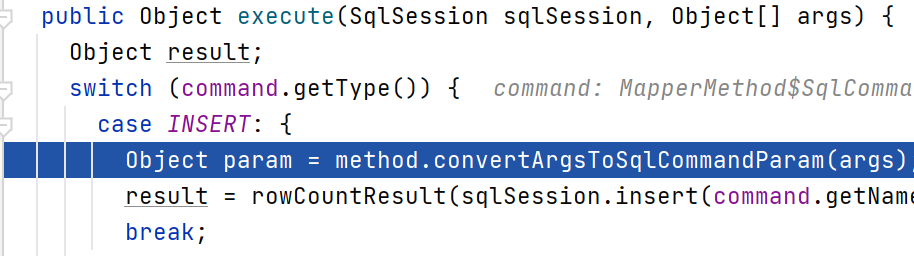
可以看到会根据SqlCommandType走不同的分支:
public enum SqlCommandType {
UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH
}
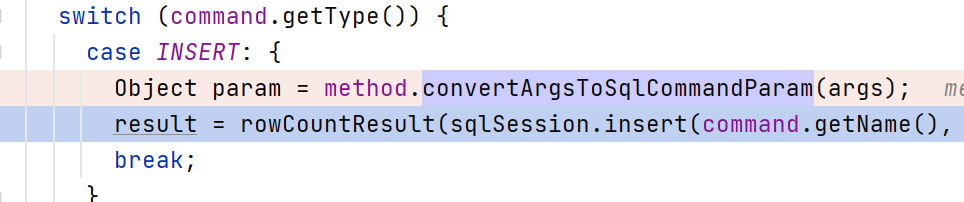
MethodSignature#convertArgsToSqlCommandParam方法会通过ParamNameResolver将传入的参数转换为SqlCommand的参数
sqlSession调用对应的insert或者update等方法,然后再处理返回的结果
而sqlSession又会调用Executor去执行,里面会涉及到缓存的处理,最终会调用mysql驱动的方法然后和数据库交互,再对返回的结果进行一系列的处理。后续的过程会涉及到执行过程中的核心组件(Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、插件等),整体的大概流程如下图所示:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gcJwjlkh-1675509884151)(https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mingshashan/note-images/doc/mybatis-mapper%E5%88%B0executor%E8%BF%87%E7%A8%8B.jpg)]
最后总结一下:
其执行过程是通过基于MapperProxy的代理类,调用到MapperMethod的invoke,然后根据SqlCommand的不同,走不同的分支处理,对返回的结果进行处理,再返回给Mapper调用方法。






















 371
371











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








