题目:实现字典树(前缀树)
Implement a trie with insert, search, and startsWith methods.
Note:
You may assume that all inputs are consist of lowercase letters a-z.
题意:
实现字典树,包含插入,查找和前缀查找方法。
Note:
1、你可以假设所有的输入只包含小写字母a-z。
转载地址:来自 Grandyang的博客,http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4491665.html
Grandyang的博客,http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4491665.html
思路:
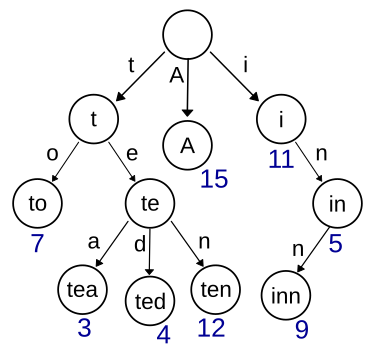
这道题让我们实现一个重要但又有些复杂的数据结构-字典树, 又称前缀树或单词查找树,详细介绍可以参见网友董的博客,例如,一个保存了8个键的trie结构,"A", "to", "tea", "ted", "ten", "i", "in", and "inn".如下图所示:
字典树主要有如下三点性质:
1. 根节点不包含字符,除根节点意外每个节点只包含一个字符。
2. 从根节点到某一个节点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该节点对应的字符串。
3. 每个节点的所有子节点包含的字符串不相同。
字母树的插入(Insert)、删除( Delete)和查找(Find)都非常简单,用一个一重循环即可,即第i 次循环找到前i 个字母所对应的子树,然后进行相应的操作。实现这棵字母树,我们用最常见的数组保存(静态开辟内存)即可,当然也可以开动态的指针类型(动态开辟内存)。至于结点对儿子的指向,一般有三种方法:
1、对每个结点开一个字母集大小的数组,对应的下标是儿子所表示的字母,内容则是这个儿子对应在大数组上的位置,即标号;
2、对每个结点挂一个链表,按一定顺序记录每个儿子是谁;
3、使用左儿子右兄弟表示法记录这棵树。
三种方法,各有特点。第一种易实现,但实际的空间要求较大;第二种,较易实现,空间要求相对较小,但比较费时;第三种,空间要求最小,但相对费时且不易写。
我们先来看第一种实现方法,这种方法实现起来简单直观,字母的字典树每个节点要定义一个大小为26的子节点指针数组,然后用一个标志符用来记录到当前位置为止是否为一个词,初始化的时候讲26个子节点都赋为空。那么insert操作只需要对于要插入的字符串的每一个字符算出其的位置,然后找是否存在这个子节点,若不存在则新建一个,然后再查找下一个。查找词和找前缀操作跟insert操作都很类似,不同点在于若不存在子节点,则返回false。查找次最后还要看标识位,而找前缀直接返回true即可。
代码:C++版:60ms
class TrieNode {
public:
// Initialize your data structure here.
TrieNode *child[26];
bool isWord;
TrieNode() : isWord(false) {
for (auto &a : child) a = NULL;
}
};
class Trie {
public:
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
// Inserts a word into the trie.
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode *p = root;
for (auto &a : word) {
int i = a - 'a';
if (!p->child[i]) p->child[i] = new TrieNode();
p = p->child[i];
}
p->isWord = true;
}
// Returns if the word is in the trie.
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode *p = root;
for (auto &a : word) {
int i = a - 'a';
if (!p->child[i]) return false;
p = p->child[i];
}
return p->isWord;
}
// Returns if there is any word in the trie
// that starts with the given prefix.
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode *p = root;
for (auto &a : prefix) {
int i = a - 'a';
if (!p->child[i]) return false;
p = p->child[i];
}
return true;
}
private:
TrieNode* root;
};
// Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Trie trie;
// trie.insert("somestring");
// trie.search("key");
























 308
308

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








