LinkedList 源码分析
LinkedList 简介
Java源码中的linked list 实际上是数据结构中的双向链表(Doubly-linked list)。实现了List和 Dequeue 接口。针对index的操作会从头或者尾开始进行遍历。LinkedList 线程不安全。
AbstractSequentialList 抽象类
官方解释,这个抽象类提供了一个高效实现“Sequential access” (例如link list)数据结构的方式。“Sequential access” 按照我的理解是一种由前节点定位到下一节点,不需要连续地址块存储的数据。与此相对的是 “random access” 也就是需要连续内存块存储的数据结构,例如数组。“random access” 的数据结构需要实现 AbstractList 接口。
结构
代码结构与AbstractList类似。
LinkedList 线程安全的实现
在多线程环境,更改list结构的行为(eg. add/delete)。需要将LinkedList 安全化,方法如下
- 将其封装在线程安全的对象中;
- 通过 Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList()) 声明;
import java.util.List;
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
private List list;
public MyThread(List l) {
list = l;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for(int i=0;i<2;i++) {
list.add("apple"+i);
}
}
}
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class MyIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList());
for(int i=0;i<5; i++) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyThread(list));
t.start();
System.out.println(list.toString());
}
}
}
LinkedList 源码
两种构造器
一种构造一个空的LinkedList,一种可以将实现了Collection的任一对象转为LinkedList类型。
public LinkedList() {}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
首尾节点 的 get, remove, add
1. get
java提供了getFirst(), getLast()。写法相似,简单易懂。
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
2. remove
removeFirst 通过private的方法unlinkFirst实现,需要注意的是需删除的节点item和next都置为null,以便java垃圾回收时候释放内存。与removeFirst类似,removeLast 调用unlinkLast。实现方式类似。
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
3.add
addFirst(E e) 通过调用private linkFirst实现。
声明一个prev为null,item为参数,next为原首结点空节点,原首结点prev由null改为新节点。
需要注意,addLast 与 add() 的实现方式相同。但是add() 会返回true。
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
contains(Object o)
是否包含给定对象,如果包含返回首次查到的index,否则返回。从前向后遍历。
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
与indexOf类似,lastIndexOf() 返回最后一次出现的位置。
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
remove(Object o) 以及 clear()
1. remove(Object o)
与contains方法类似,一旦找到,执行unlink方法删除。前节点的next指向原节点的next,原节点下一节点的prev指向原节点的前一节点。原节点prev,item,next都设为null。
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
2. clear()
删除所有
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
addAll:
- 首先检测index,如果index<0 或者>size 抛IndexOutOfBoundsException异常;
- 从指定位置开始,插入指定 collection 的所有元素;插入指定collection 的所有元素;
1. addAll
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//检测 index
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
// 如果再尾节点加数组,前继节点为last,后继节点为空。
// 反之,前继节点为index前一位的节点,后继节点为index位的节点
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
2. node(int index)
二分法查询。
E get(index),E set(int index, E element) 也是通过调用node()实现。
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
LinkedList 实现的 Queue 的操作
E peek() : 返回首结点
E element():返回首结点,抛异常
E poll():返回并删除首结点
E remove(): 返回并删除首结点,抛异常
boolean offer(E e):调用add(), 添加结点
boolean offerFirst(E e):调用add(), 添加首结点
boolean offerLast(E e) :看起来和offer作用一致
E peekFirst(): 看起来和peek作用一致, since 1.6
E peekLast(): 返回尾节点,since 1.6
E pollFirst():和poll作用一致,since 1.6
E pollLast():和remove作用一致,since 1.6
void push(E e):调用 addFirst(e),since 1.6
void pop():调用 removeFirst(),since 1.6
boolean removeFirstOccurrence():调用 remove(o),since 1.6
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o): since 1.6, 从后遍历,调用unlink删除第一个匹配项
内部类
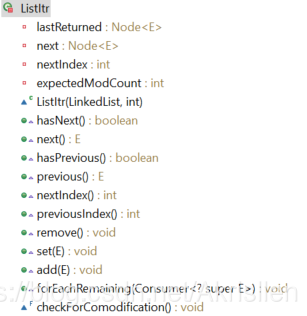
1. ListItr:
2. Node
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
3. DescendingIterator
since 1.6 可以逆向遍历
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}





















 3470
3470











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








