负载均衡就是用来帮助我们将众多的客户端请求合理的分配到各个服务器,以达到服务端资源的充分利用和更少的请求时间,它是日活亿级用户的网站架构中最重要的手段。而Ribbon实现正向代理的软负载均衡,Spring cloud Feign默认集成Ribbon,所以注解@FeignClient的类,默认实现了ribbon的功能,在之前的spring cloud-feign源码中已经提过LoadBalancerFeignClient(this.lbClientFactory.create方法实现了负载均衡)。本文基于spring-cloud-starter-feign 1.4.4.RELEASE。
目录
3.2 Spring Cloud Netflix 提供默认的
前言
大型网站架构的演变
1. 单台服务器简单访问

2. 多台web-server

3. 功能模块拆分后多台web-server(改dns太不方便了)

4. 动静分离+热备(keepalived)

5. 系统规模增大(nginx也扛不住了)引入4层负载均衡LVS
nginx工作在网络的第7层,所以它可以针对http应用本身来做分流策略,比如针对域名、目录结构等。而Lvs工作在网络4层(先改写tcp/ip的目标地址【ip+port】再转发),抗负载能力强,性能高,能达到F5的60%,对内存和CPU资源消耗比较低,且稳定,可靠性高。通常4层负载均衡比7层负载均衡效率更高性能更好。它能撑的并发量取决于机器的内存大小,一般来说撑个几十万并发问题不大!


6. 亿级的PV
为了应对亿级的PV,一般会在DNS端配多个Lvs集群的地址,Lvs层就没有必要再进行扩展新的节点了

nginx负载均衡
nginx是一个高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器,也是一个通用的TCP/UDP代理服务器,最初由俄罗斯人Igor Sysoev编写。
正向代理
意思是一个位于客户端和原始服务器(origin server)之间的服务器,为了从原始服务器取得内容,客户端向代理发送一个请求并指定目标(原始服务器),然后代理向原始服务器转交请求并将获得的内容返回给客户端。正向代理是为我们服务的,即为客户端服务的,客户端可以根据正向代理访问到它本身无法访问到的服务器资源。正向代理对我们是透明的,对服务端是非透明的,即服务端并不知道自己收到的是来自代理的访问还是来自真实客户端的访问。
你可以简单的理解问题:客户端负载均衡,它适用于企业内部微服务之间(内网)
反向代理
(Reverse Proxy)方式是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个反向代理服务器。反向代理是为服务端服务的,反向代理可以帮助服务器接收来自客户端的请求,帮助服务器做请求转发,负载均衡等。反向代理对服务端是透明的,对我们是非透明的,即我们并不知道自己访问的是代理服务器,而服务器知道反向代理在为他服务。
你可以简单的理解问题:服务端负载均衡,它适用于外网接口
使用方法非常简单,在server中拦截响应请求,并将请求转发到Upstream中配置的服务器列表。
server {
server_name xx.server.com;
listen 80;
location /api {
proxy_pass http://balanceServer;
}
}
//默认轮询,这种策略是可以正常工作的,但是如果其中某一台服务器压力太大,出现延迟,会影响所有分配在这台服务器下的用户
upstream balanceServer {
server 10.1.22.33:12345;
server 10.1.22.34:12345;
server 10.1.22.35:12345;
}
//最小连接数策略,将请求优先分配给压力较小的服务器,它可以平衡每个队列的长度,并避免向压力大的服务器添加更多的请求
upstream balanceServer {
least_conn;
server 10.1.22.33:12345;
server 10.1.22.34:12345;
server 10.1.22.35:12345;
}
//最快响应时间策略,依赖于NGINX Plus,优先分配给响应时间最短的服务器。
upstream balanceServer {
fair;
server 10.1.22.33:12345;
server 10.1.22.34:12345;
server 10.1.22.35:12345;
}
//客户端ip绑定,来自同一个ip的请求永远只分配一台服务器,有效解决了动态网页存在的session共享问题
upstream balanceServer {
ip_hash;
server 10.1.22.33:12345;
server 10.1.22.34:12345;
server 10.1.22.35:12345;
}
1. Ribbon功能说明
Ribbon实现客户端的负载均衡,负载均衡器提供很多对http和tcp的行为控制。Ribbon主要包括如下功能:
- RoundRobinRule,轮训策略,默认策略
- RandomRule,随机,使用Random对象从服务列表中随机选择一个服务
- RetryRule,轮询 + 重试
- WeightedResponseTimeRule,优先选择响应时间快,此策略会根据平均响应时间计算所有服务的权重,响应时间越快,服务权重越重、被选中的概率越高。此类有个DynamicServerWeightTask的定时任务,默认情况下每隔30秒会计算一次各个服务实例的权重。刚启动时,如果统计信息不足,则使用RoundRobinRule策略,等统计信息足够,会切换回来
- AvailabilityFilteringRule,可用性过滤,会先过滤掉以下服务:由于多次访问故障而断路器处于打开的服务、并发的连接数量超过阈值,然后对剩余的服务列表按照RoundRobinRule策略进行访问
- BestAvailableRule,优先选择并发请求最小的,刚启动时吗,如果统计信息不足,则使用RoundRobinRule策略,等统计信息足够,才会切换回来
- ZoneAvoidanceRule,可以实现避免可能访问失效的区域(zone)
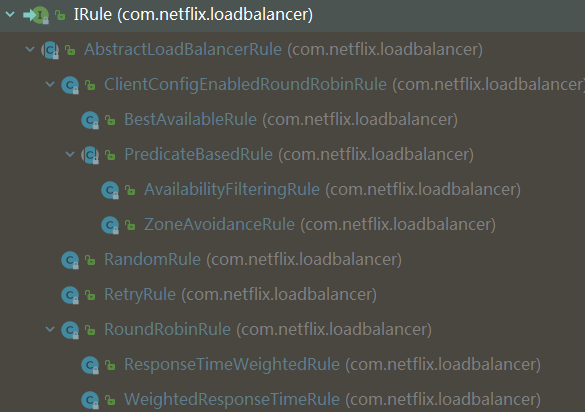
2. 主要组件
Ribbon主要包含如下组件:
- IRule,上面讲过
- IPing,接口定义了我们如何“ping”服务器检查是否活着
- ServerList,定义了获取服务器的列表接口,存储服务列表
- ServerListFilter,接口允许过滤配置或动态获得的候选列表服务器
- ServerListUpdater,接口使用不同的方法来做动态更新服务器列表
- IClientConfig,定义了各种api所使用的客户端配置,用来初始化ribbon客户端和负载均衡器,默认实现是DefaultClientConfigImpl
- ILoadBalancer,接口定义了各种软负载,动态更新一组服务列表及根据指定算法从现有服务器列表中选择一个服务
2.1 IPing
- NIWSDiscoveryPing ,不执行真正的ping。如果Discovery Client认为是在线,则程序认为本次心跳成功,服务活着
- PingUrl ,使用HttpClient调用服务的一个URL,如果调用成功,则认为本次心跳成功,表示此服务活着
- NoOpPing ,永远返回true,即认为服务永远活着
- DummyPing ,默认实现,默认返回true,即认为服务永远活着
2.2 ServerList
服务列表分为静态和动态。如果是动态的,后台有个线程会定时刷新和过滤服务列表
ConfigurationBasedServerList
从配置文件中获取所有服务列表,比如:
kxtx-oms.ribbon.listOfServers=www.microsoft.com:80,www.yahoo.com:80,www.google.com:80
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList
从Eureka Client中获取服务列表。此值必须通过属性中的VipAddress来标识服务器集群。DynamicServerListLoadBalancer(之前也提过)会调用此对象动态获取服务列表。
DomainExtractingServerList
代理类,根据ServerList的值实现具体的逻辑
2.3 ServerListFilter
ServerListFilter是DynamicServerListLoadBalancer用于过滤从ServerList实现返回的服务器的组件。
ZoneAffinityServerListFilter
过滤掉所有的不和客户端在相同zone的服务,如果和客户端相同的zone不存在,才不过滤不同zone有服务。启用此配置使用:
kxtx-oms.ribbon.EnableZoneAffinity=true
ZonePreferenceServerListFilter
ZoneAffinityServerListFilter的子类,但是比较的zone是发布环境里面的zone。过滤掉所有和客户端环境里的配置的zone的不同的服务,如果和客户端相同的zone不存在,才不进行过滤。
ServerListSubsetFilter
ZoneAffinityServerListFilter的子类,确保客户端仅看到由ServerList实现返回的整个服务器的固定子集。 它还可以定期用新服务器替代可用性差的子集中的服务器。要启用此过滤器:
# 选择ServerList获取模式
kxtx-oms.ribbon.NIWSServerListClassName=com.netflix.niws.loadbalancer.DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList
# the server must register itself with Eureka server with VipAddress "myservice"
kxtx-oms.ribbon.DeploymentContextBasedVipAddresses=myservice
kxtx-oms.ribbon.NIWSServerListFilterClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.ServerListSubsetFilter
# only show client 5 servers. default is 20.
kxtx-oms.ribbon.ServerListSubsetFilter.size=52.4 ServerListUpdater
被DynamicServerListLoadBalancer用于动态的更新服务列表。
PollingServerListUpdater
默认的实现策略。此对象会启动一个定时线程池,定时执行更新策略
EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater
当收到缓存刷新的通知,会更新服务列表
2.5 ILoadBalancer
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer组合Rule、IPing、ServerList、ServerListFilter、ServerListUpdater 实现类,实现动态更新和过滤更新服务列表
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer的子类,主要加入zone的因素。统计每个zone的平均请求的情况,保证从所有zone选取对当前客户端服务最好的服务组列表
3. 配置
如果你没有任何配置,则ribbon会使用DefaultClientConfigImpl里的值,有全集配置和局部配置。
配置属性格式:<clientName>.<nameSpace>.<propertyName>=<value>
<clientName>:这是调用ribbon的客户端名称,如果此值为没有配置,则此条属性会作用到所有的客户端
<nameSpace>:默认值为 “ribbon”
<propertyName>:所有的可用的属性都在com.netflix.client.conf.CommonClientConfigKey
3.1 通过配置文件
配置ribbon组合接口使用哪个具体的实现类(xx表示类的全限定名称),更多
格式:<clientName>.<nameSpace>.NFLoadBalancerClassName=xx
###全集配置(设置连接超时时间)
ribbon.ConnectTimeout=600
###局部配置
kxtx-oms.ribbon.ConnectTimeout=3000
3.2 Spring Cloud Netflix 提供默认的
| IClientConfig | DefaultClientConfigImpl |
| IRule | ZoneAvoidanceRule |
| IPing | DummyPing |
| ServerList | ConfigurationBasedServerList |
| ServerListFilter | ZonePreferenceServerListFilter |
| ILoadBalancer | ZoneAwareLoadBalancer |
| ServerListUpdater | PollingServerListUpdater |
4. 源码解析
读spring cloud ribbon源码还是采用按之前解析spring cloud-feign和Spring Cloud Hystrix源码一样的套路,首先要从ribbon加载实例化过程上入手,要知道你做了哪些(加了什么配置或自定义类),spring boot又自动帮你干(向ioc容器注入)了什么,这很重要!接入spring cloud ribbon也是需要两步:
第一步:隐式模式(用户不需要做什么,但你要知道),spirng boot会自动加载ribbon的配置类RibbonAutoConfiguration(spring-cloud-netflix-core-1.4.4.RELEASE.jar/META-INF/spring.factories),为ribbon提供运行所需要的环境(各种相关对象)
第二步:在配置类中添加@RibbonClient或者@RibbonClients(多个),注册类型为RibbonClientSpecification的bean,然后由SpringClientFactory完成对每一个RibbonClientSpecification创建子spring上下文。
注:@RibbonClient可以为每个serviceId(微服务)使用属于自己的负载均衡配置类(IClientConfig、IRule、IPing、ServerList、ILoadBalancer... )
4.1 RibbonAutoConfiguration
RibbonAutoConfiguration定义了Ribbon需要的spring ioc中一些公共的东西,它里面有非常多重要的东西,有子容器管理类,有非懒加载机制等!
RibbonApplicationContextInitializer
ribbon.eager-load.enabled=true //开启Ribbon的饥饿加载模式
ribbon.eager-load.clients=hello-service, user-service //指定需要饥饿加载的客户端名称、服务名
RibbonApplicationContextInitializer本质是一个ioc的事件监听器,主要的作用是根据定义的每个Ribbon Client初始化响应的子容器。知道了它的作用后,你可能会问:饥饿加载模式是个什么鬼?
饥饿加载模式其实就是提前加载(ioc容器初始化后加载),那你又会问:为何需要提前加载呢?
Ribbon进行客户端负载均衡的Client并不是在服务启动的时候就初始化好的,而是在调用的时候才会去创建相应的Client,所以第一次调用的耗时不仅仅包含发送HTTP请求的时间,还包含了创建RibbonClient的时间,这样一来如果创建时间速度较慢(需要创建子容器),同时设置的超时时间又比较短的话,很容易就会出现:第一次请求经常会超时,而之后的调用就没有问题了!
这时候,你可能就对SpringClientFactory比较好奇了吧!
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ IClient.class, RestTemplate.class, AsyncRestTemplate.class, Ribbon.class})
@RibbonClients
@AutoConfigureAfter(name = "org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientAutoConfiguration")
@AutoConfigureBefore({LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class, AsyncLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableConfigurationProperties({RibbonEagerLoadProperties.class, ServerIntrospectorProperties.class})
public class RibbonAutoConfiguration {
//获取ioc中RibbonClientSpecification(每个RibbonClient都会有一个)
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RibbonClientSpecification> configurations = new ArrayList<>();
//饥饿加载模式配置
@Autowired
private RibbonEagerLoadProperties ribbonEagerLoadProperties;
//子容器管理器(后面会讲)
@Bean
public SpringClientFactory springClientFactory() {
SpringClientFactory factory = new SpringClientFactory();
factory.setConfigurations(this.configurations);
return factory;
}
//负载均衡客户端(LoadBalancerInterceptor需要)
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
public LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient() {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerClient(springClientFactory());
}
//饥饿加载模式
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "ribbon.eager-load.enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer ribbonApplicationContextInitializer() {
return new RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(springClientFactory(),
ribbonEagerLoadProperties.getClients());
}
}
//事件驱动的Ribbon client初始化组件
public class RibbonApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent> {
private final SpringClientFactory springClientFactory;
//List of Ribbon client names
private final List<String> clientNames;
public RibbonApplicationContextInitializer(SpringClientFactory springClientFactory,
List<String> clientNames) {
this.springClientFactory = springClientFactory;
this.clientNames = clientNames;
}
private void initialize() {
if (clientNames != null) {
for (String clientName : clientNames) {
//创建对应的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
this.springClientFactory.getContext(clientName);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
initialize();
}
}4.2 SpringClientFactory
SpringClientFactory非常重要,它为每个@RibbonClient创建一个子容器,并通过serviceId获取子容器中的IClient、ILoadBalancer、IClientConfig、RibbonLoadBalancerContext、AnnotationConfigApplicationContext。
因此可以看出Ribbon实现了子容器的隔离,非常棒的做法!
public class SpringClientFactory extends NamedContextFactory<RibbonClientSpecification> {
static final String NAMESPACE = "ribbon";
public SpringClientFactory() {
//RibbonClientConfiguration后面会介绍
super(RibbonClientConfiguration.class, NAMESPACE, "ribbon.client.name");
}
/**
* 根据serviceId获取rest client
* FeignLoadBalancer就是它的实现类,还有RibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient(HttpClient)、OkHttpLoadBalancingClient(OkHttp)
*/
public <C extends IClient<?, ?>> C getClient(String name, Class<C> clientClass) {
return getInstance(name, clientClass);
}
/**
* 根据serviceId获取ILoadBalancer(上面讲过)
*/
public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer(String name) {
return getInstance(name, ILoadBalancer.class);
}
/**
* 根据serviceId获取IClientConfig(上面讲过)
*/
public IClientConfig getClientConfig(String name) {
return getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
}
/**
* 根据serviceId获取RibbonLoadBalancerContext
* FeignLoadBalancer有继承RibbonLoadBalancerContext
*/
public RibbonLoadBalancerContext getLoadBalancerContext(String serviceId) {
return getInstance(serviceId, RibbonLoadBalancerContext.class);
}
static <C> C instantiateWithConfig(Class<C> clazz, IClientConfig config) {
return instantiateWithConfig(null, clazz, config);
}
static <C> C instantiateWithConfig(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context,
Class<C> clazz, IClientConfig config) {
C result = null;
try {
Constructor<C> constructor = clazz.getConstructor(IClientConfig.class);
result = constructor.newInstance(config);
} catch (Throwable e) {
// Ignored
}
if (result == null) {
result = BeanUtils.instantiate(clazz);
if (result instanceof IClientConfigAware) {
((IClientConfigAware) result).initWithNiwsConfig(config);
}
if (context != null) {
context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory().autowireBean(result);
}
}
return result;
}
@Override
public <C> C getInstance(String name, Class<C> type) {
C instance = super.getInstance(name, type);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
}
IClientConfig config = getInstance(name, IClientConfig.class);
return instantiateWithConfig(getContext(name), type, config);
}
//根据serviceId获取Ioc容器(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)
@Override
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
return super.getContext(name);
}
}
//与上面的是继承关系
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification> implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
//所有的子容器映射关系
private Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap();
//获取一个子容器
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
Map var2 = this.contexts;
synchronized(this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
//创建子容器
this.contexts.put(name, this.createContext(name));
}
}
}
return (AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)this.contexts.get(name);
}
//创建一个子容器
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
//注入@RibbonClient的configuration
Class[] var3 = ((NamedContextFactory.Specification)this.configurations.get(name)).getConfiguration();
int var4 = var3.length;
for(int var5 = 0; var5 < var4; ++var5) {
Class<?> configuration = var3[var5];
context.register(new Class[]{configuration});
}
}
Iterator var9 = this.configurations.entrySet().iterator();
while(true) {
Entry entry;
do {
if (!var9.hasNext()) {
//注入RibbonClientConfiguration与配置
context.register(new Class[]{PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class, this.defaultConfigType});
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(this.propertySourceName, Collections.singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
context.refresh();
return context;
}
entry = (Entry)var9.next();
} while(!((String)entry.getKey()).startsWith("default."));
Class[] var11 = ((NamedContextFactory.Specification)entry.getValue()).getConfiguration();
int var12 = var11.length;
for(int var7 = 0; var7 < var12; ++var7) {
Class<?> configuration = var11[var7];
context.register(new Class[]{configuration});
}
}
}
}4.3 RibbonClientConfiguration
RibbonClientConfiguration也很重要,每个子容器中都会注入RibbonClientConfiguration。
//定义了单个ribbon client需要的各个组件
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
//Order is important here, last should be the default, first should be optional
// see https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/2086#issuecomment-316281653
@Import({HttpClientConfiguration.class, OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class, RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class})
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
public static final int DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 1000;
public static final int DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT = 1000;
@Value("${ribbon.client.name}")
private String name = "client";
// TODO: maybe re-instate autowired load balancers: identified by name they could be
// associated with ribbon clients
@Autowired
private PropertiesFactory propertiesFactory;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {
DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();
config.loadProperties(this.name);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout, DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
config.set(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout, DEFAULT_READ_TIMEOUT);
return config;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name);
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();
rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return rule;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, name);
}
return new DummyPing();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name);
}
ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {
return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerListFilter<Server> ribbonServerListFilter(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerListFilter.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerListFilter.class, config, name);
}
ZonePreferenceServerListFilter filter = new ZonePreferenceServerListFilter();
filter.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return filter;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RibbonLoadBalancerContext ribbonLoadBalancerContext(ILoadBalancer loadBalancer,
IClientConfig config, RetryHandler retryHandler) {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerContext(loadBalancer, config, retryHandler);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RetryHandler retryHandler(IClientConfig config) {
return new DefaultLoadBalancerRetryHandler(config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector() {
return new DefaultServerIntrospector();
}
@PostConstruct
public void preprocess() {
setRibbonProperty(name, DeploymentContextBasedVipAddresses.key(), name);
}
}4.4 LoadBalancerFeignClient
Client本身就是(执行get/post)rest客户端,而LoadBalancerFeignClient在它的基础上具备负载均衡的功能,负载均衡器的加载时通过CachingSpringLoadBalancerFactory完成的。
public class LoadBalancerFeignClient implements Client {
//包装了SpringClientFactory 的实现
private CachingSpringLoadBalancerFactory lbClientFactory;
private SpringClientFactory clientFactory;
//执行请求
@Override
public Response execute(Request request, Request.Options options) throws IOException {
try {
URI asUri = URI.create(request.url());
String clientName = asUri.getHost();
URI uriWithoutHost = cleanUrl(request.url(), clientName);
FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest ribbonRequest = new FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest(
this.delegate, request, uriWithoutHost);
IClientConfig requestConfig = getClientConfig(options, clientName);
//执行的是FeignLoadBalancer.execute(后面介绍)
return lbClient(clientName).executeWithLoadBalancer(ribbonRequest,
requestConfig).toResponse();
}
catch (ClientException e) {
IOException io = findIOException(e);
if (io != null) {
throw io;
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//加载配置
IClientConfig getClientConfig(Request.Options options, String clientName) {
IClientConfig requestConfig;
if (options == DEFAULT_OPTIONS) {
requestConfig = this.clientFactory.getClientConfig(clientName);
} else {
requestConfig = new FeignOptionsClientConfig(options);
}
return requestConfig;
}
//加载负载均衡组件
private FeignLoadBalancer lbClient(String clientName) {
return this.lbClientFactory.create(clientName);
}
}4.5 FeignLoadBalancer
前提:如果你使用的Feign的方式与其他服务通讯的话,那FeignLoadBalancer的确是入口!LoadBalancerContext通过getServerFromLoadBalancer方法获取一个Server(内部调用调用ILoadBalancer的chooseServer方法)。
默认是不启用重试,如果启用重试则创建RetryableFeignLoadBalancer,否则创建FeignLoadBalancer。
public class FeignLoadBalancer extends
AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient<FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonRequest, FeignLoadBalancer.RibbonResponse> {
protected int connectTimeout;
protected int readTimeout;
protected IClientConfig clientConfig;
protected ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector;
public FeignLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer lb, IClientConfig clientConfig,
ServerIntrospector serverIntrospector) {
super(lb, clientConfig);
this.setRetryHandler(RetryHandler.DEFAULT);
this.clientConfig = clientConfig;
this.connectTimeout = clientConfig.get(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout);
this.readTimeout = clientConfig.get(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout);
this.serverIntrospector = serverIntrospector;
}
//执行请求调用
@Override
public RibbonResponse execute(RibbonRequest request, IClientConfig configOverride)
throws IOException {
Request.Options options;
if (configOverride != null) {
options = new Request.Options(
configOverride.get(CommonClientConfigKey.ConnectTimeout,
this.connectTimeout),
(configOverride.get(CommonClientConfigKey.ReadTimeout,
this.readTimeout)));
}
else {
options = new Request.Options(this.connectTimeout, this.readTimeout);
}
Response response = request.client().execute(request.toRequest(), options);
return new RibbonResponse(request.getUri(), response);
}
}
//FeignLoadBalancer的父类
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient<S extends ClientRequest, T extends IResponse> extends LoadBalancerContext implements IClient<S, T>, IClientConfigAware {
//真正执行负载均衡
public T executeWithLoadBalancer(final S request, final IClientConfig requestConfig) throws ClientException {
RequestSpecificRetryHandler handler = getRequestSpecificRetryHandler(request, requestConfig);
LoadBalancerCommand<T> command = LoadBalancerCommand.<T>builder()
.withLoadBalancerContext(this)
.withRetryHandler(handler)
.withLoadBalancerURI(request.getUri())
.build();
try {
return command.submit(
new ServerOperation<T>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
URI finalUri = reconstructURIWithServer(server, request.getUri());
S requestForServer = (S) request.replaceUri(finalUri);
try {
return Observable.just(AbstractLoadBalancerAwareClient.this.execute(requestForServer, requestConfig));
}
catch (Exception e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
})
.toBlocking()
.single();
} catch (Exception e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof ClientException) {
throw (ClientException) t;
} else {
throw new ClientException(e);
}
}
}
}
//继承FeignLoadBalancer
public class RetryableFeignLoadBalancer extends FeignLoadBalancer implements ServiceInstanceChooser {
}
public class LoadBalancerCommand<T> {
private Observable<Server> selectServer() {
return Observable.create(new OnSubscribe<Server>() {
@Override
public void call(Subscriber<? super Server> next) {
try {
//负载均衡,选择一个sever
Server server = loadBalancerContext.getServerFromLoadBalancer(loadBalancerURI, loadBalancerKey);
next.onNext(server);
next.onCompleted();
} catch (Exception e) {
next.onError(e);
}
}
});
}
public Observable<T> submit(final ServerOperation<T> operation) {
final ExecutionInfoContext context = new ExecutionInfoContext();
if (listenerInvoker != null) {
try {
listenerInvoker.onExecutionStart();
} catch (AbortExecutionException e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
final int maxRetrysSame = retryHandler.getMaxRetriesOnSameServer();
final int maxRetrysNext = retryHandler.getMaxRetriesOnNextServer();
// Use the load balancer
Observable<T> o =
(server == null ? selectServer() : Observable.just(server))
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
@Override
// Called for each server being selected
public Observable<T> call(Server server) {
context.setServer(server);
final ServerStats stats = loadBalancerContext.getServerStats(server);
// Called for each attempt and retry
Observable<T> o = Observable
.just(server)
.concatMap(new Func1<Server, Observable<T>>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(final Server server) {
context.incAttemptCount();
loadBalancerContext.noteOpenConnection(stats);
if (listenerInvoker != null) {
try {
listenerInvoker.onStartWithServer(context.toExecutionInfo());
} catch (AbortExecutionException e) {
return Observable.error(e);
}
}
final Stopwatch tracer = loadBalancerContext.getExecuteTracer().start();
return operation.call(server).doOnEach(new Observer<T>() {
private T entity;
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
recordStats(tracer, stats, entity, null);
// TODO: What to do if onNext or onError are never called?
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
recordStats(tracer, stats, null, e);
logger.debug("Got error {} when executed on server {}", e, server);
if (listenerInvoker != null) {
listenerInvoker.onExceptionWithServer(e, context.toExecutionInfo());
}
}
@Override
public void onNext(T entity) {
this.entity = entity;
if (listenerInvoker != null) {
listenerInvoker.onExecutionSuccess(entity, context.toExecutionInfo());
}
}
private void recordStats(Stopwatch tracer, ServerStats stats, Object entity, Throwable exception) {
tracer.stop();
loadBalancerContext.noteRequestCompletion(stats, entity, exception, tracer.getDuration(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS), retryHandler);
}
});
}
});
if (maxRetrysSame > 0)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysSame, true));
return o;
}
});
if (maxRetrysNext > 0 && server == null)
o = o.retry(retryPolicy(maxRetrysNext, false));
return o.onErrorResumeNext(new Func1<Throwable, Observable<T>>() {
@Override
public Observable<T> call(Throwable e) {
if (context.getAttemptCount() > 0) {
if (maxRetrysNext > 0 && context.getServerAttemptCount() == (maxRetrysNext + 1)) {
e = new ClientException(ClientException.ErrorType.NUMBEROF_RETRIES_NEXTSERVER_EXCEEDED,
"Number of retries on next server exceeded max " + maxRetrysNext
+ " retries, while making a call for: " + context.getServer(), e);
}
else if (maxRetrysSame > 0 && context.getAttemptCount() == (maxRetrysSame + 1)) {
e = new ClientException(ClientException.ErrorType.NUMBEROF_RETRIES_EXEEDED,
"Number of retries exceeded max " + maxRetrysSame
+ " retries, while making a call for: " + context.getServer(), e);
}
}
if (listenerInvoker != null) {
listenerInvoker.onExecutionFailed(e, context.toFinalExecutionInfo());
}
return Observable.error(e);
}
});
}
}4.6 LoadBalancerInterceptor
在读完FeignLoadBalancer的时候,你可能会想:我并没有使用Feign的方式与其他服务通讯,而是直接使用了spring的RestTemplate,那整个交换是怎样的呢?
的确,Spring RestTemplate(封装了 HTTP 相关方法的模板类)非常好用,通过setInterceptors实现负载均衡的。HttpClient的RibbonLoadBalancingHttpClient()、OkHttp的OkHttpLoadBalancingClient也是同理!
//自启动配置(spring.factories)
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(RestTemplate.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(LoadBalancerClient.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(LoadBalancerRetryProperties.class)
public class LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration {
//启动负载均衡,获取所有的RestTemplate
@LoadBalanced
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<RestTemplate> restTemplates = Collections.emptyList();
//SmartInitializingSingleton是容器级:非lazy单例Bean实例化完成后的回调方法
@Bean
public SmartInitializingSingleton loadBalancedRestTemplateInitializer(
final List<RestTemplateCustomizer> customizers) {
return new SmartInitializingSingleton() {
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
for (RestTemplate restTemplate : LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration.this.restTemplates) {
for (RestTemplateCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
//对restTemplate再次重新定义
customizer.customize(restTemplate);
}
}
}
};
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("org.springframework.retry.support.RetryTemplate")
static class LoadBalancerInterceptorConfig {
//定义负载均衡拦截器
@Bean
public LoadBalancerInterceptor ribbonInterceptor(
LoadBalancerClient loadBalancerClient,
LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
return new LoadBalancerInterceptor(loadBalancerClient, requestFactory);
}
//RestTemplateCustomizer是RestTemplate的加工类
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RestTemplateCustomizer restTemplateCustomizer(
final LoadBalancerInterceptor loadBalancerInterceptor) {
return new RestTemplateCustomizer() {
@Override
public void customize(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
List<ClientHttpRequestInterceptor> list = new ArrayList<>(
restTemplate.getInterceptors());
list.add(loadBalancerInterceptor);
//核心所在
restTemplate.setInterceptors(list);
}
};
}
}
}
//RestTemplate请求拦截器
public class LoadBalancerInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {
private LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer;
private LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory;
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer, LoadBalancerRequestFactory requestFactory) {
this.loadBalancer = loadBalancer;
this.requestFactory = requestFactory;
}
public LoadBalancerInterceptor(LoadBalancerClient loadBalancer) {
// for backwards compatibility
this(loadBalancer, new LoadBalancerRequestFactory(loadBalancer));
}
@Override
public ClientHttpResponse intercept(final HttpRequest request, final byte[] body,
final ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {
final URI originalUri = request.getURI();
String serviceName = originalUri.getHost();
Assert.state(serviceName != null, "Request URI does not contain a valid hostname: " + originalUri);
//构建LoadBalancerRequest请求,并请求RibbonLoadBalancerClient.execute
return this.loadBalancer.execute(serviceName, requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution));
}
}如果你对spring cloud Ribbon的内部实现也比较敢兴趣,建议线程spring cloud-feign入手,一层一层的了解。























 531
531











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








