前置条件
下载pytest包
Tools-Python Integrated Tools-Default test runner:改为pytest
命名要点
文件以test_开头或以_test结尾
类以Test开头
方法/函数以test_开头
包名无限制,每个包下必须含有_init_.py文件
请问为什么网上说每个包下面必须要有__init__.py文件 - 提问区 - 测试人社区
注:测试类中不可以添加_init_构造函数
用例结构
class TestDemo:
def setup(self):
资源准备(例如打开应用或者页面,连
接数据库等)
def teardown(self):
资源销毁(例如关闭应用或者页面,断
连数据库等)
def test_demo(self):
测试具体步骤及断言Pytest测试框架结构
setup_module,teardown_module全局模块级,每个模块前各执行一次
setup_class,teardown_class类级,只在类前后各执行一次
setup_function,teardown_function函数级,在类外,函数前后各执行一次
setup_method,teardown_method方法级,在类中,方法前后各执行一次
import pytest;
def setup_module():
print("资源准备_module")
def teardown_module():
print("资源销毁_module")
def inc(x):
return x + 1
def test_wer():
print(1)
def test_ans():
assert inc(4) == 5
def setup_function():
print("资源准备")
def teardown_function():
print("资源销毁")
class TestDemo:
def setup_method(self):
print("setup");
def teardown_method(self):
print("teardown");
def setup_class(self):
print("setup_class");
def teardown_class(self):
print("teardown_class");
def test_demo01(self):
print("test_demo01");
def test_demo02(self):
print("test_demo02");
运行结果如下:

参数化用例
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize(...)
def test_...(...):
...单参数
import pytest
search_list = ['appium','selenium','pytest']
@pytest.mark.parametrize('name',search_list)
def test_search(name):
assert name in search_list多参数
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[("3+5",8),("2+5",7)])
def test_mark_more(test_input, expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
笛卡尔积
import pytest;
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input",["1+2","1+3"])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("expected",[3,4])
def test_para3(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected运行结果如下:

用例重命名ids
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[("3+5",8),("2+5",7)]
,ids=["case1","case2"])
def test_mark_more(test_input, expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected重命名前:

重命名后:

补充:python的eval函数_python eval-CSDN博客
标记测试用例
在方法前添加@pytest.mark.标签名
执行特定测试用例
pytest ….py -vs -m 标签名
import pytest
def double(a):
return a * 2;
@pytest.mark.int
def test_int():
assert double(2) == 4
@pytest.mark.float
def test_float():
assert double(2.0) == 4.0
@pytest.mark.str
def test_str1():
assert double("2") == '22'
@pytest.mark.str
def test_str2():
assert double("3") == '33'pytest test_mark.py -vs -m str执行命令后结果如下:

pytest.ini(在根目录下创建该文件)
【Python】深入理解pytest.ini的配置方法和参数_pytest.ini文件创建在哪儿-CSDN博客
markers定义测试标记
[pytest]
markers = int
float
str定义前:
![]()
定义后(不再进行报错):
![]()
跳过用例
方案一 在方法前添加
@pytest.mark.skip(reason=…)
import pytest
@pytest.mark.skip
def test_skip1():
print(1)
@pytest.mark.skip(reason="代码尚未编译")
def test_skip2():
print(1)@pytest.matk.skipif(condition=…,reason=…)
@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.platform == 'win32', reason="work on windows")
def test_skip4():
print("win32")
@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.platform == 'darwin', reason="does not work on macOS")
def test_skip5():
print("mac")sys.platform为win32,运行结果如下:
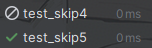
方案二 在方法中添加
pytest.skip(…)
def test_skip3():
print("start")
if(1 == 1):
pytest.skip("false")
print("end")if语句条件成立,执行跳过语句,运行结果如下:

预期失败用例
方案一 在方法前添加
@pytest.mark.xfail(reason=…)
@pytest.mark.xfail
def test_xfail1():
assert 2 == 3 另可以自定义标签为xfail,skip,skipif等
这里定义为xfail
xfail = pytest.mark.xfail
@xfail(reason="success")
def test_xfail_1():
assert 2 == 2
@xfail(reason="false")
def test_xfail_2():
assert 2 == 3test_xfail_1运行结果如下:
![]()
test_xfail_2运行结果如下:

方案二 在方法中添加
pytest.xfail(…)
def test_xfail3():
print("start")
pytest.xfail(reason="bug")
assert 2 == 2在函数中调用pytest.xfail,后续语句不会执行

运行用例
右键文件夹打开对应Terminal或者直接在Terminal中cd到对应文件夹
执行文件
pytest 文件名.py
执行类
pytest 文件名.py::类名
执行方法
pytest 文件名.py::方法名
pytest 文件名.py::类名::方法名
常用命令行参数
-x 用例一旦失败就立刻停止执行
-v 打印详细日志
-s 打印输出日志(一般-vs一起使用)
-k 执行包含某个关键字的测试用例(用例名中包含关键字也会被执行)
--maxfail 允许失败的最大用例个数(达到则立刻停止执行)
--lf 执行上次失败的测试用例
--ff 优先执行上次失败的测试用例,再执行剩余的测试用例
举例
pytest -k "1" -v执行结果:

Python执行Pytest
方案一 main函数调用
import pytest
if __name__ == "__main__":
#1.运行当前目录下所有符合规则的用例,包括子目录
pytest.main()
#2.运行具体文件用例(可具体到类、方法)
pytest.main(['test_mark.py','-vs'])
#3.运行某个标签
pytest.main(['test_mark.py','-vs','-m','str'])执行方式:
python 文件名.py方案二 python-m pytest调用pytest
python -m pytest 文件名.pyPytest异常处理
pytest.raises()
捕获特定异常
获取捕获的异常的细节
发生异常则后面的代码不会被执行
import pytest
def test_raise1():
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match='must be 0 or None'):
raise ValueError('must be 0 or None')
def test_raise2():
with pytest.raises(ValueError) as exc_info:
raise ValueError('must be 0 or None')
assert exc_info.value.args[0] == 'must be 0 or None'




















 669
669

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








