android4 SystemUI 流程分析
什么是SystemUI?
对于Phone来说SystemUI指的是:StatusBar(状态栏)、NavigationBar(导航栏)。而对于Tablet或者是TV来说SystemUI指的是:CombinedBar(包括了StatusBar和NavigationBar)。
启动后Phone界面上的信号,蓝牙标志,Wifi标志等等这些状态显示标志都会在StatusBar上显示。当我们的设备开机后,首先
需要给用户呈现的就是各种界面同时也包括了我们的SystemUI,因此对于整个Android系统来说,SystemUI都有举足轻重的作用。
现在就从代码开始一步步的分析
1、启动流程
代码路径:fameworks/base/packages/SystemUI
建立工程导入到eclipse中代码具体图示:
先从 AndroidManifest.xml 看看有哪些东东,以前说过android中有四大组件,这里就有如下的三大部分:
系统服务 Service :
SystemUIService
TakeScreenshotService
LoadAverageService
广播接收器 BroadcastReceive:
BootReceiver
Activity 应用:
USB的挺多哟...
UsbStorageActivity
UsbConfirmActivity
UsbPermissionActivity
UsbStorageActivity
UsbAccessoryUriActivity
NetworkOverLimitActivity
<!-- started from ... somewhere -->
Nyandroid
具体定义请看 AndroidManifest.xml 文件,上面只是简单的列一下
先看第一个Activity -- Nyandroid 这里做了什么呢?
就是网上传说中的 好多安卓机器人飞过去。。。。其中代码很简单,简单说一下动画效果的代码:
public class FlyingCat extends ImageView {
public FlyingCat(Context context, AttributeSet as) {
super(context, as);
setImageResource(R.drawable.nyandroid_anim); // @@@
if (DEBUG) setBackgroundColor(0x80FF0000);
}
...
}定义在 frameworks\base\packages\SystemUI\res\drawable\nyandroid_anim.xml
<animation-list
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:oneshot="false">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid00" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid01" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid02" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid03" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid04" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid05" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid06" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid07" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid08" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid09" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid10" android:duration="80" />
<item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid11" android:duration="80" />
</animation-list>相关图片在: frameworks\base\packages\SystemUI\res\drawable-nodpi 如图示:
然后再看最重要的服务:SystemUIService
一般来说,Service启动一般由开机广播或者StartService/BindService这几种方式来启动。既然这个Service是一个系统
服务,应该是由系统这边启动,那么看下 SystemServer.java ,果然发现如下启动代码:
startSystemUi(contextF);
static final void startSystemUi(Context context) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.android.systemui",
"com.android.systemui.SystemUIService"));
Slog.d(TAG, "Starting service: " + intent);
context.startService(intent);
}对于Android启动流程请看如下系统文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7346203 android启动--深入理解init进程
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7349986 android启动--深入理解zygote
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7351691 android启动--深入理解zygote (II)
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7353910 android启动--深入理解启动HOME
那么就继续跟踪 SystemUIService 中代码:
/**
* The class names of the stuff to start.
*/
final Object[] SERVICES = new Object[] {
0, // system bar or status bar, filled in below.
com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class,
};
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// Pick status bar or system bar.
IWindowManager wm = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE));
try {
SERVICES[0] = wm.canStatusBarHide()
? R.string.config_statusBarComponent
: R.string.config_systemBarComponent;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failing checking whether status bar can hide", e);
}
final int N = SERVICES.length;
mServices = new SystemUI[N];
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Class cl = chooseClass(SERVICES[i]);
Slog.d(TAG, "loading: " + cl);
try {
mServices[i] = (SystemUI)cl.newInstance();
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
mServices[i].mContext = this;
Slog.d(TAG, "running: " + mServices[i]);
mServices[i].start();
}
}在这代码中:
SERVICES[0] = wm.canStatusBarHide()
? R.string.config_statusBarComponent
: R.string.config_systemBarComponent;
通过AIDL获取WindowManager对象并调用 wm.canStatusBarHide() 这个代码在哪里呢?
查看: frameworks/base/policy/src/com/android/internal/policy/impl/PhoneWindowManager.java
public boolean canStatusBarHide() {
return mStatusBarCanHide;
}
public void setInitialDisplaySize(int width, int height) {
...
// Determine whether the status bar can hide based on the size
// of the screen. We assume sizes > 600dp are tablets where we
// will use the system bar.
int shortSizeDp = shortSize
* DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT
/ DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEVICE;
mStatusBarCanHide = shortSizeDp < 600;
}从以上代码来看,shortSizeDp小于600dp时,则系统会认为该设备是Phone反之则认为是Tablet。
根据mStatusBarCanHide的值,设定StatusBar或者SystemBar(CombinedBar)的高度,以及是否显示NavigationBar。
2、StatusBar(状态栏)及NavigationBar(导航栏)
如果是 StatusBar 则 SERVICES[0] 存放 com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.PhoneStatusBar 否则存放
com.android.systemui.statusbar.tablet.TabletStatusBar
SERVICES[1] 存放 com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class
从我的机器上打印来看,
E/SystemServer( 1299): Starting service: Intent { cmp=com.android.systemui/.SystemUIService }
D/SystemUIService( 1382): running: com.android.systemui.statusbar.tablet.TabletStatusBar@415b8b20
D/SystemUIService( 1382): running: com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI@416b5ae8
I/PowerUI ( 1382): start
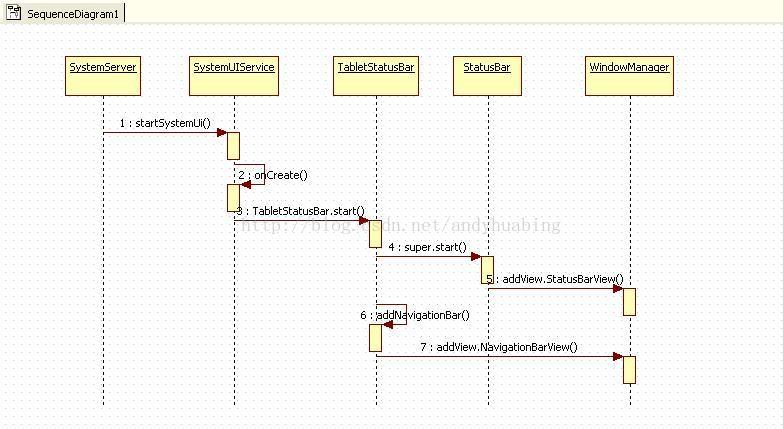
然后调用 mServices[i].start();那么就分析 TabletStatusBar 中的start方法吧
@Override
public void start() {
super.start(); // will add the main bar view
}调用到 frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/StatusBar.java
public void start() {
// First set up our views and stuff.
View sb = makeStatusBarView();
// Connect in to the status bar manager service
StatusBarIconList iconList = new StatusBarIconList();
ArrayList<IBinder> notificationKeys = new ArrayList<IBinder>();
ArrayList<StatusBarNotification> notifications = new ArrayList<StatusBarNotification>();
mCommandQueue = new CommandQueue(this, iconList);
mBarService = IStatusBarService.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.STATUS_BAR_SERVICE));
int[] switches = new int[7];
ArrayList<IBinder> binders = new ArrayList<IBinder>();
try {
mBarService.registerStatusBar(mCommandQueue, iconList, notificationKeys, notifications,
switches, binders);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// If the system process isn't there we're doomed anyway.
}
disable(switches[0]);
setSystemUiVisibility(switches[1]);
topAppWindowChanged(switches[2] != 0);
// StatusBarManagerService has a back up of IME token and it's restored here.
setImeWindowStatus(binders.get(0), switches[3], switches[4]);
setHardKeyboardStatus(switches[5] != 0, switches[6] != 0);
// Set up the initial icon state
int N = iconList.size();
int viewIndex = 0;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
StatusBarIcon icon = iconList.getIcon(i);
if (icon != null) {
addIcon(iconList.getSlot(i), i, viewIndex, icon);
viewIndex++;
}
}
// Set up the initial notification state
N = notificationKeys.size();
if (N == notifications.size()) {
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
addNotification(notificationKeys.get(i), notifications.get(i));
}
} else {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Notification list length mismatch: keys=" + N
+ " notifications=" + notifications.size());
}
// Put up the view
final int height = getStatusBarHeight();
final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
height,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TOUCHABLE_WHEN_WAKING
| WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH,
PixelFormat.OPAQUE);
// the status bar should be in an overlay if possible
final Display defaultDisplay
= ((WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE))
.getDefaultDisplay();
if (ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx(defaultDisplay)) {
lp.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
}
lp.gravity = getStatusBarGravity();
lp.setTitle("StatusBar");
lp.packageName = mContext.getPackageName();
lp.windowAnimations = R.style.Animation_StatusBar;
WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(sb, lp);
if (SPEW) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Added status bar view: gravity=0x" + Integer.toHexString(lp.gravity)
+ " icons=" + iconList.size()
+ " disabled=0x" + Integer.toHexString(switches[0])
+ " lights=" + switches[1]
+ " menu=" + switches[2]
+ " imeButton=" + switches[3]
);
}
mDoNotDisturb = new DoNotDisturb(mContext);
}在这里,完成了SystemUI的整个初始化以及设置过程,并最终呈现到界面上。
启动过程中完成如下操作:
1、获取icon list,addIcon(iconList.getSlot(i), i, viewIndex, icon);
2、获取notification,addNotification(notificationKeys.get(i), notifications.get(i));
3、显示StatusBar,WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(sb, lp);
显示NavigationBar,WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(
mNavigationBarView, getNavigationBarLayoutParams());
时序图如下:
3、最近任务缩略图显示
长按home键,列出最近启动过的任务缩略图,重要的两个类
// Recent apps
private RecentsPanelView mRecentsPanel;
private RecentTasksLoader mRecentTasksLoader;
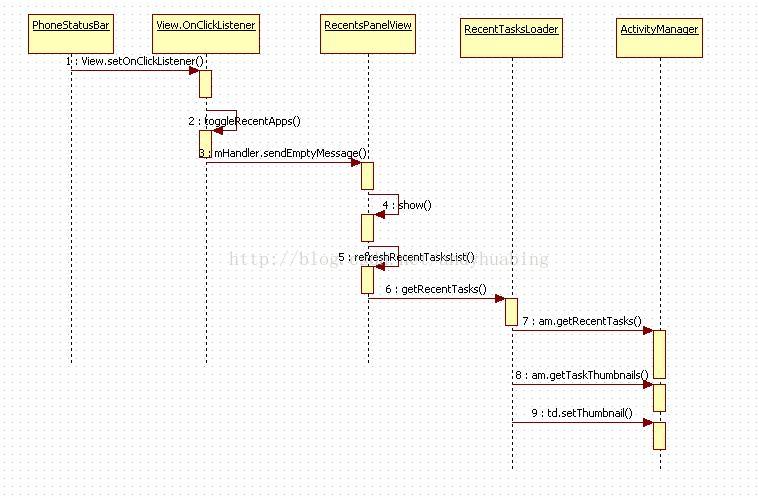
SystemUI 获取按键事件,获取缩略图并将其显示出来,最后响应view上按键响应相应事件:
对于我们来说,关注点主要有如下几个:
1、缩略图如何获取
RecentsPanelView.java 中
refreshRecentTasksList(recentTaskDescriptions);
-->
mRecentTaskDescriptions = mRecentTasksLoader.getRecentTasks();
-->
RecentTasksLoader.java 中
// return a snapshot of the current list of recent apps
ArrayList<TaskDescription> getRecentTasks() {
cancelLoadingThumbnails();
ArrayList<TaskDescription> tasks = new ArrayList<TaskDescription>();
final PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
final ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager)
mContext.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final List<ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo> recentTasks =
am.getRecentTasks(MAX_TASKS, ActivityManager.RECENT_IGNORE_UNAVAILABLE);
ActivityInfo homeInfo = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN).addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME)
.resolveActivityInfo(pm, 0);
HashSet<Integer> recentTasksToKeepInCache = new HashSet<Integer>();
int numTasks = recentTasks.size();
// skip the first task - assume it's either the home screen or the current activity.
final int first = 1;
recentTasksToKeepInCache.add(recentTasks.get(0).persistentId);
for (int i = first, index = 0; i < numTasks && (index < MAX_TASKS); ++i) {
final ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo recentInfo = recentTasks.get(i);
TaskDescription item = createTaskDescription(recentInfo.id,
recentInfo.persistentId, recentInfo.baseIntent,
recentInfo.origActivity, recentInfo.description, homeInfo);
if (item != null) {
tasks.add(item);
++index;
}
}
// when we're not using the TaskDescription cache, we load the thumbnails in the
// background
loadThumbnailsInBackground(new ArrayList<TaskDescription>(tasks));
return tasks;
}
这里利用 ActivityManager 中的方法:getRecentTasks 获取当前任务的列表,然后再利用 getTaskThumbnails 获取
按键View 就是几个按键相应的View
public View getRecentsButton() {
return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.recent_apps);
}
public View getMenuButton() {
return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.menu);
}
public View getBackButton() {
return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.back);
}
public View getHomeButton() {
return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.home);
}相应的应用缩略图,调用序列图如下:
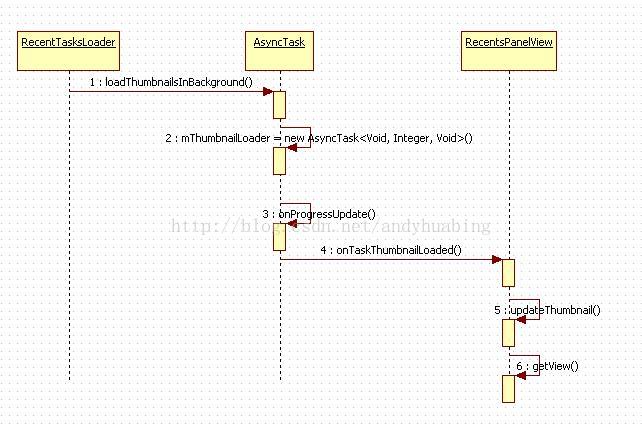
2、显示缩略图
public void show(boolean show, boolean animate,
ArrayList<TaskDescription> recentTaskDescriptions) {
if (show) {
// Need to update list of recent apps before we set visibility so this view's
// content description is updated before it gets focus for TalkBack mode
refreshRecentTasksList(recentTaskDescriptions);
// if there are no apps, either bring up a "No recent apps" message, or just
// quit early
boolean noApps = (mRecentTaskDescriptions.size() == 0);
if (mRecentsNoApps != null) { // doesn't exist on large devices
mRecentsNoApps.setVisibility(noApps ? View.VISIBLE : View.INVISIBLE);
} else {
if (noApps) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Nothing to show");
return;
}
}
}else {
mRecentTasksLoader.cancelLoadingThumbnails();
mRecentTasksDirty = true;
}
...
}
如果 mRecentsNoApps 为空则表示没有任务,显示 "No recent apps" 否则显示应用列表
否则则显示任务的缩略图。时序图如下:
3、点击某个缩略图执行
这里分为点击某个缩略图执行程序及长按缩略图执行程序
这里直接继承了 View.OnItemClickListener 所以可以直接执行子项按键事件
public class RecentsPanelView extends RelativeLayout implements OnItemClickListener, RecentsCallback,
StatusBarPanel, Animator.AnimatorListener, View.OnTouchListener
处理点击事件方法:
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
handleOnClick(view);
}
public void handleOnClick(View view) {
TaskDescription ad = ((ViewHolder) view.getTag()).taskDescription;
final Context context = view.getContext();
final ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager)
context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
if (ad.taskId >= 0) {
// This is an active task; it should just go to the foreground.
am.moveTaskToFront(ad.taskId, ActivityManager.MOVE_TASK_WITH_HOME);
} else {
Intent intent = ad.intent;
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCHED_FROM_HISTORY
| Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_TASK_ON_HOME
| Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Starting activity " + intent);
context.startActivity(intent);
}
hide(true);
}
注意代码:context.startActivity(intent); 这里就是执行对应的 Activity
处理长按键点击事件方法:
public void handleLongPress(
final View selectedView, final View anchorView, final View thumbnailView) {
thumbnailView.setSelected(true);
PopupMenu popup = new PopupMenu(mContext, anchorView == null ? selectedView : anchorView);
popup.getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.recent_popup_menu, popup.getMenu());
popup.setOnMenuItemClickListener(new PopupMenu.OnMenuItemClickListener() {
public boolean onMenuItemClick(MenuItem item) {
if (item.getItemId() == R.id.recent_remove_item) {
mRecentsContainer.removeViewInLayout(selectedView);
} else if (item.getItemId() == R.id.recent_inspect_item) {
ViewHolder viewHolder = (ViewHolder) selectedView.getTag();
if (viewHolder != null) {
final TaskDescription ad = viewHolder.taskDescription;
startApplicationDetailsActivity(ad.packageName);
mBar.animateCollapse();
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Oops, no tag on view " + selectedView);
}
} else {
return false;
}
return true;
}
});
popup.setOnDismissListener(new PopupMenu.OnDismissListener() {
public void onDismiss(PopupMenu menu) {
thumbnailView.setSelected(false);
}
});
popup.show();
}
这里弹出一个PopupMenu,分别是 A:"Remove from list" 及 B:"App Info"
其中A项表示将此任务移除出列表,执行 mRecentsContainer.removeViewInLayout(selectedView);
另外B是启动另外一个Acitivty列出应用信息:
private void startApplicationDetailsActivity(String packageName) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_APPLICATION_DETAILS_SETTINGS,
Uri.fromParts("package", packageName, null));
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
getContext().startActivity(intent);
}
总结:
这里详细的对SystemUI 的两个最重要的 StatusBar NavigationBar(SystemUIService) 及缩略图代码流程分析。
因此各家厂商根据自家的需求,需要定制SystemUI或者美化SystemUI,不同的平台也会有不同的修改,但大体框架是没有变的,
无非是在原有基础上的修修改改或者增加一些自己的类等等。
























 1575
1575

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








