开学了,找工作也正式拉开了序幕,每天光自己看书,也很没劲,和大家一起分享分享,交流一下笔试面试过程中的各种算法题目,如有问题,欢迎指正,希望大家一起进步。。。
下面是对数据结构二叉树的一些基本操作,可能在面试中都会涉及到。我们都知道二叉树的定义本身就是一种递归定义,所以对树的大部分操作都可以通过递归的方式进行,但递归不是万能的,因为递归的本身是一件很浪费内存资源的操作,所以在选择算法的时候要权衡各种因素,选取最合理的算法。下图Fig 1 是下面代码中举例会用到的图:
Fig 1
在本文中,所讨论的二叉树采取以下的定义方式:
- template<typename Type>
- struct BiNode{
- Type data;
- BiNode *left;
- BiNode *right;
- };
1.二叉树的创建
下面的创建是采用递归的方式进行创建,节点的内容为字符。节点的创建方式是先序的方式,先创建根节点,然后是左子树,最后是右子树。
- /**
- *Create Binary Tree
- */
- BiNode<char> * CreateBiTree()
- {
- BiNode<char> *root;
- char data;
- cin>>data;
- if(data == '$')
- return NULL;
- root = new BiNode<char>;
- root->data = data;
- root->left = CreateBiTree();
- root->right = CreateBiTree();
- return root;
- }
2.二叉树的各种遍历
下面的算法是二叉树的各种遍历,包括先序,中序,层次遍历,其中有非递归和递归的算法,关于后序遍历这里没有列举,因为后序的非递归相对比较复杂,每个节点要进出栈两次,在面试的过程中一般面试官不是变态的话,不会考后序的非递归算法的。
2.1 先序遍历
下面是先序遍历的递归算法:
- /**
- * recursively pre-order traverse the binary tree
- * 先序遍历递归算法
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void PreOrder( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return;
- cout<<root->data<<endl;
- PreOrder(root->left);
- PreOrder(root->right);
- }
- /**
- * non-recursively pre-order traverse the binary tree
- * 先序遍历非递归算法
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void PreOrder_NonRecursive( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return;
- stack<BiNode<Type> *> nodeStack;
- nodeStack.push(root);
- while(!nodeStack.empty())
- {
- BiNode<Type> *node = nodeStack.top();
- nodeStack.pop();
- cout<<node->data<<endl;
- if(node->right)
- nodeStack.push(node->right);
- if(node->left)
- nodeStack.push(node->left);
- }
- }
2.2 中序遍历
下面是中序遍历的递归算法:
- /**
- * recursively in-order traverse the binary tree
- * 中序遍历递归算法
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void InOrder( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return;
- InOrder(root->left);
- cout<<root->data<<endl;
- InOrder(root->right);
- }
- /**
- * non-recursively in-order traverse the binary tree
- * 中序遍历非递归算法
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void InOrder_NonRecursive( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- stack<BiNode<Type> *> nodeStack;
- BiNode<Type> *node = root;
- while (node != NULL || !nodeStack.empty())
- {
- if (node != NULL)
- {
- nodeStack.push(node);
- node = node->left;
- }
- else
- {
- node = nodeStack.top();
- nodeStack.pop();
- cout<<node->data<<endl;
- node = node->right;
- }
- }
- }
2.3 层次遍历
二叉树的层次遍历就是按照节点的深度从上往下,从左往右依次访问树中的每一个节点。下面这种方法是通过队列来完成的,首先将根节点入队列,然后重复进行如下操作:读取队头节点元素,并将节点的左右孩子写入队列,直到队列为空。
- /**
- * level order traverse the binary tree
- * method 1
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void LevelOrder_1( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- queue<BiNode<Type> *> nodeQueue;
- nodeQueue.push(root);
- while (!nodeQueue.empty())
- {
- BiNode<Type> *node = nodeQueue.front();
- nodeQueue.pop();
- cout<<node->data<<" ";
- if(node->left)
- nodeQueue.push(node->left);
- if(node->right)
- nodeQueue.push(node->right);
- }
- }
- /**
- * level order traverse the binary tree
- * method 2
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void LevelOrder_2( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- //GetBinTreeHeight()函数用于获取二叉树的高度,后面会有介绍
- for (int i = 1; i <= GetBinTreeHeight(root); ++i)
- {
- PrintKthLevelOrder(root, i);
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- /**
- * print the k(th) level node of binary tree
- * 打印二叉树的第K层的节点
- *
- * @param k the level, its value must be 1 <= k <= tree height
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void PrintKthLevelOrder( BiNode<Type> *root, int k)
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- if(k == 1)
- {
- cout<<root->data<<" ";
- return;
- }
- PrintKthLevelOrder(root->left, k - 1);
- PrintKthLevelOrder(root->right, k - 1);
- }
- /**
- * level order traverse the binary tree
- * method 3
- */
- template <typename Type>
- void LevelOrder_3( BiNode<Type> *root )
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return;
- vector<BiNode<Type> *> nodeVec;
- nodeVec.push_back(root);
- int cur, last;
- cur = 0, last = 1;
- while(cur < nodeVec.size())
- {
- cout<<nodeVec[cur]->data<<" ";
- if(nodeVec[cur]->left != NULL)
- nodeVec.push_back(nodeVec[cur]->left);
- if(nodeVec[cur]->right != NULL)
- nodeVec.push_back(nodeVec[cur]->right);
- ++cur;
- if (cur == last)
- {
- last = nodeVec.size();
- cout<<endl;
- }
- }
- }
3.二叉树的高度
二叉树的高度可以通过后序遍历的思想,递归的统计节点的左子树和右子树的高度,然后取左右子树高度的最高值,然后加1,就是该层节点的高度。代码如下:- /**
- * calculate the height of binary tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- int GetBinTreeHeight( BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return 0;
- int lHeight = GetBinTreeHeight(root->left);
- int rHeight = GetBinTreeHeight(root->right);
- if(lHeight < rHeight)
- return rHeight + 1;
- return lHeight + 1;
- }
4.二叉树第K层节点的个数
也是通过后序遍历的思想,分别求节点左右子树在第K层的节点个数,然后求和。这里对传入的k,随着递归深度的加深,逐渐减1,直到k为1。- /**
- * calculate the node counts in k(th) level
- *
- * @param k the level, its value must be 1 <= k <= tree height
- */
- template <typename Type>
- int GetNodeCountsKthLevel( BiNode<Type> *root, int k)
- {
- //检测k否超过二叉树的高度
- if (root == NULL || k < 1 || k > GetBinTreeHeight(root))
- return 0;
- if(k == 1)
- return 1;
- return GetNodeCountsKthLevel(root->left, k - 1) \
- + GetNodeCountsKthLevel(root->right, k - 1);
- }
5.叶子节点的个数
和前面的道理一样,在二叉树的操作中,递归才是王道。。。- /**
- * calculate the leaf node counts
- */
- template <typename Type>
- int GetLeavesCounts( BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- if (root == NULL)
- return 0;
- if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
- return 1;
- return GetLeavesCounts(root->left) + GetLeavesCounts(root->right);
- }
6.二叉树节点的个数
- /**
- * calculate the tree's node counts
- */
- template <typename Type>
- int GetNodeCounts( BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return 0;
- return GetNodeCounts(root->left) + GetNodeCounts(root->right) + 1;
- }
7.二叉排序树转换成排序的双向链表
这个已经在前面的博客中写过,详见: http://blog.csdn.net/anonymalias/article/details/92048258.二叉树的子结构
二叉树的子结构的定义是:一个二叉树为另一个二叉树的子集,如下图所示: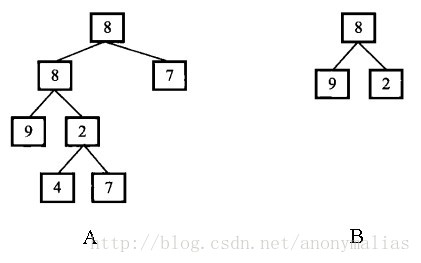
Fig 2 B为A的一个子结构
- /**
- * judge the binary tree 'rootB' is a substructure of 'rootA'or not
- */
- template <typename Type>
- bool IsSubStruct(BiNode<Type> *rootA, BiNode<Type> *rootB)
- {
- if (rootA == NULL || rootB == NULL)
- return false;
- bool result = false;
- if (rootA->data == rootB->data)
- result = ISSameStruct(rootA, rootB);
- if(!result)
- result = IsSubStruct(rootA->left, rootB);
- if(!result)
- result = IsSubStruct(rootA->right, rootB);
- return result;
- }
- //用于判断二叉树B是否是A开始的一部分
- template<typename Type>
- bool ISSameStruct(BiNode<Type> *rootA, BiNode<Type> *rootB)
- {
- if(rootB == NULL)
- return true;
- if(rootA == NULL)
- return false;
- if(rootA->data != rootB->data)
- return false;
- return ISSameStruct(rootA->left, rootB->left) && ISSameStruct(rootA->right, rootB->right);
- }
8.二叉树的镜像
二叉树镜像的概念就是左右子树交换,所以判断起来也很简单,代码如下:- /**
- * judge the binary tree 'rootA' is a mirror of 'rootB' or not
- */
- template<typename Type>
- bool ISMirror(BiNode<Type> *rootA, BiNode<Type> *rootB)
- {
- if(rootA == NULL && rootB == NULL)
- return true;
- if(rootA == NULL || rootB == NULL)
- return false;
- if(rootA->data != rootB->data)
- return false;
- return ISMirror(rootA->left, rootB->right) && ISMirror(rootA->right, rootB->left);
- }
- return ISMirror(rootA->left, rootB->left) && ISMirror(rootA->right, rootB->right);
9.平衡二叉树的判断
我们都知道平衡二叉树的定义:空树或左右子树的高度差不超过1,且左右子树也都是平衡二叉树。代码如下:- /**
- * judge the binary tree whether it is a balanced tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- bool IsBalanced(BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- int height = 0;
- return SubIsBalanced(root, height);
- }
- template <typename Type>
- bool SubIsBalanced(BiNode<Type> *root, int &height)
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- {
- height = 0;
- return true;
- }
- int lH, rH;
- int result = SubIsBalanced(root->left, lH) && SubIsBalanced(root->right, rH);
- if (result)
- {
- if(lH - rH <= 1 && lH - rH >= -1)
- {
- height = (lH > rH ? lH + 1 : rH + 1);
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
10.完全二叉树的判断
完全二叉树的定义如下:若设二叉树的深度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树,我见过最简单的方法是:通过广度遍历即层次遍历的思想,将各个节点入队列,对于存在空洞的节点( 左右孩子的节点存在NULL),把它的两个孩子也入队列,当访问到队列中为NULL的节点,根据完全二叉树的定义,此时二叉树已经结束,即队列中的其他元素全部为NULL,否则该树不是完全二叉树。代码如下:- /**
- * judge the binary tree whether it is a completed tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- bool IsCompletedBiTree(BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return true;
- queue<BiNode<Type> *> nodeQue;
- nodeQue.push(root);
- while(!nodeQue.empty())
- {
- BiNode<Type> *node = nodeQue.front();
- nodeQue.pop();
- if (node == NULL)
- {
- while (!nodeQue.empty())
- {
- if(nodeQue.front() != NULL)
- return false;
- nodeQue.pop();
- }
- return true;
- }
- nodeQue.push(node->left);
- nodeQue.push(node->right);
- }
- //实际上不会执行到这一步
- return true;
- }
11.满二叉树的判断
满二叉树的判断相对比较简单,可以通过判断每个节点的左右子树的高度是否相同来实现,满二叉树的所以节点的左右子树的高度都是一样的。代码如下:- /**
- * judge the binary tree whether it is a full tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- bool IsFullBiTree(BiNode<Type> *root)
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- return true;
- int height;
- return SubIsFullBiTree(root, height);
- }
- template <typename Type>
- bool SubIsFullBiTree(BiNode<Type> *root, int &height)
- {
- if(root == NULL)
- {
- height = 0;
- return true;
- }
- int lH, rH;
- if (SubIsFullBiTree(root->left, lH) && SubIsFullBiTree(root->right, rH))
- {
- if (lH == rH)
- {
- height = lH + 1;
- return true;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
12.重建二叉树
根据二叉树的先序和中序遍历的结果(不含有重复的节点),重建此二叉树,该题的的解决思路也是通过二叉树递归定义的思想。我们知道二叉树先序遍历的一个节点,在中序遍历中会把以该节点为根的二叉树分为左右两部分,根据这点,可以递归的重建二叉树,具体代码如下:- /**
- * rebuild the binary tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- BiNode<Type> * RebuildBiTree(const Type *pre, const Type *in, int len)
- {
- if(pre == NULL || in == NULL || len <= 0)
- return NULL;
- BiNode<Type> * root = new BiNode<Type>;
- root->data = pre[0];
- int index;
- for (index = 0; index < len; ++index)
- {
- if (in[index] == pre[0])
- break;
- }
- //can not find the 'pre[0]' in the 'in[]'
- if(index == len)
- return NULL;
- root->left = RebuildBiTree(pre + 1, in, index);
- root->right = RebuildBiTree(pre + index + 1, in + index + 1, len - index - 1);
- return root;
- }
13.判断序列是否是二叉排序树的后序遍历序列
我们都知道二叉排序树的中序遍历的结果是一个递增序列,后序遍历序列最后的元素是根节点,通过最后的元素将遍历序列分割成两部分,左半部分都小于根节点的值,右半部分都大于该节点的值,如果不能分成这两部分,那么该序列就不是二叉排序树的后序遍历序列。代码如下:- /**
- * judge the serial is post-order traversal of binary search tree
- */
- template <typename Type>
- bool IsBSTPostOrder(const Type *post, int len)
- {
- if(post == NULL || len <= 0)
- return false;
- int index;
- //查找小于根节点的左子树节点
- for (index = 0; index < len - 1; ++index)
- {
- if(post[index] > post[len - 1])
- break;
- }
- //判断剩下的节点是否都为右子树的节点,即是否都大于根节点的值
- for (int i = index; i < len - 1; ++i)
- {
- if(post[i] < post[len - 1])
- return false;
- }
- bool result = true;
- if(index > 0)
- result = IsBSTPostOrder(post, index);
- if(result && index < len - 1)
- result = IsBSTPostOrder(post + index, len - index - 1);
- return result;
- }
就先写这么多吧,后面还会继续添加,累死了。。。
有新的问题大家可以提出来,一起讨论,共同进步...<^_^>。。。
Sept 2nd - 3rd, 2013 @lab
























 361
361

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








