阻塞队列 (BlockingQueue)是Java util.concurrent包下重要的数据结构,BlockingQueue提供了线程安全的队列访问方式:当阻塞队列
进行插入数据时,如果队列已满,线程将会阻塞等待直到队列非满;从阻塞队列取数据时,如果队列已空,线程将会阻塞等待直到队列非空。
并发包下很多高级同步类的实现都是基于BlockingQueue实现的。
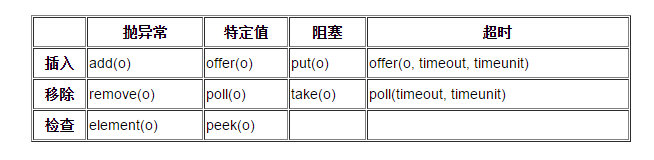
BlockingQueue 的操作方法
BlockingQueue 具有 4 组不同的方法用于插入、移除以及对队列中的元素进行检查。如果请求的操作不能得到立即执行的话,每个方法的表现也不同。这些方法如下:
四组不同的行为方式解释:
- 抛异常:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,抛一个异常。
- 特定值:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,返回一个特定的值(常常是 true / false)。
- 阻塞:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,该方法调用将会发生阻塞,直到能够执行。
- 超时:如果试图的操作无法立即执行,该方法调用将会发生阻塞,直到能够执行,但等待时间不会超过给定值。返回一个特定值以告知该操作是否成功(典型的是true / false)。
无法向一个 BlockingQueue 中插入 null。如果你试图插入 null,BlockingQueue 将会抛出一个 NullPointerException。
可以访问到 BlockingQueue 中的所有元素,而不仅仅是开始和结束的元素。比如说,你将一个对象放入队列之中以等待处理,但你的应用想要将其取消掉。那么你可以调用诸如 remove(o) 方法来将队列之中的特定对象进行移除。但是这么干效率并不高(译者注:基于队列的数据结构,获取除开始或结束位置的其他对象的效率不会太高),因此你尽量不要用这一类的方法,除非你确实不得不那么做。
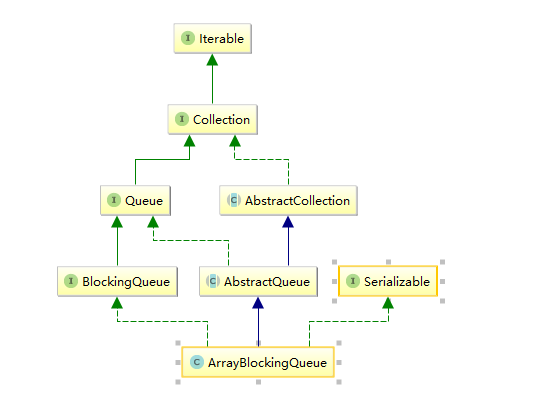
ArrayBlockingQueue的继承关系:
ArrayBlockingQueue的源码分析:
废话不多讲,我们直接来分析ArrayBlockingQueue的源码
先看构造函数:
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity);
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) ;
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,Collection<? extends E> c);
以下是构造的主要过程:
- public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
- if (capacity <= 0)
- throw new IllegalArgumentException();
- this.items = new Object[capacity]; //初始化数组
- lock = new ReentrantLock(fair); //根据传的参数决定是否使用公平锁
- notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); //当队列不为空的时候将唤醒此条件
- notFull = lock.newCondition(); //当队列容量没有充满的时候唤醒此条件
- }
以下是主要的属性
- final Object[] items;
- int takeIndex;
- int putIndex;
- int count;
- /** Main lock guarding all access */
- final ReentrantLock lock;
- /** Condition for waiting takes */
- private final Condition notEmpty;//为空时需要阻塞
- /** Condition for waiting puts */
- private final Condition notFull;//容量满时需要阻塞
接下来我们将分析最主要的两个方法:take 和 put
take从队列中拿出一个元素,如果队列为空将会阻塞直到队列不为空并且能够获取到元素
put将一个元素放入队列,如果队列容量已满将会阻塞直到队列容量不满并且能够入队
以下是take的流程:
- public E take() throws InterruptedException {
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();//可以看出是通过lock来响应中断的
- try {
- while (count == 0)
- notEmpty.await();//如果队列中没有数据,将会一直阻塞。
- return dequeue();
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * 只发生在持有锁的时候
- * Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
- * Call only when holding lock.
- */
- private E dequeue() {
- // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
- // assert items[takeIndex] != null;
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
- items[takeIndex] = null;
- if (++takeIndex == items.length)
- takeIndex = 0;
- count--;
- if (itrs != null)
- itrs.elementDequeued();
- notFull.signal();//通知notFull condition 队列已经有空位了 可以入队了。
- return x;
- }
put操作类似
- public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
- checkNotNull(e);
- final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
- lock.lockInterruptibly();
- try {
- while (count == items.length)
- notFull.await();
- enqueue(e);
- } finally {
- lock.unlock();
- }
- }
- /**
- * Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.
- * Call only when holding lock.
- */
- private void enqueue(E x) {
- // assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
- // assert items[putIndex] == null;
- final Object[] items = this.items;
- items[putIndex] = x;
- if (++putIndex == items.length)
- putIndex = 0;
- count++;
- notEmpty.signal();
- }






















 3448
3448

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








