需要了解知识:
1.IO模型:参考 IO与操作系统关系(一) JAVA几种IO工作机制及特点(二)
2.jetty容器: 参考 JETTY基本架构
1.jetty 模块分析
详细参考官网:http://wiki.eclipse.org/Jetty/Reference/Dependencies (jetty模块依赖)
1.1 jetty依赖树:
This diagram shows the compile dependencies for the Jetty project. The external dependencies are listed on the right hand side and all other modules shown are part of the project.
1.2 jetty核心模块(http客户端 服务端通讯模块)
(官方解释)The jetty-util, jetty-io and jetty-http jars form the core of the jetty HTTP handler (generation and parsing) that is used for both the jetty-client and the jetty-server。
如下图:
我们平常最关心的就是 client 如何 server进行通讯,如何实现io通讯的,所以以下几个模块需要了解:
jetty-client:
jetty-server:
jetty-http:
jetty-io:
jetty-util:

1.3 jetty模块结构分析
注:下面讲解jetty核心代码类是用到jetty8中的selectChannelConnector,这里大家参考jetty8 API,jetty9已更换实现类为ServerConnector:
jetty8 api:http://download.eclipse.org/jetty/8.1.17.v20150415/apidocs/
1.3.1 添加依赖jetty插件,从search.maven.org 下载:
<!-- jetty -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty.aggregate</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-all-server</artifactId>
<version>8.1.18.v20150929</version>
</dependency> 
1.3.2 Jetty Connector的实现类图:
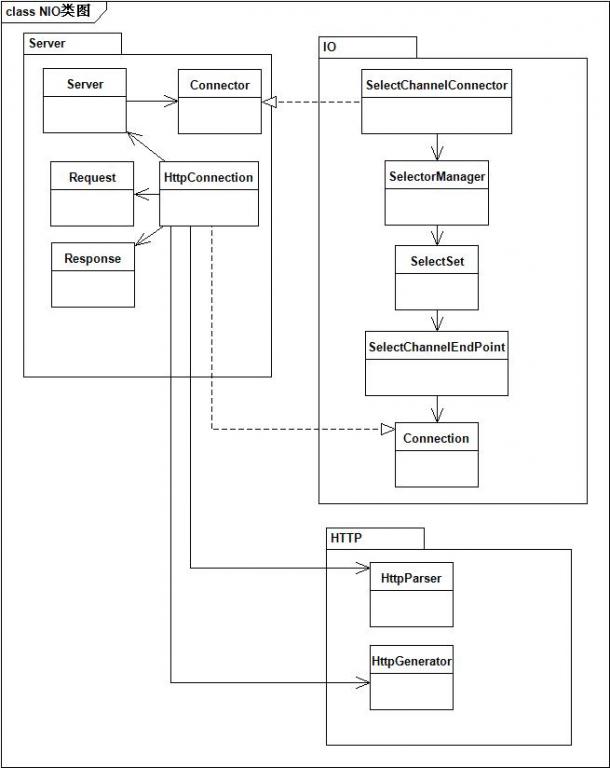
其中:
SelectChannelConnector 负责组装各组件
SelectSet 负责侦听客户端请求
SelectChannelEndPoint 负责IO的读和写
HttpConnection 负责逻辑处理
在整个服务端处理请求的过程可以分为三个阶段,时序图如下所示:
阶段一:监听并建立连接
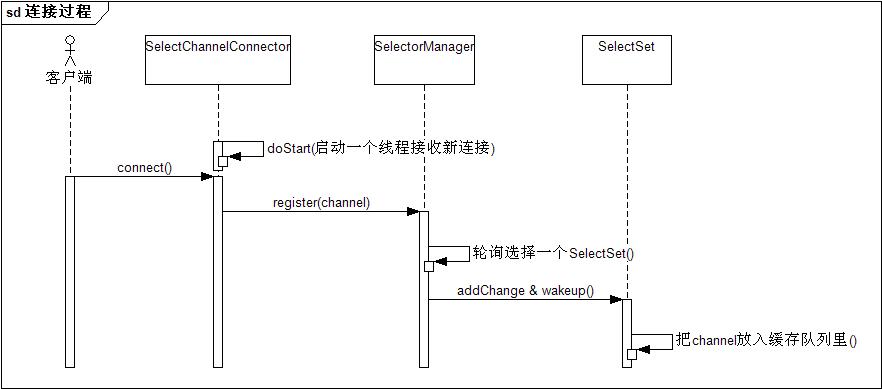
这一过程主要是启动一个线程负责accept新连接,监听到后分配给相应的SelectSet,分配的策略就是轮询。
SelectChannelConnector核心方法:
1.创建SelectorManager 用于接收客户端请求 dispatch()
private final SelectorManager _manager = new ConnectorSelectorManager();
/*
* @see org.eclipse.jetty.server.server.AbstractConnector#doStart()
*/
@Override
protected void doStart() throws Exception
{
_manager.setSelectSets(getAcceptors());
_manager.setMaxIdleTime(getMaxIdleTime());
_manager.setLowResourcesConnections(getLowResourcesConnections());
_manager.setLowResourcesMaxIdleTime(getLowResourcesMaxIdleTime());
super.doStart();// 1.1会调用open方法启动server监听端口1.2 同时创建线程池接收连接
}
/* --------------------------1.1 启动监听端口port---------------------------------- */
public void open() throws IOException
{
synchronized(this)
{
if (_acceptChannel == null)
{
// Create a new server socket
_acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// Set to blocking mode
_acceptChannel.configureBlocking(true);
// Bind the server socket to the local host and port
_acceptChannel.socket().setReuseAddress(getReuseAddress());
InetSocketAddress addr = getHost()==null?new InetSocketAddress(getPort()):new InetSocketAddress(getHost(),getPort());
_acceptChannel.socket().bind(addr,getAcceptQueueSize());
_localPort=_acceptChannel.socket().getLocalPort();
if (_localPort<=0)
throw new IOException("Server channel not bound");
addBean(_acceptChannel);
}
}
}
/* ----------------------1.2 启动一个线程池监听 客户端连接,默认是1个---------------------- */
@Override
public void accept(int acceptorID) throws IOException
{
ServerSocketChannel server;
synchronized(this)
{
server = _acceptChannel;
}
if (server!=null && server.isOpen() && _manager.isStarted())
{
SocketChannel channel = server.accept();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
Socket socket = channel.socket();
configure(socket);
_manager.register(channel); //SelectorManager管理所有channel
}
}
/** Register a channel 注册channel到selectSet
* @param channel
*/
public void register(SocketChannel channel)
{
// The ++ increment here is not atomic, but it does not matter.
// so long as the value changes sometimes, then connections will
// be distributed over the available sets.
int s=_set++;
if (s<0)
s=-s;
s=s%_selectSets;
SelectSet[] sets=_selectSet;
if (sets!=null)
{
SelectSet set=sets[s];
set.addChange(channel);
set.wakeup();
}
}
阶段二:监听客户端的请求
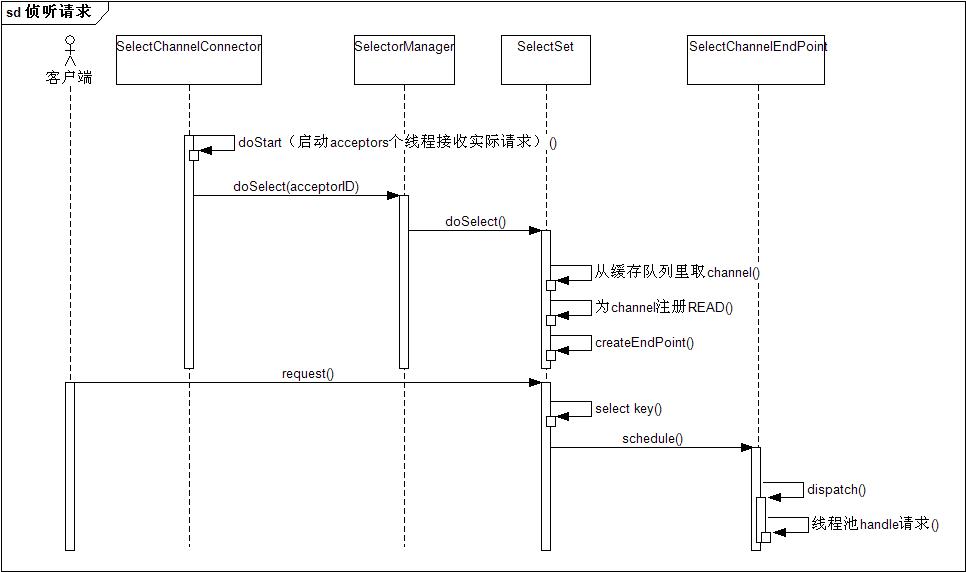
这一过程主要是启动多个线程(线程数一般为服务器CPU的个数,dubbo的nio配置 cpu核数+1),让SelectSet监听所管辖的channel队列,每个SelectSet维护一个Selector,这个Selector监听队列里所有的channel,一旦有读事件,从线程池里拿线程去做处理请求.
selectorManager交由线程去处理 dispatch()
/* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.eclipse.component.AbstractLifeCycle#doStart()
*/
@Override
protected void doStart() throws Exception
{
_selectSet = new SelectSet[_selectSets];
for (int i=0;i<_selectSet.length;i++)
_selectSet[i]= new SelectSet(i);
super.doStart();
// start a thread to Select
for (int i=0;i<getSelectSets();i++)
{
final int id=i;
boolean selecting=dispatch(new Runnable()
{
public void run()
{
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
int priority=Thread.currentThread().getPriority();
try
{
SelectSet[] sets=_selectSet;
if (sets==null)
return;
SelectSet set=sets[id];
Thread.currentThread().setName(name+" Selector"+id);//按selector创建
if (getSelectorPriorityDelta()!=0)
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.currentThread().getPriority()+getSelectorPriorityDelta());
LOG.debug("Starting {} on {}",Thread.currentThread(),this);
while (isRunning())
{
try
{
set.doSelect();//Select and dispatch tasks
}
catch(IOException e)
{
LOG.ignore(e);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
LOG.warn(e);
}
}
}
finally
{
LOG.debug("Stopped {} on {}",Thread.currentThread(),this);
Thread.currentThread().setName(name);
if (getSelectorPriorityDelta()!=0)
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(priority);
}
}
});
if (!selecting)
throw new IllegalStateException("!Selecting");
}
}
/* ------------------------SelectChannelEndPoint 分发处理----------------------------- */
public void dispatch()
{
synchronized(this)
{
if (_state<=STATE_UNDISPATCHED)
{
if (_onIdle)
_state = STATE_NEEDS_DISPATCH;
else
{
_state = STATE_DISPATCHED;
boolean dispatched = _manager.dispatch(_handler);
if(!dispatched)
{
_state = STATE_NEEDS_DISPATCH;
LOG.warn("Dispatched Failed! "+this+" to "+_manager);
updateKey();
}
}
}
}
}
阶段三:处理请求
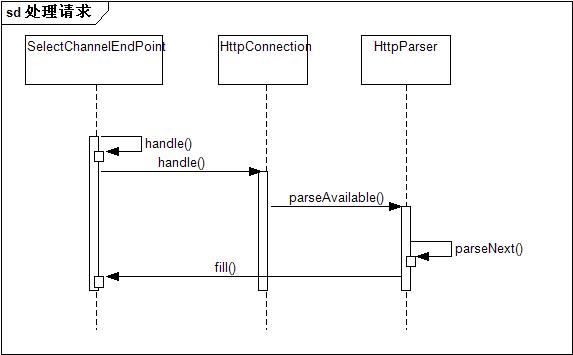
这一过程就是每次客户端请求的数据处理过程,值得注意的是为了不让后端的业务处理阻碍Selector监听新的请求,就多线程来分隔开监听请求和处理请求两个阶段。
/* ------------------------------------------------------------ */
/*
*/
protected void handle()
{
boolean dispatched=true;
try
{
while(dispatched)
{
try
{
while(true)
{
final AsyncConnection next = (AsyncConnection)_connection.handle();
if (next!=_connection)
{
LOG.debug("{} replaced {}",next,_connection);
Connection old=_connection;
_connection=next;
_manager.endPointUpgraded(this,old);
continue;
}
break;
}
}
catch (ClosedChannelException e)
{
LOG.ignore(e);
}
catch (EofException e)
{
LOG.debug("EOF", e);
try{close();}
catch(IOException e2){LOG.ignore(e2);}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
LOG.warn(e.toString());
try{close();}
catch(IOException e2){LOG.ignore(e2);}
}
catch (Throwable e)
{
LOG.warn("handle failed", e);
try{close();}
catch(IOException e2){LOG.ignore(e2);}
}
finally
{
if (!_ishut && isInputShutdown() && isOpen())
{
_ishut=true;
try
{
_connection.onInputShutdown();
}
catch(Throwable x)
{
LOG.warn("onInputShutdown failed", x);
try{close();}
catch(IOException e2){LOG.ignore(e2);}
}
finally
{
updateKey();
}
}
dispatched=!undispatch();
}
}
}
finally
{
if (dispatched)
{
dispatched=!undispatch();
while (dispatched)
{
LOG.warn("SCEP.run() finally DISPATCHED");
dispatched=!undispatch();
}
}
}
}由此可以大致总结出Jetty有关NIO使用的模式,如下图所示:
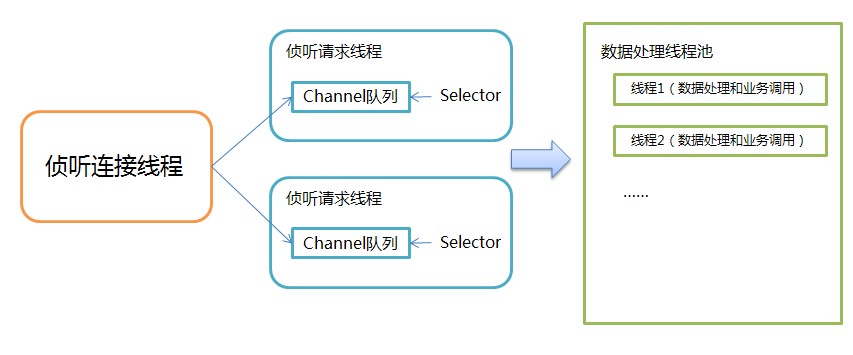
1).监听并建立连接
2).监听客户端请求
3).请求的处理
最核心就是把三件不同的事情隔离开,并用不同规模的线程去处理,最大限度地利用NIO的异步和通知特性。
1.4 启动jetty服务,观察容器线程池

参考博客:
- 1.从Jetty、Tomcat和Mina中提炼NIO构架网络服务器的经典模式(一)
- 2.从Jetty、Tomcat和Mina中提炼NIO构架网络服务器的经典模式(二)
- 3.从Jetty、Tomcat和Mina中提炼NIO构架网络服务器的经典模式(三)
- 4.JAVA NIO系列教程
- 5. Jetty的SelectChannelConnector分析










 本文深入探讨Jetty的NIO实现,分析Jetty模块结构,包括jetty-http、jetty-client、jetty-server等核心模块,重点讲解Jetty Connector的实现,如SelectChannelConnector的角色,以及监听、处理客户端请求的三个阶段。通过类图和时序图,揭示Jetty如何高效利用NIO的异步和通知特性。
本文深入探讨Jetty的NIO实现,分析Jetty模块结构,包括jetty-http、jetty-client、jetty-server等核心模块,重点讲解Jetty Connector的实现,如SelectChannelConnector的角色,以及监听、处理客户端请求的三个阶段。通过类图和时序图,揭示Jetty如何高效利用NIO的异步和通知特性。















 2466
2466

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








