代码背景
现在你正在玩植物大战僵尸,有生产者—向日葵,一次生产25阳光,消费者—豌豆射手,卷心菜投手和仙人掌,都消耗100阳光。
wait和notify实现
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 生产者消费者模式:使用Object.wait() / notify()方法实现
*/
public class ProducerConsumer {
private static final int CAPACITY = 500;
public static void main(String args[]){
int sun = 0;
Thread producer1 = new Producer("向日葵1", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread producer1 = new Producer("向日葵2", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer1 = new Consumer("豌豆射手", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer2 = new Consumer("卷心菜投手", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer3 = new Consumer("仙人掌射手", sun , CAPACITY);
producer1.start();
producer2.start();
consumer1.start();
consumer2.start();
consumer3.start();
}
/**
* 生产者
*/
public static class Producer extends Thread{
private int sun ;
String name;
int maxSize;
int i = 0;
public Producer(String name, int sun, int maxSize){
super(name);
this.name = name;
this.sun= sun;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(sun){
if(sun >= 500){
try {
System.out .println("阳光达到上限, [" + name + "] 产生的阳光 " + "需要被拿来种下植物");
sun.wait();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}x
System.out.println("[" + name + "] 生产了25阳光");
sun += 25;
sun.notifyAll();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 消费者
*/
public static class Consumer extends Thread{
private int sun;
String name;
int maxSize;
public Consumer(String name, int sun, int maxSize){
super(name);
this.name = name;
this.sun= sun;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(sun){
if(sun - 100 <= 0){
try {
System.out.println("没有阳光了, 栽种[" + name + "] 急需向日葵生产阳光");
queue.wait();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
sun -= 100;
System.out.println("种下一颗[" + name + "] 消耗100阳光" + x);
sun .notifyAll();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
上述代码一运行,啪!报错!,为啥,原来synchronized 锁对 Integer 等基本类型的包装类没有效果,采用一个Wrapper包装一下
修改后
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 生产者消费者模式:使用Object.wait() / notify()方法实现
*/
class Wrapper{
public Integer sum = 0;
}
public class Main {
private static final int CAPACITY = 300;
public static void main(String args[]){
Wrapper sun = new Wrapper();
sun.sum = 0;
Thread producer1 = new Producer("向日葵1", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread producer2 = new Producer("向日葵2", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer1 = new Consumer("豌豆射手", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer2 = new Consumer("卷心菜投手", sun , CAPACITY);
Thread consumer3 = new Consumer("仙人掌射手", sun , CAPACITY);
producer1.start();
producer2.start();
consumer1.start();
consumer2.start();
consumer3.start();
}
/**
* 生产者
*/
public static class Producer extends Thread{
private Wrapper sun ;
String name;
int maxSize;
public Producer(String name, Wrapper sun, int maxSize){
super(name);
this.name = name;
this.sun= sun;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(sun){
if(sun.sum >= maxSize){
try {
System.out .println("阳光达到上限, [" + name + "] 产生的阳光 " + "需要被拿来种下植物");
sun.wait();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
sun.sum += 25;
System.out.println("[" + name + "] 生产了25阳光,现在共有" + sun.sum + "阳光");
sun.notifyAll();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 消费者
*/
public static class Consumer extends Thread{
private Wrapper sun;
String name;
int maxSize;
public Consumer(String name, Wrapper sun, int maxSize){
super(name);
this.name = name;
this.sun= sun;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
@Override
public void run(){
while(true){
synchronized(sun){
if(sun.sum - 100 < 0){
try {
System.out.println("没有阳光了, 栽种[" + name + "] 急需向日葵生产阳光");
sun.wait();
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
sun.sum -= 100;
System.out.println("种下一颗[" + name + "] 消耗100阳光,现在共有" + sun.sum + "阳光");
sun .notifyAll();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
运行效果:

我去,怎么有负数!!!
synchronized 不能使用if只能使用while
在上面这个例子中,仙人掌射手所属的线程首先被唤醒了,通过while循环和if操作顺利消耗了所有阳光,并进入了wait状态。但是,现在卷心菜投手也被唤醒了,他没经过if判断,直接把阳光-100,然后执行下一次时才发现阳光居然是负数,马上进入wait状态,但是这时候已经迟了。所以得改成while让他先进行判断再操作。
修改代码
if(sun.sum - 100 < 0) 改为 while(sun.sum - 100 < 0)
if(sun.sum >= maxSize) 改为 while(sun.sum >= maxSize)
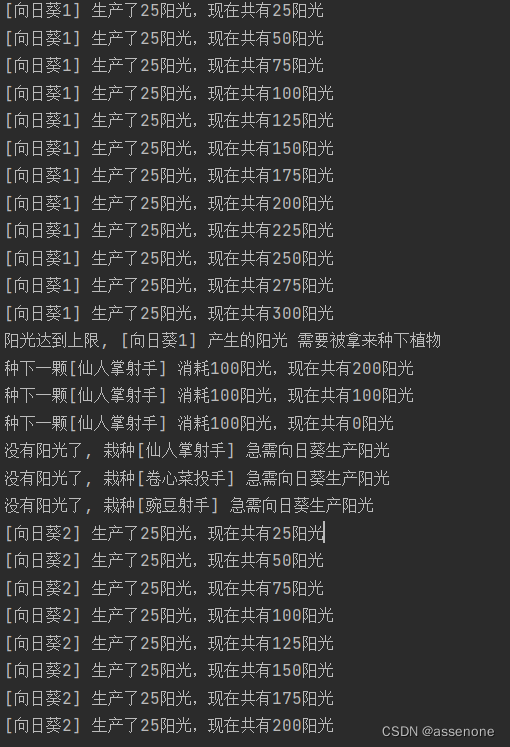
非常的完美!!!





















 269
269











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








