[0145] 斐波那契数
斐波那契数,通常用 F(n) 表示,形成的序列称为斐波那契数列。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1
F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - 2), 其中 N > 1.
给定 N,计算 F(N)。
示例 1:
输入:2
输出:1
解释:F(2) = F(1) + F(0) = 1 + 0 = 1.
示例 2:
输入:3
输出:2
解释:F(3) = F(2) + F(1) = 1 + 1 = 2.
示例 3:
输入:4
输出:3
解释:F(4) = F(3) + F(2) = 2 + 1 = 3.
提示:
0 ≤ N ≤ 30
方法一:递归
public class Solution {
public int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
return fib(N-1) + fib(N-2);
}
}
时间复杂度:O(2^N)。这是计算斐波那契数最慢的方法。因为它需要指数的时间。
空间复杂度:O(N),在堆栈中我们需要与 N 成正比的空间大小。该堆栈跟踪 fib(N) 的函数调用,随着堆栈的不断增长如果没有足够的内存则会导致 StackOverflowError。
方法二:记忆化自底向上的方法
自底向上通过迭代计算斐波那契数的子问题并存储已计算的值,通过已计算的值进行计算。减少递归带来的重复计算。
class Solution {
public int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
return memoize(N);
}
public int memoize(int N) {
int[] cache = new int[N + 1];
cache[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
cache[i] = cache[i-1] + cache[i-2];
}
return cache[N];
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),使用了空间大小为
N的数组。
方法三:记忆化自顶向下的方法
我们先计算存储子问题的答案,然后利用子问题的答案计算当前斐波那契数的答案。我们将递归计算,但是通过记忆化不重复计算已计算的值。
class Solution {
private Integer[] cache = new Integer[31];
public int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
cache[0] = 0;
cache[1] = 1;
return memoize(N);
}
public int memoize(int N) {
if (cache[N] != null) {
return cache[N];
}
cache[N] = memoize(N-1) + memoize(N-2);
return memoize(N);
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(N),内存中使用的堆栈大小。
方法四:自底向上进行迭代
class Solution {
public int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
if (N == 2) {
return 1;
}
int current = 0;
int prev1 = 1;
int prev2 = 1;
for (int i = 3; i <= N; i++) {
current = prev1 + prev2;
prev2 = prev1;
prev1 = current;
}
return current;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(N)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),仅仅使用了
current,prev1,prev2。
方法五:矩阵求幂
斐波那契数列矩阵方程:
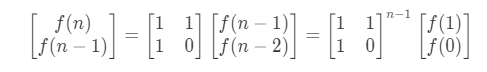
算法:
- 若 N 小于等一 1,则返回 N。
- 使用递归函数 matrixPower 计算给定矩阵 A 的幂。幂为 N-1,其中 N 是第 N 个 斐波那契
- matrixPower 函数将对 N/2 个斐波那契数进行操作。
- 在 matrixPower 中,调用 multiply 函数将两个矩阵相乘。
- 完成计算后,返回
A[0][0]得到第 N 个斐波那契数。
class Solution {
int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
int[][] A = new int[][]{{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
matrixPower(A, N-1);
return A[0][0];
}
void matrixPower(int[][] A, int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return;
}
matrixPower(A, N/2);
multiply(A, A);
int[][] B = new int[][]{{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
if (N%2 != 0) {
multiply(A, B);
}
}
void multiply(int[][] A, int[][] B) {
int x = A[0][0] * B[0][0] + A[0][1] * B[1][0];
int y = A[0][0] * B[0][1] + A[0][1] * B[1][1];
int z = A[1][0] * B[0][0] + A[1][1] * B[1][0];
int w = A[1][0] * B[0][1] + A[1][1] * B[1][1];
A[0][0] = x;
A[0][1] = y;
A[1][0] = z;
A[1][1] = w;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(logN)。
- 空间复杂度:O(logN),
matrixPower函数递归时堆栈使用的空间。
方法六:公式法
-
使用黄金分割比:
$$
\varphi = \frac{1 + \sqrt{5}}{2} \approx 1.6180339887…φ=
2
1+
5
≈1.6180339887…
$$
Binet公式 :
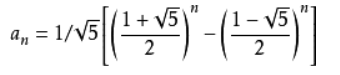
- 这里有一个链接,可以进一步了解斐波那契序列和黄金分割比之间的关系。
- 我们可以只能用常数时间和常数空间得到斐波那契数。
算法:
使用黄金分割率计算第 N 个斐波那契数。
class Solution {
public int fib(int N) {
double goldenRatio = (1 + Math.sqrt(5)) / 2;
return (int)Math.round(Math.pow(goldenRatio, N)/ Math.sqrt(5));
}
}
时间复杂度:O(1)。常数的时间复杂度,因为我们是基于 Binet 公式进行计算,没有使用循环或递归。
空间复杂度:O(1),存储黄金分割率所使用的空间。
[0146] 二叉树的所有路径
给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
\
5
输出: ["1->2->5", "1->3"]
解释: 所有根节点到叶子节点的路径为: 1->2->5, 1->3。
方法一:深度优先搜索
最直观的方法是使用深度优先搜索。在深度优先搜索遍历二叉树时,我们需要考虑当前的节点以及它的孩子节点。
- 如果当前节点不是叶子节点,则在当前的路径末尾添加该节点,并继续递归遍历该节点的每一个孩子节点。
- 如果当前节点是叶子节点,则在当前路径末尾添加该节点后我们就得到了一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径,将该路径加入到答案即可。
如此,当遍历完整棵二叉树以后我们就得到了所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。当然,深度优先搜索也可以使用非递归的方式实现。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
constructPaths(root, "", paths);
return paths;
}
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths) {
if (root != null) {
StringBuffer pathSB = new StringBuffer(path);
pathSB.append(Integer.toString(root.val));
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { // 当前节点是叶子节点
paths.add(pathSB.toString()); // 把路径加入到答案中
} else {
pathSB.append("->"); // 当前节点不是叶子节点,继续递归遍历
constructPaths(root.left, pathSB.toString(), paths);
constructPaths(root.right, pathSB.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N^2)
-
空间复杂度:O(N^2),最好情况下,当二叉树为平衡二叉树时,它的高度为 logN,此时空间复杂度为 O((logN)^2)
非递归
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return res;
//栈中节点和路径都是成对出现的,路径表示的是从根节点到当前
//节点的路径,如果到达根节点,说明找到了一条完整的路径
Stack<Object> stack = new Stack<>();
//当前节点和路径同时入栈
stack.push(root);
stack.push(root.val + "");
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
//节点和路径同时出栈
String path = (String) stack.pop();
TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop();
//如果是根节点,说明找到了一条完整路径,把它加入到集合中
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
res.add(path);
}
//右子节点不为空就把右子节点和路径压栈
if (node.right != null) {
stack.push(node.right);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val);
}
//左子节点不为空就把左子节点和路径压栈
if (node.left != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val);
}
}
return res;
}
方法二:广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
if (root == null) {
return paths;
}
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<String> pathQueue = new LinkedList<String>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
pathQueue.offer(Integer.toString(root.val));
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
String path = pathQueue.poll();
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
paths.add(path);
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.left.val).toString());
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
pathQueue.offer(new StringBuffer(path).append("->").append(node.right.val).toString());
}
}
}
return paths;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(N^2)
-
空间复杂度:O(N^2)
[0147] 特殊数组的特征值
给你一个非负整数数组 nums 。如果存在一个数 x ,使得 nums 中恰好有 x 个元素 大于或者等于 x ,那么就称 nums 是一个 特殊数组 ,而 x 是该数组的 特征值 。
注意: x 不必 是 nums 的中的元素。
如果数组 nums 是一个 特殊数组 ,请返回它的特征值 x 。否则,返回 -1 。可以证明的是,如果 nums 是特殊数组,那么其特征值 x 是 唯一的 。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [3,5]
输出:2
解释:有 2 个元素(3 和 5)大于或等于 2 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,0]
输出:-1
解释:没有满足题目要求的特殊数组,故而也不存在特征值 x 。
如果 x = 0,应该有 0 个元素 >= x,但实际有 2 个。
如果 x = 1,应该有 1 个元素 >= x,但实际有 0 个。
如果 x = 2,应该有 2 个元素 >= x,但实际有 0 个。
x 不能取更大的值,因为 nums 中只有两个元素。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [0,4,3,0,4]
输出:3
解释:有 3 个元素大于或等于 3 。
示例 4:
输入:nums = [3,6,7,7,0]
输出:-1
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
方法一:
class Solution {
public int specialArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int length = nums.length;
//x最大只能是数组最大值或者数组元素个数
int max = Math.max(nums[length - 1],length);
//处理边界特殊情况
if(nums[0] >= length) return length;
for(int i = nums[0]; i <= max; ++i){
if(((length - i -1)>=0 )&&((length - i)<length) &&(nums[length - i] >= i)&& nums[length - i -1]<i){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
[0148] 分式化简
有一个同学在学习分式。他需要将一个连分数化成最简分数,你能帮助他吗?
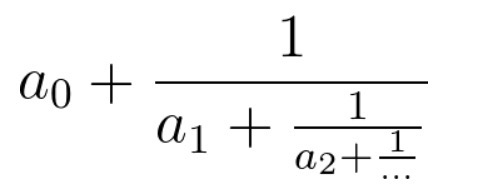
连分数是形如上图的分式。在本题中,所有系数都是大于等于0的整数。
输入的cont代表连分数的系数(cont[0]代表上图的a0,以此类推)。返回一个长度为2的数组[n, m],使得连分数的值等于n / m,且n, m最大公约数为1。
示例 1:
输入:cont = [3, 2, 0, 2]
输出:[13, 4]
解释:原连分数等价于3 + (1 / (2 + (1 / (0 + 1 / 2))))。注意[26, 8], [-13, -4]都不是正确答案。
示例 2:
输入:cont = [0, 0, 3]
输出:[3, 1]
解释:如果答案是整数,令分母为1即可。
限制:
- cont[i] >= 0
- 1 <= cont的长度 <= 10
- cont最后一个元素不等于0
- 答案的n, m的取值都能被32位int整型存下(即不超过2 ^ 31 - 1)。
方法一:递归
class Solution {
public int[] recursive(int[] count, int index) {
if (index == count.length - 1) {
return new int[]{count[index], 1};
}
int[] nextRes = recursive(count, index+1);
return new int[]{count[index] * nextRes[0] + nextRes[1], nextRes[0]};
}
public int[] fraction(int[] cont) {
return recursive(cont, 0);
}
}
方法二:
class Solution {
public int[] fraction(int[] cont) {
int[] res = new int[2];
res[0] = 1;
res[1] = 0;
for(int i = cont.length - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int temp1 = res[1];
res[1] = res[0];
res[0] = cont[i] * res[1] + temp1;
}
return res;
}
}
[0149] 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
方法一:两次遍历
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
List<TreeNode> path_p = getPath(root, p);
List<TreeNode> path_q = getPath(root, q);
TreeNode ancestor = null;
for (int i = 0; i < path_p.size() && i < path_q.size(); ++i) {
if (path_p.get(i) == path_q.get(i)) {
ancestor = path_p.get(i);
} else {
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}
public List<TreeNode> getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode target) {
List<TreeNode> path = new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
TreeNode node = root;
while (node != target) {
path.add(node);
if (target.val < node.val) {
node = node.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
path.add(node);
return path;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法二:一次遍历
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
TreeNode ancestor = root;
while (true) {
if (p.val < ancestor.val && q.val < ancestor.val) {
ancestor = ancestor.left;
} else if (p.val > ancestor.val && q.val > ancestor.val) {
ancestor = ancestor.right;
} else {
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
方法三:递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
//如果小于等于0,说明p和q位于root的两侧,直接返回即可
if ((root.val - p.val) * (root.val - q.val) <= 0)
return root;
//否则,p和q位于root的同一侧,就继续往下找
return lowestCommonAncestor(p.val < root.val ? root.left : root.right, p, q);
}
}
[0150] 写字符串需要的行数
我们要把给定的字符串 S 从左到右写到每一行上,每一行的最大宽度为100个单位,如果我们在写某个字母的时候会使这行超过了100 个单位,那么我们应该把这个字母写到下一行。我们给定了一个数组 widths ,这个数组 widths[0] 代表 ‘a’ 需要的单位, widths[1] 代表 ‘b’ 需要的单位,…, widths[25] 代表 ‘z’ 需要的单位。
现在回答两个问题:至少多少行能放下S,以及最后一行使用的宽度是多少个单位?将你的答案作为长度为2的整数列表返回。
示例 1:
输入:
widths = [10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10]
S = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
输出: [3, 60]
解释:
所有的字符拥有相同的占用单位10。所以书写所有的26个字母,
我们需要2个整行和占用60个单位的一行。
示例 2:
输入:
widths = [4,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10,10]
S = "bbbcccdddaaa"
输出: [2, 4]
解释:
除去字母'a'所有的字符都是相同的单位10,并且字符串 "bbbcccdddaa" 将会覆盖 9 * 10 + 2 * 4 = 98 个单位.
最后一个字母 'a' 将会被写到第二行,因为第一行只剩下2个单位了。
所以,这个答案是2行,第二行有4个单位宽度。
注:
- 字符串 S 的长度在 [1, 1000] 的范围。
- S 只包含小写字母。
- widths 是长度为 26的数组。
- widths[i] 值的范围在 [2, 10]。
方法一:
我们从左到右遍历字符串 S 中的每个字母,并用二元组 (lines, width) 实时统计当前的答案。当遍历到一个字母 x 时,如果 width + widths[x] <= 100,那么就更新 width 并保持 lines 不变;如果 width + widths[x] > 100,那么就将 lines 的值加 1,并将 width 置为 widths[x]。
class Solution {
public int[] numberOfLines(int[] widths, String S) {
int lines = 1, width = 0;
for (char c: S.toCharArray()) {
int w = widths[c - 'a'];
width += w;
if (width > 100) {
lines++;
width = w;
}
}
return new int[]{lines, width};
}
}
[0151] 下一个更大元素 I
给定两个 没有重复元素 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。找到 nums1 中每个元素在 nums2 中的下一个比其大的值。
nums1 中数字 x 的下一个更大元素是指 x 在 nums2 中对应位置的右边的第一个比 x 大的元素。如果不存在,对应位置输出 -1 。
示例 1:
输入: nums1 = [4,1,2], nums2 = [1,3,4,2].
输出: [-1,3,-1]
解释:
对于num1中的数字4,你无法在第二个数组中找到下一个更大的数字,因此输出 -1。
对于num1中的数字1,第二个数组中数字1右边的下一个较大数字是 3。
对于num1中的数字2,第二个数组中没有下一个更大的数字,因此输出 -1。
示例 2:
输入: nums1 = [2,4], nums2 = [1,2,3,4].
输出: [3,-1]
解释:
对于 num1 中的数字 2 ,第二个数组中的下一个较大数字是 3 。
对于 num1 中的数字 4 ,第二个数组中没有下一个更大的数字,因此输出 -1 。
提示:
- nums1和nums2中所有元素是唯一的。
- nums1和nums2 的数组大小都不超过1000。
方法一:调栈
我们可以忽略数组 nums1,先对将 nums2 中的每一个元素,求出其下一个更大的元素。随后对于将这些答案放入哈希映射(HashMap)中,再遍历数组 nums1,并直接找出答案。对于 nums2,我们可以使用单调栈来解决这个问题。
我们首先把第一个元素 nums2[1] 放入栈,随后对于第二个元素 nums2[2],如果 nums2[2] > nums2[1],那么我们就找到了 nums2[1] 的下一个更大元素 nums2[2],此时就可以把 nums2[1] 出栈并把 nums2[2] 入栈;如果 nums2[2] <= nums2[1],我们就仅把 nums2[2] 入栈。对于第三个元素 nums2[3],此时栈中有若干个元素,那么所有比 nums2[3] 小的元素都找到了下一个更大元素(即 nums2[3]),因此可以出栈,在这之后,我们将 nums2[3] 入栈,以此类推。
可以发现,我们维护了一个单调栈,栈中的元素从栈顶到栈底是单调不降的。当我们遇到一个新的元素 nums2[i] 时,我们判断栈顶元素是否小于 nums2[i],如果是,那么栈顶元素的下一个更大元素即为 nums2[i],我们将栈顶元素出栈。重复这一操作,直到栈为空或者栈顶元素大于 nums2[i]。此时我们将 nums2[i] 入栈,保持栈的单调性,并对接下来的 nums2[i + 1], nums2[i + 2] … 执行同样的操作。
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Stack < Integer > stack = new Stack < > ();
HashMap < Integer, Integer > map = new HashMap < > ();
int[] res = new int[findNums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (!stack.empty() && nums[i] > stack.peek())
map.put(stack.pop(), nums[i]);
stack.push(nums[i]);
}
while (!stack.empty())
map.put(stack.pop(), -1);
for (int i = 0; i < findNums.length; i++) {
res[i] = map.get(findNums[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(M+N)
-
空间复杂度:O(N)
[0152] 用队列实现栈
使用队列实现栈的下列操作:
- push(x) – 元素 x 入栈
- pop() – 移除栈顶元素
- top() – 获取栈顶元素
- empty() – 返回栈是否为空
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作-- 也就是 push to back, peek/pop from front, size, 和 is empty 这些操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
你可以假设所有操作都是有效的(例如, 对一个空的栈不会调用 pop 或者 top 操作)。
方法一:两个队列
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue2.offer(x);
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
方法二:一个队列
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
int n = queue.size();
queue.offer(x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue.poll();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
[0153] 统计最大组的数目
给你一个整数 n 。请你先求出从 1 到 n 的每个整数 10 进制表示下的数位和(每一位上的数字相加),然后把数位和相等的数字放到同一个组中。
请你统计每个组中的数字数目,并返回数字数目并列最多的组有多少个。
示例 1:
输入:n = 13
输出:4
解释:总共有 9 个组,将 1 到 13 按数位求和后这些组分别是:
[1,10],[2,11],[3,12],[4,13],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9]。总共有 4 个组拥有的数字并列最多。
示例 2:
输入:n = 2
输出:2
解释:总共有 2 个大小为 1 的组 [1],[2]。
示例 3:
输入:n = 15
输出:6
示例 4:
输入:n = 24
输出:5
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^4
方法一:哈希表
class Solution {
public int countLargestGroup(int n) {
int ans = 0, max = 1;
int[] count = new int[n + 1];// 统计数位和有多少
int[] sum = new int[n + 1]; //计算1-n各个元素的数位和,例如数字i的数位和是sum[i / 10] + i % 10
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
sum[i] = sum[i / 10] + i % 10;
count[sum[i]]++;
if(count[sum[i]] > max)
max = count[sum[i]];
}
for(int num : count) ans += num == max ? 1 : 0;
return ans;
}
}
[0154] 和为s的两个数字
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是s。如果有多对数字的和等于s,则输出任意一对即可。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
输出:[2,7] 或者 [7,2]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [10,26,30,31,47,60], target = 40
输出:[10,30] 或者 [30,10]
限制:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums[i] <= 10^6
方法一:
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i < j) {
int s = nums[i] + nums[j];
if(s < target) i++;
else if(s > target) j--;
else return new int[] { nums[i], nums[j] };
}
return new int[0];
}
}
[0155] 重塑矩阵
在MATLAB中,有一个非常有用的函数 reshape,它可以将一个矩阵重塑为另一个大小不同的新矩阵,但保留其原始数据。
给出一个由二维数组表示的矩阵,以及两个正整数r和c,分别表示想要的重构的矩阵的行数和列数。
重构后的矩阵需要将原始矩阵的所有元素以相同的行遍历顺序填充。
如果具有给定参数的reshape操作是可行且合理的,则输出新的重塑矩阵;否则,输出原始矩阵。
示例 1:
输入:
nums =
[[1,2],
[3,4]]
r = 1, c = 4
输出:
[[1,2,3,4]]
解释:
行遍历nums的结果是 [1,2,3,4]。新的矩阵是 1 * 4 矩阵, 用之前的元素值一行一行填充新矩阵。
示例 2:
输入:
nums =
[[1,2],
[3,4]]
r = 2, c = 4
输出:
[[1,2],
[3,4]]
解释:
没有办法将 2 * 2 矩阵转化为 2 * 4 矩阵。 所以输出原矩阵。
注意:
- 给定矩阵的宽和高范围在 [1, 100]。
- 给定的 r 和 c 都是正数。
方法一 使用队列
public class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
int[][] res = new int[r][c];
if (nums.length == 0 || r * c != nums.length * nums[0].length)
return nums;
int count = 0;
Queue < Integer > queue = new LinkedList < > ();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {
queue.add(nums[i][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
res[i][j] = queue.remove();
}
}
return res;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(m*n)
空间复杂度:O(m*n)
方法二 不用额外空间
public class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
int[][] res = new int[r][c];
if (nums.length == 0 || r * c != nums.length * nums[0].length)
return nums;
int rows = 0, cols = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {
res[rows][cols] = nums[i][j];
cols++;
if (cols == c) {
rows++;
cols = 0;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(m*n)
空间复杂度:O(m*n)
方法三 除法和取模
public class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
int[][] res = new int[r][c];
if (nums.length == 0 || r * c != nums.length * nums[0].length)
return nums;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {
res[count / c][count % c] = nums[i][j];
count++;
}
}
return res;
}
}
时间复杂度:O(m*n)
空间复杂度:O(m*n)
[0156] 用栈实现队列
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
- push(x) – 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
- pop() – 从队列首部移除元素。
- peek() – 返回队列首部的元素。
- empty() – 返回队列是否为空。
示例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue();
queue.push(1);
queue.push(2);
queue.peek(); // 返回 1
queue.pop(); // 返回 1
queue.empty(); // 返回 false
说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 – 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。 - 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)。
方法一 使用两个栈
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
int front = 0;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
if (s1.empty())
front = x;
while (!s1.isEmpty())
s2.push(s1.pop());
s2.push(x);
while (!s2.isEmpty())
s1.push(s2.pop());
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
int temp = s1.pop();
if (!s1.empty())
front = s1.peek();
return temp;
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
return front;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
方法二:
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> s1 = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> s2 = new Stack<>();
int front = 0;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
public void push(int x) {
if (s1.empty())
front = x;
s1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
if (s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty())
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return s2.pop();
}
/** Get the front element. */
public int peek() {
if (!s2.isEmpty()) {
return s2.peek();
}
return front;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty() && s2.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
[0157] Fizz Buzz
写一个程序,输出从 1 到 n 数字的字符串表示。
-
如果 n 是3的倍数,输出“Fizz”;
-
如果 n 是5的倍数,输出“Buzz”;
3.如果 n 同时是3和5的倍数,输出 “FizzBuzz”。
示例:
n = 15,
返回:
[
"1",
"2",
"Fizz",
"4",
"Buzz",
"Fizz",
"7",
"8",
"Fizz",
"Buzz",
"11",
"Fizz",
"13",
"14",
"FizzBuzz"
]
方法一: 模拟法
class Solution {
public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
// ans list
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int num = 1; num <= n; num++) {
boolean divisibleBy3 = (num % 3 == 0);
boolean divisibleBy5 = (num % 5 == 0);
if (divisibleBy3 && divisibleBy5) {
// Divides by both 3 and 5, add FizzBuzz
ans.add("FizzBuzz");
} else if (divisibleBy3) {
// Divides by 3, add Fizz
ans.add("Fizz");
} else if (divisibleBy5) {
// Divides by 5, add Buzz
ans.add("Buzz");
} else {
// Not divisible by 3 or 5, add the number
ans.add(Integer.toString(num));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
- 时间复杂度: O(N)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
方法二: 字符串连接
class Solution {
public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
// ans list
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int num = 1; num <= n; num++) {
boolean divisibleBy3 = (num % 3 == 0);
boolean divisibleBy5 = (num % 5 == 0);
String numAnsStr = "";
if (divisibleBy3) {
// Divides by 3, add Fizz
numAnsStr += "Fizz";
}
if (divisibleBy5) {
// Divides by 5, add Buzz
numAnsStr += "Buzz";
}
if (numAnsStr.equals("")) {
// Not divisible by 3 or 5, add the number
numAnsStr += Integer.toString(num);
}
// Append the current answer str to the ans list
ans.add(numAnsStr);
}
return ans;
}
}
- 时间复杂度: O(N)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
方法三 用散列表
class Solution {
public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) {
// ans list
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
// Hash map to store all fizzbuzz mappings.
HashMap<Integer, String> fizzBizzDict =
new HashMap<Integer, String>() {
{
put(3, "Fizz");
put(5, "Buzz");
}
};
for (int num = 1; num <= n; num++) {
String numAnsStr = "";
for (Integer key : fizzBizzDict.keySet()) {
// If the num is divisible by key,
// then add the corresponding string mapping to current numAnsStr
if (num % key == 0) {
numAnsStr += fizzBizzDict.get(key);
}
}
if (numAnsStr.equals("")) {
// Not divisible by 3 or 5, add the number
numAnsStr += Integer.toString(num);
}
// Append the current answer str to the ans list
ans.add(numAnsStr);
}
return ans;
}
}
- 时间复杂度: O(N)
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
[0158] 用栈操作构建数组
给你一个目标数组 target 和一个整数 n。每次迭代,需要从 list = {1,2,3…, n} 中依序读取一个数字。
请使用下述操作来构建目标数组 target :
- Push:从 list 中读取一个新元素, 并将其推入数组中。
- Pop:删除数组中的最后一个元素。
- 如果目标数组构建完成,就停止读取更多元素。
题目数据保证目标数组严格递增,并且只包含 1 到 n 之间的数字。
请返回构建目标数组所用的操作序列。
题目数据保证答案是唯一的。
示例 1:
输入:target = [1,3], n = 3
输出:["Push","Push","Pop","Push"]
解释:
读取 1 并自动推入数组 -> [1]
读取 2 并自动推入数组,然后删除它 -> [1]
读取 3 并自动推入数组 -> [1,3]
示例 2:
输入:target = [1,2,3], n = 3
输出:["Push","Push","Push"]
示例 3:
输入:target = [1,2], n = 4
输出:["Push","Push"]
解释:只需要读取前 2 个数字就可以停止。
示例 4:
输入:target = [2,3,4], n = 4
输出:["Push","Pop","Push","Push","Push"]
提示:
- 1 <= target.length <= 100
- 1 <= target[i] <= 100
- 1 <= n <= 100
- target 是严格递增的
方法一:
class Solution {
public List<String> buildArray(int[] target, int n) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
int cur = 1;
for (int num: target) {
while (cur++ < num) { res.add("Push"); res.add("Pop"); }
res.add("Push");
}
return res;
}
}
[0159] 多数元素
给定一个大小为 n 的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数大于 ⌊ n/2 ⌋ 的元素。
你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。
示例 1:
输入: [3,2,3]
输出: 3
示例 2:
输入: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
输出: 2
方法一:哈希表
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> countNums(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (!counts.containsKey(num)) {
counts.put(num, 1);
} else {
counts.put(num, counts.get(num) + 1);
}
}
return counts;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> counts = countNums(nums);
Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> majorityEntry = null;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
if (majorityEntry == null || entry.getValue() > majorityEntry.getValue()) {
majorityEntry = entry;
}
}
return majorityEntry.getKey();
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(n)
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
方法二:排序
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length / 2];
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
-
空间复杂度:O(logn)
方法三:随机化
由于一个给定的下标对应的数字很有可能是众数,我们随机挑选一个下标,检查它是否是众数,如果是就返回,否则继续随机挑选。
class Solution {
private int randRange(Random rand, int min, int max) {
return rand.nextInt(max - min) + min;
}
private int countOccurences(int[] nums, int num) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Random rand = new Random();
int majorityCount = nums.length / 2;
while (true) {
int candidate = nums[randRange(rand, 0, nums.length)];
if (countOccurences(nums, candidate) > majorityCount) {
return candidate;
}
}
}
}
-
时间复杂度:理论上最坏情况下的时间复杂度为O(∞)
-
空间复杂度:O(1)
方法四:分治
class Solution {
private int countInRange(int[] nums, int num, int lo, int hi) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = lo; i <= hi; i++) {
if (nums[i] == num) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
private int majorityElementRec(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
// base case; the only element in an array of size 1 is the majority
// element.
if (lo == hi) {
return nums[lo];
}
// recurse on left and right halves of this slice.
int mid = (hi - lo) / 2 + lo;
int left = majorityElementRec(nums, lo, mid);
int right = majorityElementRec(nums, mid + 1, hi);
// if the two halves agree on the majority element, return it.
if (left == right) {
return left;
}
// otherwise, count each element and return the "winner".
int leftCount = countInRange(nums, left, lo, hi);
int rightCount = countInRange(nums, right, lo, hi);
return leftCount > rightCount ? left : right;
}
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
return majorityElementRec(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
}
-
时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
-
空间复杂度:O(logn)
方法五:Boyer-Moore 投票算法
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;
Integer candidate = null;
for (int num : nums) {
if (count == 0) {
candidate = num;
}
count += (num == candidate) ? 1 : -1;
}
return candidate;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
[0160] 消失的数字
数组nums包含从0到n的所有整数,但其中缺了一个。请编写代码找出那个缺失的整数。你有办法在O(n)时间内完成吗?
注意:本题相对书上原题稍作改动
示例 1:
输入:[3,0,1]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:[9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1]
输出:8
方法一:
利用异或的特性,res = res ^ x ^ x。对同一个值异或两次,那么结果等于它本身
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
res ^= i;
res ^= nums[i];
}
res ^= nums.length;
return res;
}
}
方法二:
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int sum = (nums.length + 1) * nums.length / 2;
int arraySum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) arraySum += nums[i];
return sum - arraySum;
}
}
两种方法:
-
时间复杂度为O(n)
-
空间复杂度为O(1)























 97
97











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








