Storm是一个分布式的实时的流式计算框架。
Storm运行有两种模式,分别是local与remote。
Storm的local就是单进程模式(运行在单一的JVM),local模式storm(注:下文将用storm-local来表示)整合Springboot,这与我们平常的开发方式没有多大区别。storm-local又被叫做测试模式。
Storm的remote是跨进程模式,spout与bolt运行在多个JVM中,也就是说,相互之间的消息通讯要通过远程调用的方式(跨进程)。local模式的storm(注:下文将用storm-remote来表示)与storm的开发方式差别,其实也不大(想想,也不可能很大,否则,一个不易于测试的东西,谁还想用),不过,理解起来就有很大区别了,一不小心,死都不知是怎么死的。
不管是那种方式,Storm都是必须通过Spring的factory(下文称为Spring BeanFacotry)才能获得目标bean。因此,我们设计了一个公共的工具,使可以在storm的两种运行模式下都可直接获得Spring BeanFacotry。
这个工具类比较关键,先贴出来。
package com.banling.stormspr.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
/**取得Spring的上下文(也就是Factory,使通过Factory可以得到目标JavaBean)
*
* @author Ban
*
*/
public class SpringContext implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
synchronized(this) {
if(SpringContext.applicationContext == null){
SpringContext.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
}
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
}
同时,注意,必须在SpringBoot启动后并由SpringBoot初始化这个工具类SpringContext。如何做到,下文介绍。
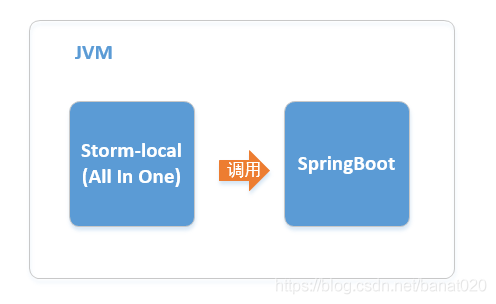
一、storm-local整合Springboot
在架构上,是这样的:
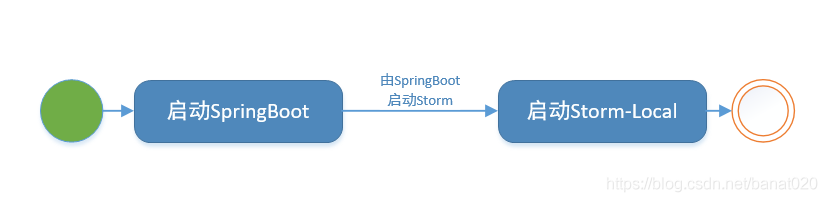
程序启动时,组件的启动顺序是这样的,先启动SpringBoot,然后在SpringBoot中启动Strom:
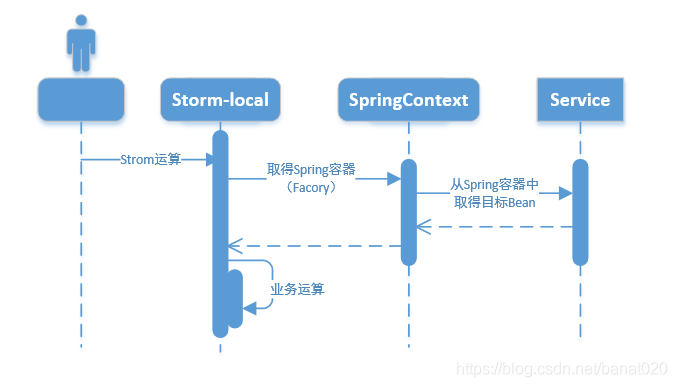
程序启动后,接着就是开始Storm运算,这时,程序运行是这样的:
下面列一个简单的storm-local例子,就是计算1到n的总数,为了扩展storm的知识点(测试),同时还做了些多余的逻辑,应用字段分组。

Storm-local源码请参考:https://github.com/banat020/storm-spr-local
1.1)数据输入
1.1.1)我们设计一个数据接口NumInService,用于获得源数据输入。这个数据接口的实例(接口的实现,请查看github源)将由Spring负责初始化并管理。
package com.banling.stormspr.service;
public interface NumInService {
int getNum();
}
1.1.2)Storm获取数据输入
package com.banling.stormspr.numcount.node;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.storm.spout.SpoutOutputCollector;
import org.apache.storm.task.TopologyContext;
import org.apache.storm.topology.OutputFieldsDeclarer;
import org.apache.storm.topology.base.BaseRichSpout;
import org.apache.storm.tuple.Fields;
import org.apache.storm.tuple.Values;
import com.banling.stormspr.config.SpringContext;
import com.banling.stormspr.service.NumInService;
/**数据输入
* @author Ban
*
*/
public class NumInSpout extends BaseRichSpout {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private SpoutOutputCollector collector;
@Override
public void open(Map conf, TopologyContext context, SpoutOutputCollector collector) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.collector=collector;
}
@Override
public void nextTuple() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
NumInService numInService=(NumInService)SpringContext.getApplicationContext().getBean("numInService");
int curNum=numInService.getNum();
if(curNum==-1) {//计算已经结束
return;
}
int groupFlag=curNum%10;//用于分组
Values values = new Values(curNum,groupFlag);
collector.emit(values);
}
@Override
public void declareOutputFields(OutputFieldsDeclarer declarer) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
declarer.declare(new Fields("inNum","groupFlag"));
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getComponentConfiguration() {
Map<String, Object> map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
//仅仅是测试,因此不要跑得太快了,设置为每50ms发送一次数据
map.put("topology.sleep.spout.wait.strategy.time.ms", 50);
return map;
}
}
注意NumInService numInService=(NumInService)SpringContext.getApplicationContext().getBean("numInService"),就是Spout<








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 685
685











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








