Description
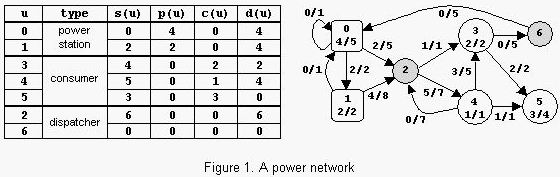
An example is in figure 1. The label x/y of power station u shows that p(u)=x and p max(u)=y. The label x/y of consumer u shows that c(u)=x and c max(u)=y. The label x/y of power transport line (u,v) shows that l(u,v)=x and l max(u,v)=y. The power consumed is Con=6. Notice that there are other possible states of the network but the value of Con cannot exceed 6.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20
7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7
(3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5
(0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15 6
Hint
采用网络流的模型来解决,在原图的基础上添加一个源点s和汇点t,对于每个发电站,从源点s引一条容量为pmax的弧;对于每个用电场所,引一条容量为cmax的弧到汇点t。
对于三元组(u,v,z),从u引一条容量为z的弧到v,最大电力消耗con就是这个网络的最大流。
采用相邻矩阵来存储网络中的流量(f[n][n])和容量(c[n][n]),采用BFS算法求增广路径时需要用一个队列q[n]和记录增广路径的数组fa[n],n是指网路中的节点个数,fa[i]为增广路径上节点i的前驱。
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n,np,nc,m,s,t;
int fa[104],f[104][104],c[104][104];
//fa[j]存储增广路径,为节点j在增广路径上的前驱节点,正数表示该弧为前向弧,负数表示该弧为后向弧
//f[][],c[][]记录网路中的流量和容量,存储方式为相邻矩阵
void pro()
{
int i,j,d,d0,ans=0;
fa[t]=1; //汇点的前驱指针初始化
while(fa[t]!=0) //如果增广路径存在
{
queue<int> q; //定义队列
q.push(s); //源点进入队尾
memset(fa,0,sizeof(fa)); //增广路径初始化
fa[s]=s; //源点的前驱指针指向自己
while((!q.empty())&&(fa[t]==0)) //如果队列非空并且没有找到至汇点的增广路径
{
i=q.front(); q.pop(); //取出队首节点
for(j=1;j<=t;j++) //枚举未在增广路径上的节点j
if(fa[j]==0)
if(f[i][j]<c[i][j]) //如果(i,j)的流量可增加,则(i,j)作为前向弧加入增广路径,j进入队列
{
fa[j]=i;
q.push(j);
}
else if(f[j][i]>0)//如果(i,j)可退流,则(i,j)作为后向弧加入增广路径,j进入队列
{
fa[j]=-i;
q.push(j);
}
}
if(fa[t]!=0)//如果找到一条从源点到汇点增广路径就改进当前流
{
d0=99999999;
i=t; //从汇点出发倒推计算最大可改进量d0
while(i!=s) //还没有倒推至源点
{
if(fa[i]>0) //i节点为尾的弧是前向弧
{if((d=c[fa[i]][i]-f[fa[i]][i])<d0)
d0=d;
}
else if(f[i][-fa[i]]<d0)//i节点为尾的弧是后向弧
d0=f[i][-fa[i]];
i=abs(fa[i]);//继续沿前驱指针倒推计算最大可改进量d0
}
ans=ans+d0; //总流量增加d0
i=t; //从汇点出发倒推调整增广路径上的流量
while(i!=s)
{
if(fa[i]>0) //若i节点为尾的弧是前向弧,则该弧流量增加d0
f[fa[i]][i]+=d0;
else
f[i][-fa[i]]-=d0;//若i节点为尾的弧是后向弧,则该弧流量减少d0
i=abs(fa[i]); //继续沿前驱指针调整流量
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;//输出最大流
}
int main()
{
int i,u,v,cc;
while(cin>>n>>np>>nc>>m)//反复输入节点数,发电站数目,用电场所数目,电力传输线数目
{
s=n+2;t=n+1; //设置源点s和汇点t
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
for(i=1;i<=m;i++) //对于原图中的边(u,v)连一条容量是cc的弧
{
while(getchar()!='(');
scanf("%d,%d)%d",&u,&v,&cc);
c[u+1][v+1]=cc;
}
for(i=1;i<=np;i++) //源点向每一个发电站连一条容量是cc的弧
{
while(getchar()!='(');
scanf("%d)%d",&u,&cc);
c[s][u+1]=cc;
}
for(i=1;i<=nc;i++) //每个用电场所向汇点连一条容量是cc的弧
{
while(getchar()!='(');
scanf("%d)%d",&u,&cc);
c[u+1][t]=cc;
}
pro(); //求最大流
}
return 0;
}







 本文探讨了如何使用网络流模型解决电力网络中最大电力消耗的问题。通过建立包含发电站、消费者和调度器的网络模型,引入源点和汇点,详细阐述了利用BFS算法寻找增广路径并计算最大流的过程。
本文探讨了如何使用网络流模型解决电力网络中最大电力消耗的问题。通过建立包含发电站、消费者和调度器的网络模型,引入源点和汇点,详细阐述了利用BFS算法寻找增广路径并计算最大流的过程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








