背景:
初始Vue.js,了解组件时Vue的主要构成部分,但组件内部的作用域是相对独立的部分,组件之间的关系一般如下图:

组件A与组件B、C之间是父子组件,组件B、C之间是兄弟组件,而组件A、D之间是隔代的关系
那么对于这些不同的关系,本文主要分享了他们之间可以采用的几种数据通信方式。例如Props、$emit/$on、Vuex等。可以根据使用场景选择适合的使用方式。
一、Prop / $emit
1、Prop是你可以在组件上注册的一些自定义特性。当一个值传递给一个Prop特性的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个属性。父组件向子组件传值,通过绑定属性来向子组件传入数据,子组件通过Props属性获取对应数据
//父组件 <template> <div> <child :title="title"></child> </div> </template> <script> import Child from './child.vue' export defalut{ name:'parent', data(){ return{ title:'我是父组件给的' } }, components:{ Child } } </script> //子组件 <template> <div> <p>{{title}}</p> </div> </template> <script> export default{ name:'child', data(){ return{ } }, props:['title'] } </script>
2、$emit 子组件向父组件传值(通过事件形式),子组件通过 $emit 事件向父组件发送消息,将自己的数据传递给父组件。

1 // 父组件 2 <template> 3 <div class="container"> 4 <div class="title">{{title}}</div> 5 <child @changeTitle="parentTitle"></child> 6 </div> 7 </template> 8 9 <script> 10 import Child from "./component/child.vue"; 11 12 export default { 13 name: "demo", 14 data: function() { 15 return { 16 title: null 17 }; 18 }, 19 components: { 20 Child 21 }, 22 methods: { 23 parentTitle(e) { 24 this.title = e; 25 } 26 } 27 }; 28 </script> 29 30 31 // 子组件 32 <template> 33 <div class="center"> 34 <button @click="childTitle">我给父组件赋值</button> 35 </div> 36 </template> 37 38 <script> 39 export default { 40 name: 'demo', 41 data() { 42 return { 43 key: 1 44 }; 45 }, 46 methods: { 47 childTitle() { 48 this.$emit('changeTitle', `我给父组件的第${this.key}次`); 49 this.key++; 50 } 51 } 52 }; 53 </script>
小总结:常用的数据传输方式,父子间传递。
二、 $emit / $on
这个方法是通过创建了一个空的 vue 实例,当做 $emit 事件的处理中心(事件总线),通过他来触发以及监听事件,方便的实现了任意组件间的通信,包含父子,兄弟,隔代组件。
1 // 父组件 2 <template> 3 <div class="container"> 4 <child1 :Event="Event"></child1> 5 <child2 :Event="Event"></child2> 6 <child3 :Event="Event"></child3> 7 </div> 8 </template> 9 10 <script> 11 import Vue from "vue"; 12 13 import Child1 from "./component/child1.vue"; 14 import Child2 from "./component/child2.vue"; 15 import Child3 from "./component/child3.vue"; 16 17 const Event = new Vue(); 18 19 export default { 20 name: "demo", 21 data: function() { 22 return { 23 Event: Event 24 }; 25 }, 26 components: { 27 Child1, 28 Child2, 29 Child3 30 }, 31 }; 32 </script> 33 34 35 // 子组件1 36 <template> 37 <div class="center"> 38 1.我的名字是:{{name}} 39 <button @click="send">我给3组件赋值</button> 40 </div> 41 </template> 42 43 <script> 44 export default{ 45 name: "demo1", 46 data() { 47 return { 48 name: "政采云" 49 }; 50 }, 51 props: { 52 Event 53 }, 54 methods: { 55 send() { 56 this.Event.$emit("message-a", this.name); 57 } 58 } 59 }; 60 </script> 61 62 63 // 子组件2 64 <template> 65 <div class="center"> 66 2.我的年龄是:{{age}}岁 67 <button @click="send">我给3组件赋值</button> 68 </div> 69 </template> 70 71 <script> 72 /* eslint-disable */ 73 export default { 74 name: "demo2", 75 data() { 76 return { 77 age: "3" 78 }; 79 }, 80 props: { 81 Event 82 }, 83 methods: { 84 send() { 85 this.Event.$emit("message-b", this.age); 86 } 87 } 88 }; 89 </script> 90 91 92 // 子组件3 93 <template> 94 <div class="center">我的名字是{{name}},今年{{age}}岁</div> 95 </template> 96 97 <script> 98 export default{ 99 name: 'demo3', 100 data() { 101 return { 102 name: '', 103 age: '' 104 }; 105 }, 106 props: { 107 Event 108 }, 109 mounted() { 110 this.Event.$on('message-a', name => { 111 this.name = name; 112 }); 113 this.Event.$on('message-b', age => { 114 this.age = age; 115 }); 116 }, 117 }; 118 </script>
小总结:巧妙的在父子,兄弟,隔代组件中都可以互相数据通信。
三、 Vuex
Vuex[1] 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有组件的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。
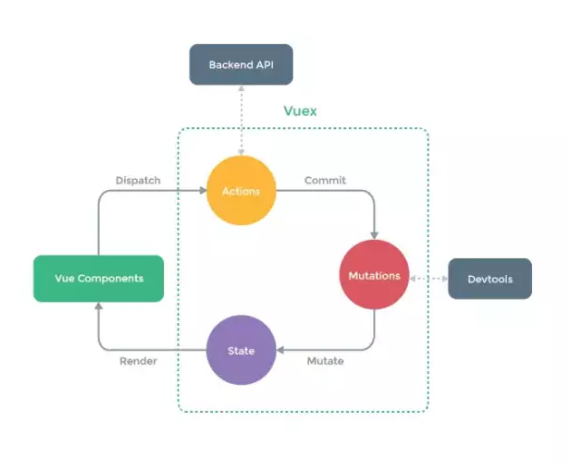
Vuex 实现了一个单项数据流,通过创建一个全局的 State 数据,组件想要修改 State 数据只能通过 Mutation 来进行,例如页面上的操作想要修改 State 数据时,需要通过 Dispatch (触发 Action ),而 Action 也不能直接操作数据,还需要通过 Mutation 来修改 State 中数据,最后根据 State 中数据的变化,来渲染页面。

1 // index.js 2 import Vue from 'vue'; 3 import Tpl from './index.vue'; 4 import store from './store'; 5 6 new Vue({ 7 store, 8 render: h => h(Tpl), 9 }).$mount('#app'); 10 11 12 // store 13 import Vue from 'vue'; 14 import Vuex from 'vuex'; 15 16 Vue.use(Vuex); 17 18 const store = new Vuex.Store({ 19 state: { 20 count: 1 21 }, 22 mutations: { 23 increment(state) { 24 state.count++; 25 }, 26 reduce(state) { 27 state.count--; 28 } 29 }, 30 actions: { 31 actIncrement({ commit }) { 32 commit('increment'); 33 }, 34 actReduce({ commit }) { 35 commit('reduce'); 36 } 37 }, 38 getters: { 39 doubleCount: state => state.count*2 40 } 41 }); 42 43 export default store; 44 45 46 // vue文件 47 <template> 48 <div class="container"> 49 <p>我的count:{{count}}</p> 50 <p>doubleCount:{{doubleCount}}</p> 51 <button @click="this.actIncrement">增加</button> 52 <button @click="this.actReduce">减少</button> 53 </div> 54 </template> 55 56 <script> 57 import { mapGetters, mapActions, mapState } from "vuex"; 58 59 export default { 60 name: "demo", 61 data: function() { 62 return {}; 63 }, 64 components: {}, 65 props: {}, 66 computed: { 67 ...mapState(["count"]), 68 ...mapGetters(["doubleCount"]) 69 }, 70 methods: { 71 ...mapActions(["actIncrement", "actReduce"]) 72 } 73 }; 74 </script>
Vuex 中需要注意的点:
Mutation :是修改State数据的唯一推荐方法,且只能进行同步操作。
Getter :Vuex 允许在Store中定义 “ Getter”(类似于 Store 的计算属性)。Getter 的返回值会根据他的依赖进行缓存,只有依赖值发生了变化,才会重新计算。
本段只是简单介绍了一下 Vuex 的运行方式,更多功能例如 Module 模块请参考官网[2] 。
小总结:统一的维护了一份共同的 State 数据,方便组件间共同调用。
四、 $attrs / $listeners
Vue 组件间传输数据在 Vue 2.4 版本后有了新方法。除了 Props 外,还有了 $attrs / $listeners。
• $attrs: 包含了父作用域中不作为 Prop 被识别 (且获取) 的特性绑定(Class 和 Style 除外)。当一个组件没有声明任何 Prop 时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定 (Class 和 Style 除外),并且可以通过 v-bind="$attrs" 传入内部组件——在创建高级别的组件时非常有用。
• $listeners: 包含了父作用域中的 (不含 .native 修饰器的) v-on 事件监听器。它可以通过 v-on="$listeners" 传入内部组件
下面来看个例子
1 // 父组件 2 <template> 3 <div class="container"> 4 <button style="backgroundColor:lightgray" @click="reduce">减dd</button> 5 <child1 :aa="aa" :bb="bb" :cc="cc" :dd="dd" @reduce="reduce"></child1> 6 </div> 7 </template> 8 9 <script> 10 import Child1 from './component/child1.vue'; 11 export default { 12 name: 'demo', 13 data: function() { 14 return { 15 aa: 1, 16 bb: 2, 17 cc: 3, 18 dd: 100 19 }; 20 }, 21 components: { 22 Child1 23 }, 24 methods: { 25 reduce() { 26 this.dd--; 27 } 28 } 29 }; 30 </script> 31 32 33 // 子组件1 34 <template> 35 <div> 36 <div class="center"> 37 <p>aa:{{aa}}</p> 38 <p>child1的$attrs:{{$attrs}}</p> 39 <button @click="this.reduce1">组件1减dd</button> 40 </div> 41 <child2 v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></child2> 42 </div> 43 </template> 44 45 <script> 46 import child2 from './child2.vue'; 47 export default { 48 name: 'demo1', 49 data() { 50 return {}; 51 }, 52 props: { 53 aa: Number 54 }, 55 components: { 56 child2 57 }, 58 methods: { 59 reduce1() { 60 this.$emit('reduce'); 61 } 62 } 63 }; 64 </script> 65 66 67 // 子组件2 68 <template> 69 <div> 70 <div class="center"> 71 <p>bb:{{bb}}</p> 72 <p>child2的$attrs:{{$attrs}}</p> 73 <button @click="this.reduce2">组件2减dd</button> 74 </div> 75 <child3 v-bind="$attrs"></child3> 76 </div> 77 </template> 78 79 <script> 80 import child3 from './child3.vue'; 81 export default { 82 name: 'demo1', 83 data() { 84 return {}; 85 }, 86 props: { 87 bb: Number 88 }, 89 components: { 90 child3 91 }, 92 methods: { 93 reduce2() { 94 this.$emit('reduce'); 95 } 96 } 97 }; 98 </script> 99 100 101 // 子组件3 102 <template> 103 <div class="center"> 104 <p>child3的$attrs:{{$attrs}}</p> 105 </div> 106 </template> 107 108 <script> 109 export default { 110 name: 'demo3', 111 data() { 112 return {}; 113 }, 114 props: { 115 dd: String 116 }, 117 }; 118 </script>
简单来说,$attrs 里存放的是父组件中绑定的非 props 属性,$listeners 里面存放的是父组件中绑定的非原生事件。
小总结:当传输数据、方法较多时,无需一一填写的小技巧。
五、 Provider / Inject
Vue 2.2 版本以后新增了这两个 API , 这对选项需要一起使用,以允许一个祖先组件向其所有子孙后代注入一个依赖,不论组件层次有多深,并在其上下游关系成立的时间里始终生效。 简单来说,就是父组件通过 Provider 传入变量,任意子孙组件通过 Inject 来拿到变量。
1 // 父组件 2 <template> 3 <div class="container"> 4 <button @click="this.changeName">我要改名字了</button> 5 <p>我的名字:{{name}}</p> 6 <child1></child1> 7 </div> 8 </template> 9 10 <script> 11 import Child1 from './component/child1.vue'; 12 export default { 13 name: 'demo', 14 data: function() { 15 return { 16 name: '政采云' 17 }; 18 }, 19 // provide() { 20 // return { 21 // name: this.name //这种绑定方式是不可响应的 22 // }; 23 // }, 24 provide() { 25 return { 26 obj: this 27 }; 28 }, 29 components: { 30 Child1 31 }, 32 methods: { 33 changeName() { 34 this.name = '政采云前端'; 35 } 36 } 37 }; 38 </script> 39 40 41 // 子组件 42 <template> 43 <div> 44 <div class="center"> 45 <!-- <p>子组件名字:{{name}}</p> --> 46 <p>子组件名字:{{this.obj.name}}</p> 47 </div> 48 <child2></child2> 49 </div> 50 </template> 51 52 <script> 53 import child2 from './child2.vue'; 54 55 export default { 56 name: 'demo1', 57 data() { 58 return {}; 59 }, 60 props: {}, 61 // inject: ["name"], 62 inject: { 63 obj: { 64 default: () => { 65 return {}; 66 } 67 } 68 }, 69 components: { 70 child2 71 }, 72 }; 73 </script>
需要注意的是: Provide 和 Inject 绑定并不是可响应的。这是刻意为之的。然而,如果你传入了一个可监听的对象,那么其对象的属性还是可响应的。
所以,如果采用的是我代码中注释的方式,父级的 name 如果改变了,子组件this.name 是不会改变的,仍然是 政采云 ,而当采用代码中传入一个监听对象,修改对象中属性值,是可以监听到修改的。
Provider / Inject 在项目中需要有较多公共传参时使用还是颇为方便的。
小总结:传输数据父级一次注入,子孙组件一起共享的方式。
六、 $parent / $children & $refs
• $parent / $children: 指定已创建的实例之父实例,在两者之间建立父子关系。子实例可以用 this.$parent 访问父实例,子实例被推入父实例的 $children 数组中。
• $refs: 一个对象,持有注册过 ref 特性[3] 的所有 DOM 元素和组件实例。ref 被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息。引用信息将会注册在父组件的 $refs 对象上。如果在普通的 DOM 元素上使用,引用指向的就是 DOM 元素;如果用在子组件上,引用就指向组件。
1 // 父组件 2 <template> 3 <div class="container"> 4 <p>我的title:{{title}}</p> 5 <p>我的name:{{name}}</p> 6 <child1 ref="comp1"></child1> 7 <child2 ref="comp2"></child2> 8 </div> 9 </template> 10 11 <script> 12 import Child1 from './component/child1.vue'; 13 import Child2 from './component/child2.vue'; 14 export default { 15 name: 'demo', 16 data: function() { 17 return { 18 title: null, 19 name: null, 20 content: '就是我' 21 }; 22 }, 23 components: { 24 Child1, 25 Child2 26 }, 27 mounted() { 28 const comp1 = this.$refs.comp1; 29 this.title = comp1.title; 30 comp1.sayHello(); 31 this.name = this.$children[1].title; 32 }, 33 }; 34 </script> 35 36 37 // 子组件1-ref方式 38 <template> 39 <div> 40 <div class="center">我的父组件是谁:{{content}}</div> 41 </div> 42 </template> 43 44 <script> 45 export default { 46 name: 'demo1', 47 data() { 48 return { 49 title: '我是子组件', 50 content: null 51 }; 52 }, 53 mounted() { 54 this.content = this.$parent.content; 55 }, 56 methods: { 57 sayHello() { 58 window.alert('Hello'); 59 } 60 } 61 }; 62 </script> 63 64 65 // 子组件2-children方式 66 <template> 67 <div> 68 <div class="center"></div> 69 </div> 70 </template> 71 72 <script> 73 export default{ 74 name: 'demo1', 75 data() { 76 return { 77 title: '我是子组件2' 78 }; 79 }, 80 }; 81 </script>
通过例子可以看到这两种方式都可以父子间通信,而缺点也很统一,就是都不能跨级以及兄弟间通信。
小总结:父子组件间共享数据以及方法的便捷实践之一。
总结
组件间不同的使用场景可以分为 3 类,对应的通信方式如下:
• 父子通信:Props / $emit,$emit / $on,Vuex,$attrs / $listeners,provide/inject,$parent / $children&$refs
• 兄弟通信:$emit / $on,Vuex
• 隔代(跨级)通信:$emit / $on,Vuex,provide / inject,$attrs / $listeners





















 128
128











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








