直接上代码
int i = 0;
//***1
const int * ref11 = &i;
int * &refn11 = ref11;
int * const ref12 = &i;
int * &refn12 = ref12;
int * ref13 = &i;
const int * &refn13 = ref13;
int * ref14 = &i;
int * const &refn14 = ref14;
//***2
int * const ref21 = &i;
int * const &refn21 = ref21;
int * const ref22 = &i;
const int * &refn22 = ref22;
const int * ref23 = &i;
const int * &refn23 = ref23;
const int * ref24 = &i;
int * const &refn24 = ref24;
//***3
const int * const ref31 = &i;
int * const &refn31 = ref31;
const int * const ref32 = &i;
const int * &refn32 = ref32;
int * const ref33 = &i;
const int * const&refn33 = ref33;
const int * ref34 = &i;
const int * const&refn34 = ref34;
//***4
const int * const ref41 = &i;
const int * const &refn41 = ref41;采用gcc编译器4.7版本,开启c++11支持,输出为:
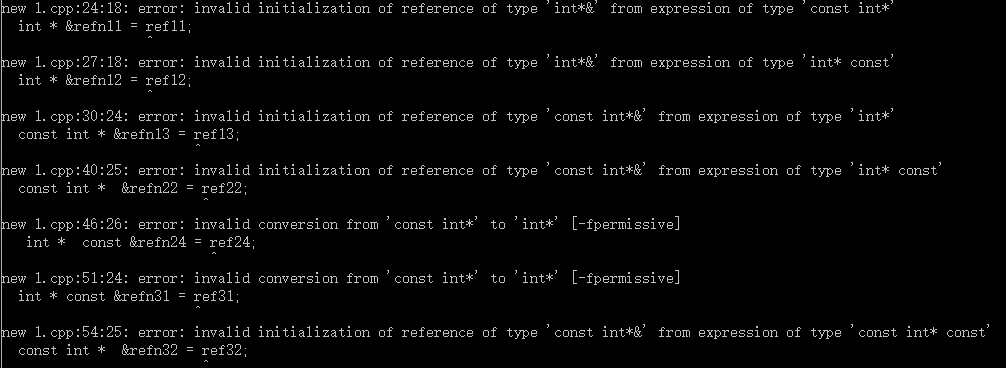
结果表明:
1、引用的指针对象,其底层const必须与引用的指针类型严格匹配
2、非常量引用,其顶层const不被忽略
3、常量引用,可以忽略所引用指针的顶层const,但不能忽略底层const
























 1522
1522

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








