热点数据的缓存
意思即为把经常被访问的数据存储到redis中,以后再查找该数据时,优先从redis中查询,如果redis没有被命中,则才会查询数据。并把查询的结果放入redis中以便下次能从redis中获取。
这样就可以提高查询效率, 降低数据库的访问频率,减少数据库的压力。
那什么样的数据适合放入缓存呢?
查询频率高的数据、 修改频率低的数据、 数据安全性要求不高的。
实例:
创建一个springboot项目,导入依赖,修改配置文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>#数据源
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/qy666?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=1234
#redis
spring.redis.host=192.168.184.130
spring.redis.port=6380
#mybatis-plus
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
配置缓存和序列化文件
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题),过期时间600秒
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600)) //缓存过期10分钟 ---- 业务需求。
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))//设置key的序列化方式
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer)) //设置value的序列化
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}
}实体类
@Data
@TableName("tbl_dept")
public class Dept {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer did;
@TableField(value = "d_name")
private String dname;
private String loc;
}
dao层
public interface DeptDao extends BaseMapper<Dept> {
}
service层 在需要缓存的方法上加上相应注解
public interface DeptService {
Dept findById(Integer id);
int delete(Integer id);
Dept insert(Dept dept);
Dept update(Dept dept);
}
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl implements DeptService {
@Autowired
private DeptDao deptDao;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "dept",key = "#id")
public Dept findById(Integer id) {
Dept dept = deptDao.selectById(id);
return dept;
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "dept",key = "#id")
public int delete(Integer id){
int row = deptDao.deleteById(id);
return row;
}
@Override
public Dept insert(Dept dept){
int insert = deptDao.insert(dept);
return dept;
}
@Override
@CachePut(cacheNames = "dept",key = "#dept.did")
public Dept update(Dept dept){
int i = deptDao.updateById(dept);
return dept;
}
}
controller层
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/dept")
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
private DeptService deptService;
@GetMapping("/getById/{id}")
public Dept getById(@PathVariable Integer id ){
Dept dept = deptService.findById(id);
return dept;
}
@GetMapping("/delete/{id}")
public int delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
return deptService.delete(id);
}
@GetMapping("/insert")
public Dept insert(Dept dept){
return deptService.insert(dept);
}
@GetMapping("/update")
public Dept update(Dept dept){
return deptService.update(dept);
}
}
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.aaa.dao")
@EnableCaching
public class Qy168SpringbootRedis02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Qy168SpringbootRedis02Application.class, args);
}
}
测试结果
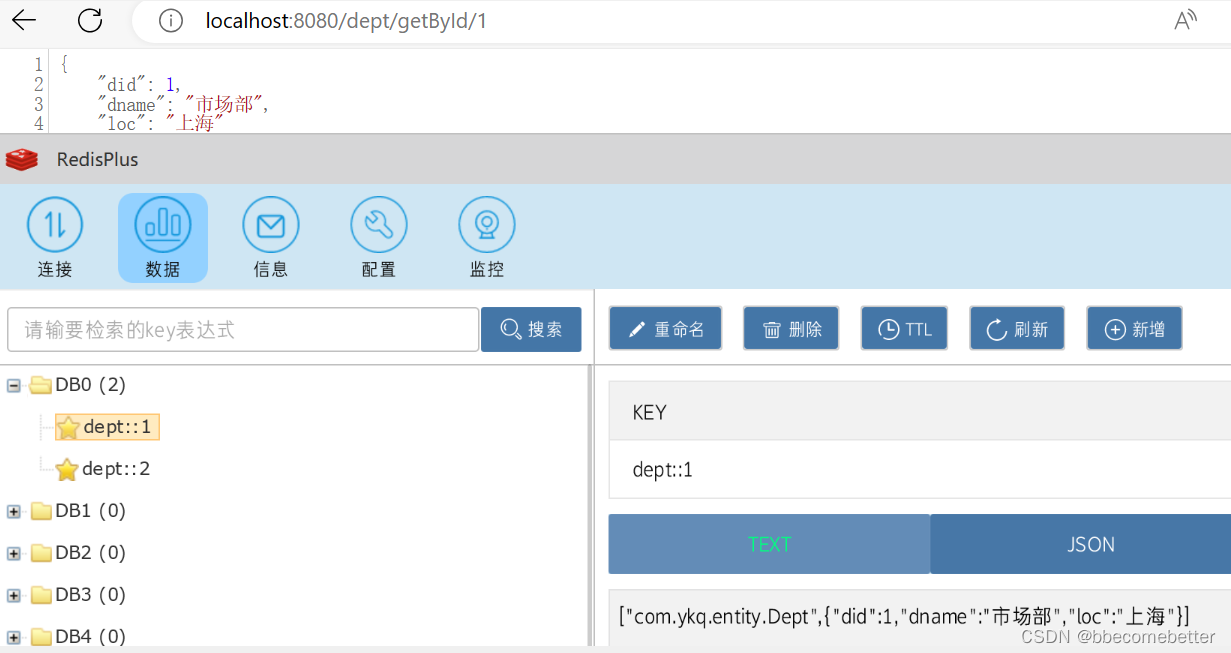
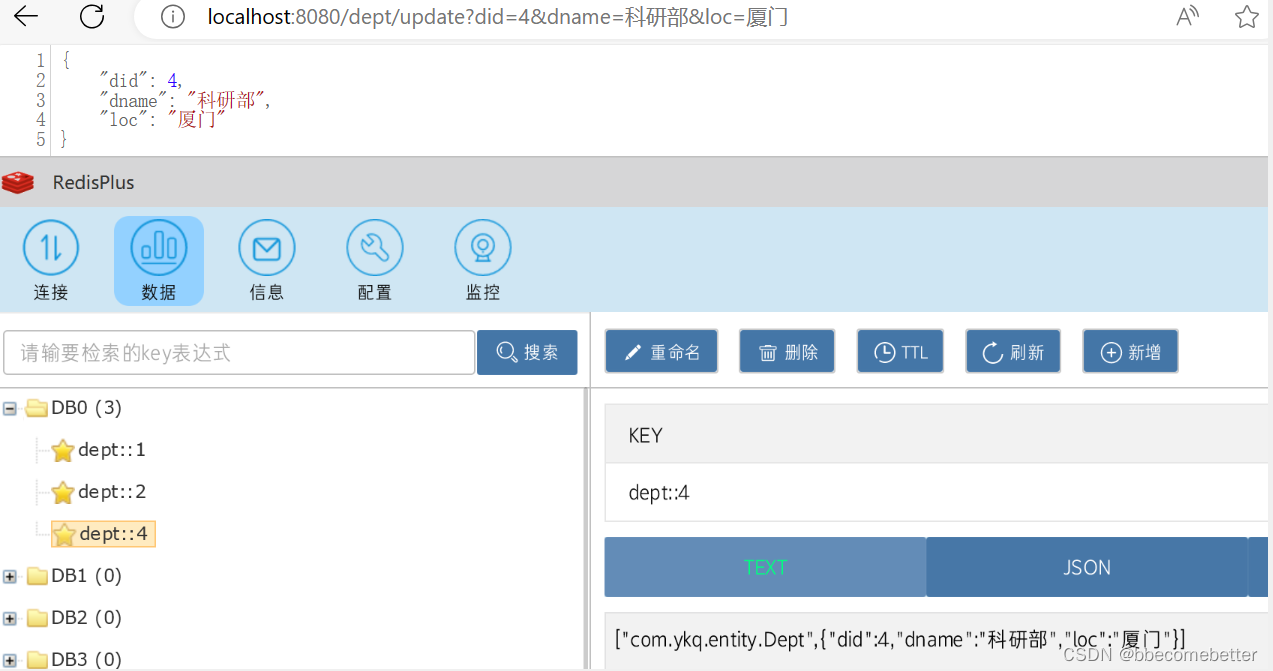

此时可以看到,redis中已经有了数据信息。
使用redis实现分布式锁
当我们使用一个出售服务时,如果系统的并发量太高,就可能会出现线程安全问题,出现重卖、超卖的情况发生,举个例子:
实例:
创建一个spring boot项目,导入依赖,修改配置文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
server.port=8088
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=1234
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/qy666?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
# 配置redis服务器的地址
spring.redis.host=192.168.184.130
spring.redis.port=6380实体类
@Data
@TableName("tbl_stock")
public class Stock {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private int productid;
@TableField("num")
private int stock;
}
dao层(这里没有使用mybatis puls 体验了下mybatis注解的使用)
@Mapper
public interface StockDao {
@Select("select num from tbl_stock where productid=#{productid}")
int findById(Integer productid);
@Update("update tbl_stock set num=num-1 where productid=#{productid} ")
void update(Integer productid);
}
controller层
@RestController
public class StockController {
@Autowired
private StockService02 stockService;
//根据商品编号减库存
@GetMapping("/incr/{productid}")
public String incr(@PathVariable Integer productid){
return stockService.decrement(productid);
}
}
service层
@Service
public class StockService02 {
@Autowired
private StockDao stockDao;
public String decrement(Integer productid) {
int num = stockDao.findById(productid);
if (num > 0) {
stockDao.update(productid);
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个";
} else {
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。";
}
}
}
这时我们使用jmeter测压工具,来并发访问出售功能
 此时出现了重卖和超卖的线程安全问题。
此时出现了重卖和超卖的线程安全问题。
想解决这个问题只需要加上锁即可。
@Service
public class StockService02 {
@Autowired
private StockDao stockDao;
public String decrement(Integer productid) {
synchronized (this) {
int num = stockDao.findById(productid);
if (num > 0) {
stockDao.update(productid);
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个";
} else {
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。";
}
}
}
}
但是,如果我们访问的是一个出售服务的集群,那么后台的服务器就有可能同时拿到统一把锁,这时还会出现超卖,重卖的问题。
这时就需要我们的redis来解决此问题了。
redis单线程
当使用了redis,当线程拿锁时就会进行排队,这样就不会出现同时拿锁的现象了。
只需修改service层代码
@Service
public class StockService02 {
@Autowired
private StockDao stockDao;
//---通过jmeter压测后发现商品出现--线程安全问题。
//--如何解决上面的线程安全问题: 加锁。【自动锁synchronized 或手动锁 Lock】
//--如果我们现在的项目部署时为一个集群--如果再高并发下使用【自动锁synchronized 或手动锁 Lock】有出现了线程安全问题。【自动锁synchronized 或手动锁 Lock】他们属于jvm锁。
//--如何解决集群下线程安全问题。
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public String decrement(Integer productid) {
ValueOperations<String, String> forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Boolean flag = forValue.setIfAbsent("product::" + productid, "xxxxx", 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (flag) {
try {
int num = stockDao.findById(productid);
if (num > 0) {
stockDao.update(productid);
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个";
} else {
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。";
}
} finally {
redisTemplate.delete("prodcut::" + productid);
}
} else {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return decrement(productid);
}
}
}
redis实现分布式的缺陷
"当使用了redis,当线程拿锁时就会进行排队,这样就不会出现同时拿锁的现象了。",虽然这么说,但是,如果程序的运行时间太长,超过了redis锁的时间,那么就会出现Bug,超过了锁的时间,就会再拿一把锁,释放第一把锁时,会释放最后拿到的锁。这也是redis实现分布式的缺陷。
我们可以使用第三方插件redisson来解决这个问题,redisson提供了一个看门狗机制,如果加锁后,检测到程序还在运行时,就延长锁的生存时间。
还是这个实例,在依赖中引入redisson
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.23.4</version>
</dependency> 在启动类中创建一个RedissonClient对象,交于spring容器管理
@Bean //返回的对象交于spring容器来管理
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.223.158:6379");
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
修改service层代码
@Service
public class StockService02 {
@Autowired
private StockDao stockDao;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
public String decrement(Integer productid) {
//获取指定的锁对象
RLock rlock = redissonClient.getLock("product::" + productid);
//加锁
rlock.lock(30,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
//如果返回true表示获取锁成功,返回的是false表示获取锁失败
int num = stockDao.findById(productid);
if (num > 0) {
stockDao.update(productid);
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存剩余:" + (num - 1) + "个";
} else {
System.out.println("商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。");
return "商品编号为:" + productid + "的商品库存不足。";
}
}finally {
//释放锁资源
rlock.unlock();
}
}
}
扩充知识:缓存穿透、雪崩等
什么是缓存穿透?
缓存穿透就是数据库中没有该数据,缓存中也没有该数据,这时有人恶意访问这种数据。
解决方案:
1、在控制层对一些不合法的数据进行校验。
2、使用布隆过滤器。把数据库中存在的id放入一个大的bitmap数组中,当查询一个不存在的id时就会被该过滤器过滤掉。
3、把数据中查询的空对象也存入缓存中。但是这个对象的存储时间一般不超过5分钟。
什么是缓存雪崩?
所谓的缓存雪崩就是缓存中出现大量数据过期的现象,而就在这时有大量的请求访问这些数据。压力顶到数据库。从而造成数据库压力过大。
会出现缓存雪崩的情况和解决方案:
1、项目刚上线。---预先把数据存放的缓存中
2、存中的数据在某个时间端内出现大量过期。 ---设置散列的过期时间。
3、redis宕机。----搭建redis集群
如何保证缓存数据和数据库数据一致?
1、合理的设置缓存的过期时间
2、 当执行CUD操作时,要同步修改缓存数据。





















 591
591











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








