ListView在android的开发中使用较为频繁,在这篇文章中,我们将介绍ListView搭配适配器(BaseAdapter)的使用。
ListView就好像是一个装视图(View)的容器,其作用就是将多个相似的视图垂直的展示出来。
适配器(Adapter)可以将数据映射到视图上,是连接数据和视图的桥梁。android提供了多种适配器,其中BaseAdapter为通用适配器,其使用方便灵活,通用性高,所以在开发中使用较多。本篇文章的目的就是将上一篇中解析出来的数据用Listview展示出来。
大概步骤:
1、ListView子视图布局
2、重写适配器
3、设计主布局
4、用Activity将数据显示出来
1、item_emp.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/emp_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:textSize="30sp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/emp_age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/emp_name"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/emp_name"
android:layout_marginLeft="50dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
2、重写适配器EmpAdapter
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
* 当系统开始绘制ListView的时候,首先调用getCount()方法。
* 得到它的返回值,即ListView的长度。然后系统调用getView()
* 方法,根据这个长度逐一绘制ListView的每一行。也就是说,如果让
* getCount()返回1,那么只显示一行。而getItem()和
* getItemId()则在需要处理和取得Adapter中的数据时调用。
*
*/
//继承BaseAdapter,重写BaseAdapter中的方法
public class EmpAdapter extends BaseAdapter
{
private Context context;
private List<Employee> empList;
public EmpAdapter(Context context,List<Employee> empList)
{
this.context = context;
this.empList = empList;
}
public void freshView(List<Employee> list)
{
this.empList = list;
//刷新数据
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
@Override
public int getCount()
{
return empList == null ? 0 : empList.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position)
{
return empList == null ? null : empList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position)
{
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
ViewHolder holder = null;
if(convertView == null)
{
//ListView子视图布局
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.item_emp, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.emp_name = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.emp_name);
holder.emp_age = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.emp_age);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}else{
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
String empName = empList.get(position).getName();
holder.emp_name.setText(empName);
int age = empList.get(position).getAge();
holder.emp_age.setText(String.valueOf(age));
return convertView;
}
//一种优化的方法,避免系统重复的画一个视图
class ViewHolder {
public TextView emp_name;
public TextView emp_age;
}
}
3、主布局文件activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="部门:" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/deptment"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:textSize="40sp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_emp_total"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_below="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="总人数:" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/emp_total"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/txt_emp_total"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/txt_emp_total"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:textSize="40sp"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/emp_info"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/txt_emp_total"
android:layout_below="@+id/txt_emp_total"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:textSize="40sp"
android:text="员工信息" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/emp_list"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/dep_name"
android:layout_below="@+id/emp_info"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp" >
</ListView>
</RelativeLayout>4、Activity代码
package com.example.test;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
private Context context;
private TextView depName;// 部门名称
private TextView depTotal;// 部门总人数
private ListView empList;
private DepartmentInfo depInfo;
private EmpAdapter adapter;
// 此处的json数据时我们的一个示例,为了看出效果,我们多加了几条数据
String jsonString = "{\"department\": \"研发\"," + "\"total\": 30,"
+ "\"employeeList\": [" + "{\"name\": \"张三\",\"age\": 24},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25},"
+ "{\"name\": \"李四\",\"age\": 25}]}";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 设置布局
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
context = MainActivity.this;
// 初始化视图
initView();
// 加载数据
loadData();
}
private void initView()
{
depName = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.deptment);
depTotal = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.emp_total);
empList = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.emp_list);
adapter = new EmpAdapter(context, null);
empList.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void loadData()
{
// 启动一个线程来加载数据
new Thread()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
// 解析json数据
depInfo = JsonUtil.parseJson(jsonString);
}
}.start();
// 发送消息通知数据加载完毕
handler.sendEmptyMessage(0x101);
}
private Handler handler = new Handler()
{
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
if (msg.what == 0x101)
{
depName.setText(depInfo.getDepName());
depTotal.setText(String.valueOf(depInfo.getTotal()));
// 刷新数据
adapter.freshView(depInfo.getEmpList());
}
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
};
}
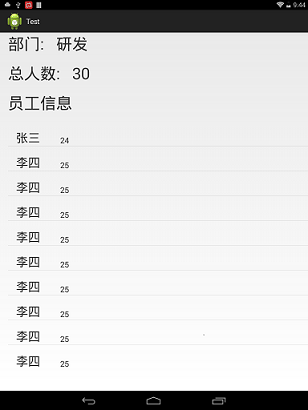
看看运行效果:
这布局设计得相当糟糕,继续努力……






















 1578
1578

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








