1、题目
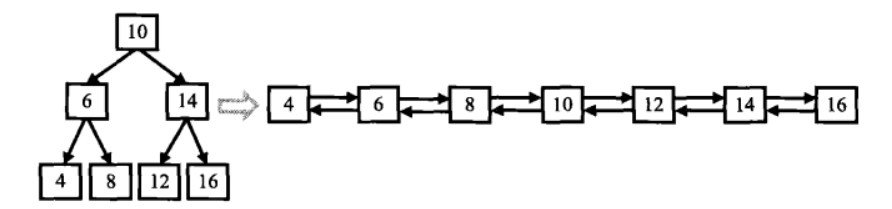
输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。比如输入图1中左边的二叉搜索树,则输出转换之后的排序双向链表。
图1 一棵二叉搜索树及转换之后的排序双向链表
二叉树结点的定义如下:
struct BinaryTreeNode
{
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* m_pRight;
};2、分析思路
在二叉树中,每个结点都有两个指向子结点的指针,而在双向链表中,每个结点也有两个指针,且二叉搜索树也是一种排序的数据结构,因此在理论上有可能实现二叉搜索树和排序的双向链表的转换。
在搜索二叉树中,左子结点的值总是小于父结点的值,右子结点的值总是大于父结点的值,因此在转换成排序的双向链表时,原先指向左子结点的指针调整为链表中指向前一个结点的指针,原先指向右子结点的指针调整为链表中指向后一个结点指针。
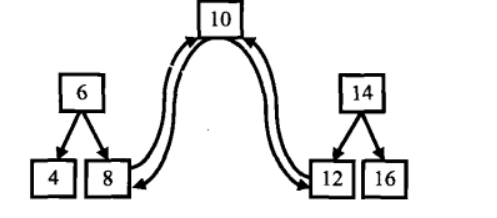
而且二叉搜索树的中序遍历恰好是排序的。当遍历到根结点的时候,我们把树看成三部分:值为10的结点,根结点值为6的左子树,根结点值为14的右子树。如图2所示。
图2 把二叉树看成三部分
按照中序遍历的顺序,当我们遍历转换到根结点(10)的时,它的左子树已经转换成一个排序的链表了,并且处在链表中的最后一个结点是当前值最大的结点。我们把值为8的结点和根结点连接起来,此时链表中的最后一个结点就是10了。接着去遍历转换右子树,并把根结点和右子树中最小的结点连接起来。由于遍历和转换过程是一样的,我们可以用递归实现。
3、参考代码(剑指Offer)
void ConvertNode(BinaryTreeNode* pNode, BinaryTreeNode** pLastNodeInList);
BinaryTreeNode* Convert(BinaryTreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
BinaryTreeNode *pLastNodeInList = NULL;
ConvertNode(pRootOfTree, &pLastNodeInList);
// pLastNodeInList指向双向链表的尾结点,
// 我们需要返回头结点
BinaryTreeNode *pHeadOfList = pLastNodeInList;
while(pHeadOfList != NULL && pHeadOfList->m_pLeft != NULL)
pHeadOfList = pHeadOfList->m_pLeft;
return pHeadOfList;
}
void ConvertNode(BinaryTreeNode* pNode, BinaryTreeNode** pLastNodeInList)
{
if(pNode == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreeNode *pCurrent = pNode;
if (pCurrent->m_pLeft != NULL)
ConvertNode(pCurrent->m_pLeft, pLastNodeInList);
pCurrent->m_pLeft = *pLastNodeInList;
if(*pLastNodeInList != NULL)
(*pLastNodeInList)->m_pRight = pCurrent;
*pLastNodeInList = pCurrent;
if (pCurrent->m_pRight != NULL)
ConvertNode(pCurrent->m_pRight, pLastNodeInList);
}
// ====================测试代码====================
void PrintDoubleLinkedList(BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = pHeadOfList;
printf("The nodes from left to right are:\n");
while(pNode != NULL)
{
printf("%d\t", pNode->m_nValue);
if(pNode->m_pRight == NULL)
break;
pNode = pNode->m_pRight;
}
printf("\nThe nodes from right to left are:\n");
while(pNode != NULL)
{
printf("%d\t", pNode->m_nValue);
if(pNode->m_pLeft == NULL)
break;
pNode = pNode->m_pLeft;
}
printf("\n");
}
void DestroyList(BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = pHeadOfList;
while(pNode != NULL)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNext = pNode->m_pRight;
delete pNode;
pNode = pNext;
}
}
void Test(char* testName, BinaryTreeNode* pRootOfTree)
{
if(testName != NULL)
printf("%s begins:\n", testName);
PrintTree(pRootOfTree);
BinaryTreeNode* pHeadOfList = Convert(pRootOfTree);
PrintDoubleLinkedList(pHeadOfList);
}
// 10
// / \
// 6 14
// /\ /\
// 4 8 12 16
void Test1()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode14 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(14);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode12 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(12);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode16 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(16);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode6, pNode14);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode4, pNode8);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode14, pNode12, pNode16);
Test("Test1", pNode10);
DestroyList(pNode4);
}
// 5
// /
// 4
// /
// 3
// /
// 2
// /
// 1
void Test2()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode5, pNode4, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, pNode3, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, pNode2, NULL);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, pNode1, NULL);
Test("Test2", pNode5);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
// 1
// \
// 2
// \
// 3
// \
// 4
// \
// 5
void Test3()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode2 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(2);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode3 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(3);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode4 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(4);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode1, NULL, pNode2);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode2, NULL, pNode3);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode3, NULL, pNode4);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode4, NULL, pNode5);
Test("Test3", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
// 树中只有1个结点
void Test4()
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode1 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(1);
Test("Test4", pNode1);
DestroyList(pNode1);
}
// 树中没有结点
void Test5()
{
Test("Test5", NULL);
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
return 0;
}
























 530
530











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








