前言:
数据挖掘中的关联分析可以分成频繁项集的挖掘和关联规则的生成两个步骤,而Apriori算法是找频繁项集最常用到的一种算法。
关于关联分析和频繁项集请见:什么是关联分析?
中言:
我们还是利用购物篮的例子来讲述Apriori算法的思路。
购物篮信息如下:
TID Items 001 Cola, Egg, Ham 002 Cola, Diaper, Beer 003 Cola, Diaper, Beer, Ham 004 Diaper, Beer TID代表交易流水号,Items代表一次交易的商品。
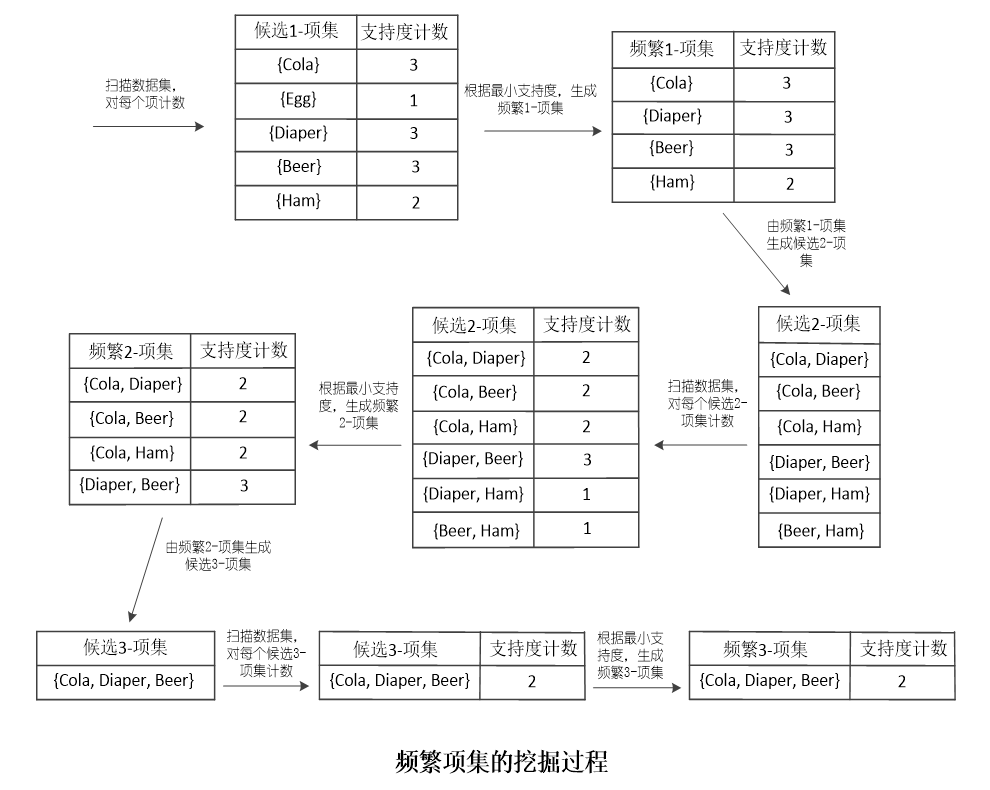
我们Apriori算法的最终目的就是要找出数据集中的频繁项集,把最小支持度阈值设为50%,则最终挖掘结果如下(后面的数字表示该项集的支持度计数):
频繁1-项集:
{Cola} 3
{Diaper} 3
{Beer} 3
{Ham} 2频繁2-项集:
{Cola, Diaper} 2
{Cola, Beer} 2
{Cola,Ham} 2
{Diaper, Beer} 3频繁3-项集:
{Cola, Diaper, Beer} 2
Apriori算法的思路是由频繁(k-1)-项集生成候选k-项集,然后根据最小支持度判断该候选k-项集是否是频繁k-项集。
例如先找出所有1-项集,然后筛选出里面的频繁1-项集; 根据频繁1-项集生成候选2-项集,然后筛选出里面的频繁2-项集; 再根据频繁2-项集生成候选3-项集,从里面筛选出频繁3-项集;·······
那么问题来了,如何从频繁(k-1)-项集生成候选k-项集呢?
答案是利用Apriori性质:一个频繁项集的任一子集也应该是频繁子集(用反证法容易证明,略)。所以如果一个项集是非频繁项集,那么它的超集也应该是非频繁项集。
例如{Cola, Diaper}是频繁项集,所以{Cola}和{Diaper}也应该是频繁项集。因为{Egg}是非频繁项集,所以{Cola, Egg}也是非频繁项集。
从频繁1-项集生成候选2-项集的步骤是:把频繁1-项集和频繁1-项集排列组合成2-项集,把含有非频繁子项集的2-项集去掉,就是候选2-项集了。
从频繁2-项集生成候选三项集的步骤是:把频繁2-项集和频繁1-项集排列组合成3-项集:{Cola, Diaper, Beer}、{Cola, Diaper, Ham}、{Cola, Beer, Ham}、{Diaper, Beer, Ham}。
因为{Diaper, Ham}不是频繁2-项集,所以含有{Diaper, Ham}的{Cola, Diaper, Ham}不是候选3-项集,去掉。因为{Beer, Ham}不是频繁2-项集,所以含有{Beer, Ham}的{Cola, Beer, Ham}、{Diaper, Beer, Ham}不是候选3-项集,去掉。
所以候选3-项集只有{Cola, Diaper, Beer}。
购物篮频繁项集的挖掘过程如下:
Apriori算法描述如下(代码源自《数据挖掘原理与实践》):
算法:Apriori 算法的频繁项集的产生
输入:数据集D;最小支持度阈值min_sup
输出:D 中的频繁项集L
(1) L1 = find_frequent_1-itemset( D );
(2) for( k=2; Lk−1≠Φ ; k++)
(3) {
(4) Ck = apriori_gen( Lk−1 ); // 产生候选项集
(5) for all transactions t ∈ D
(6) {
(7) Ct = subset( Ck , t); // 识别 t 包含的所有候选
(8) for all candidates c∈Ct
(9) {
(10) c.count++; // 支持度计数增值
(11) }
(12) }
(13) Lk = { c∈Ck | c.count≥min_sup} // 提取频繁k-项集
(14) }
(15) return L=∪kLk ;
procedure apriori_gen( Lk−1 )
(1) for each itemset l1∈Lk−1
(2) for each itemset l2∈Lk−1
(3) if( l1 [1]= l2 [1] ∧…∧ ( l1 [k-2]= l2 [k-2] ) ∧ ( l1 [k-1]< l2 [k-2] ) then
(4) {
(5) c = join( l1 , l2 ); // 连接:产生候选
(6) if has_infrequent_subset( c, Lk−1 ) then
(7) delete c; // 减枝:移除非频繁的候选
(8) else
(9) add c to Ck
(10) }
(11) return Ck ;
procedure has_infrequent_subset( c, Lk−1 )
// 使用先验知识判断候选项集是否频繁
(1) for each ( k-1 )-subset s of c
(2) if s ∉Lk−1 then
(3) return TRUE;
(4) return FALSE;
后言:
我们可以看到,Apriori算法是通过频繁(k-1)-项集找到频繁k-项集的,虽然可以通过Apriori性质进行减枝,去掉一部分子集为非频繁项集的候选项集,但还是需要不断地扫描数据集,不断地求候选项集的支持度计数从而判断它是否是频繁项集。如果数据集足够大的时候,这种算法的效率还是挺让人捉急的!
然后,FP-Growth算法就华丽丽的出现了,请见FP-Growth算法的介绍、FP_Growth算法python实现。























 2456
2456

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








